In a clinical trial, 27 out of 845 patients taking a prescription drug daily complained of flulike symptoms. Suppose that it is known that 2.9% of patients taking competing drugs complain of flulike symptoms. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that more than 2.9% of this drug's users experience flulike symptoms as a side effect at the a 0.01 level of significance? Because npo (1-Po) =D 10, the sample size is V 5% of the population size, and the sample (Round to one decimal place as needed.) V the requirements for testing the hypothesis satisfied. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Ho: TI versus H,: V0 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Find the test statistic, zo Zn = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Choose the correct conclusion below. O A. Since P-value > a, do not reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms. O B. Since P-value a, reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms.
In a clinical trial, 27 out of 845 patients taking a prescription drug daily complained of flulike symptoms. Suppose that it is known that 2.9% of patients taking competing drugs complain of flulike symptoms. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that more than 2.9% of this drug's users experience flulike symptoms as a side effect at the a 0.01 level of significance? Because npo (1-Po) =D 10, the sample size is V 5% of the population size, and the sample (Round to one decimal place as needed.) V the requirements for testing the hypothesis satisfied. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Ho: TI versus H,: V0 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Find the test statistic, zo Zn = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Choose the correct conclusion below. O A. Since P-value > a, do not reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms. O B. Since P-value a, reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
Help 11
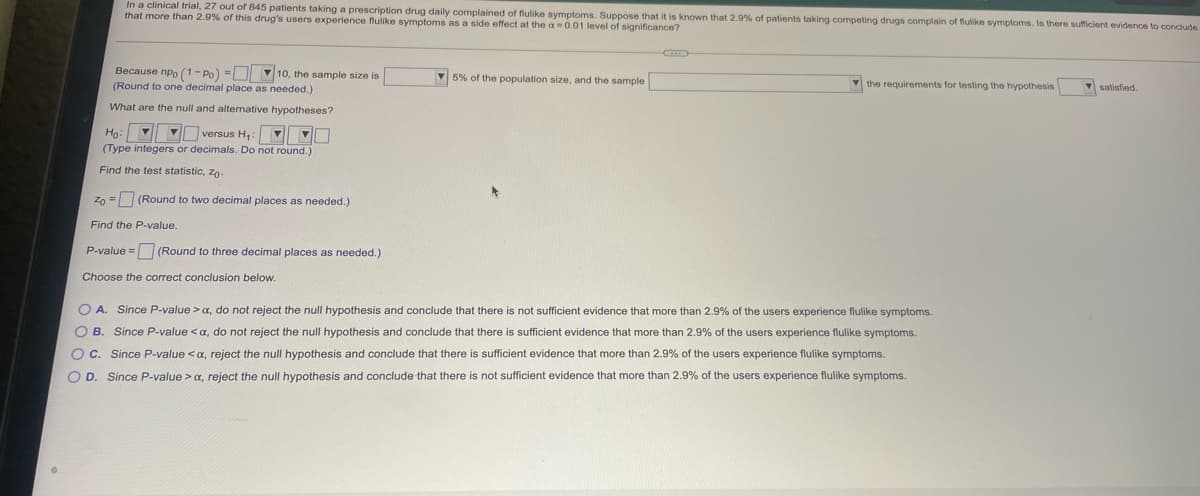
Transcribed Image Text:In a clinical trial, 27 out of 845 patients taking a prescription drug daily complained of flulike symptoms. Suppose that it is known that 2.9% of patients taking competing drugs complain of flulike symptoms. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude
that more than 2.9% of this drug's users experience flulike symptoms as a side effect at the a 0.01 level of significance?
Because npo (1- Po) =D 10, the sample size is
(Round to one decimal place as needed.)
V 5% of the population size, and the sample
V the requirements for testing the hypothesis
satisfied.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses?
Ho: VI versus H,: V0
(Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)
Find the test statistic, zo-
Zn = (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Find the P-value.
P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Choose the correct conclusion below.
O A. Since P-value >a, do not reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms.
O B. Since P-value < a, do not reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms.
OC. Since P-value <a, reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms.
O D. Since P-value > a, reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence that more than 2.9% of the users experience flulike symptoms.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning