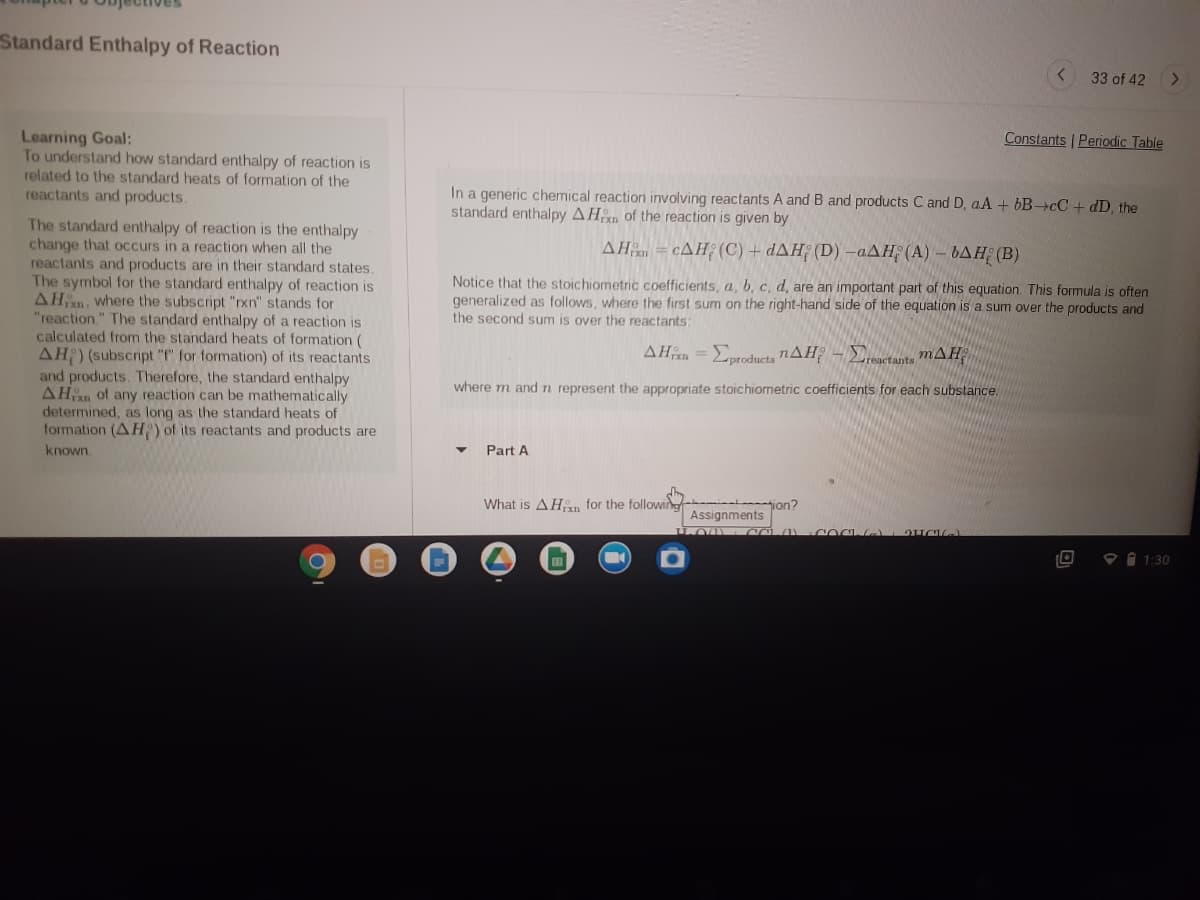
In a generic chemical reaction involving reactants A and B and products C and D, aA + 6B+cC + dD, the standard enthalpy AHn of the reaction is given by AH = cAH; (C) + dAH; (D) –aAH (A) - bAH (B) Notice that the stoichiometric coefficients, a, b, c, d, are an important part of this equation. This formula is often generalized as follows, where the first sum on the right-hand side of the equation is a sum over the products and the second sum is over the reactants: AHn = Eproducts nAH - Ectants mAH %3D where m and n represent the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients for each substance. Part A What is AHn for the following ion? Assignments 1:30
In a generic chemical reaction involving reactants A and B and products C and D, aA + 6B+cC + dD, the standard enthalpy AHn of the reaction is given by AH = cAH; (C) + dAH; (D) –aAH (A) - bAH (B) Notice that the stoichiometric coefficients, a, b, c, d, are an important part of this equation. This formula is often generalized as follows, where the first sum on the right-hand side of the equation is a sum over the products and the second sum is over the reactants: AHn = Eproducts nAH - Ectants mAH %3D where m and n represent the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients for each substance. Part A What is AHn for the following ion? Assignments 1:30
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter15: Energy And Chemical Change
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 112A: sample of natural gas is analyzed and found to be88.4% methane (CH4) and 11.6% ethane (C2H6) bymass....
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Constants Periodic Table
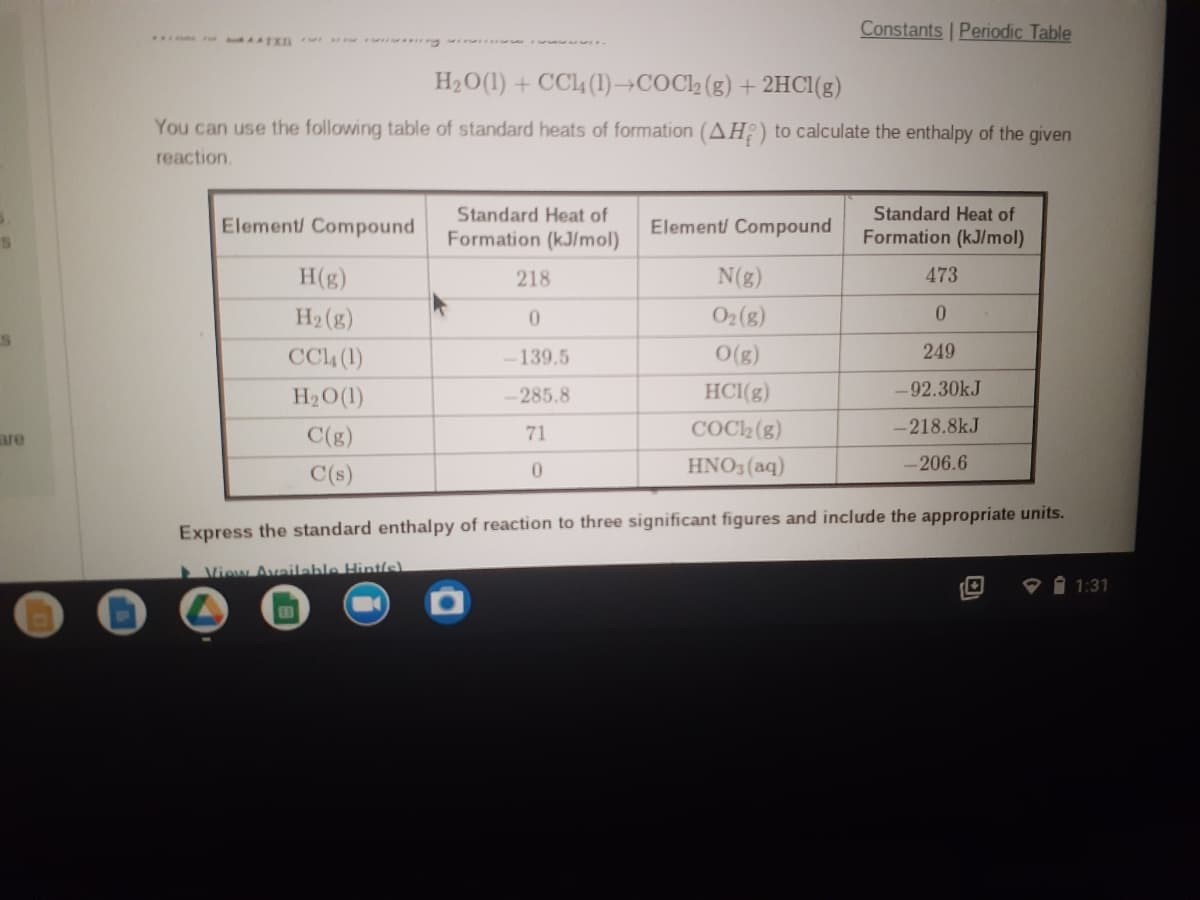
.. L n g
H2O(1) + CC4 (1)→COCl2 (g) + 2HCI(g)
You can use the following table of standard heats of formation (AH;) to calculate the enthalpy of the given
reaction.
Standard Heat of
Formation (kJ/mol)
Standard Heat of
Element/ Compound
Element/ Compound
Formation (kJ/mol)
H(g)
218
N(g)
473
H2 (g)
O2(g)
0.
CC4 (1)
-139.5
O(g)
249
H2O(1)
-285.8
HC1(g)
-92.30kJ
are
C(g)
71
COC2 (g)
-218.8kJ
C(s)
HNO3 (aq)
-206.6
Express the standard enthalpy of reaction to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
View Available Hint/s)
O 1 1:31
Transcribed Image Text:Standard Enthalpy of Reaction
33 of 42
Learning Goal:
To understand how standard enthalpy of reaction is
related to the standard heats of formation of the
reactants and products.
Constants Periodic Table
In a generic chemical reaction involving reactants A and B and products C and D, aA + bB-cC + dD, the
standard enthalpy AHn of the reaction is given by
The standard enthalpy of reaction is the enthalpy
change that occurs in a reaction when all the
reactants and products are in their standard states.
The symbol for the standard enthalpy of reaction is
AHn, where the subscript "rxn" stands for
"reaction." The standard enthalpy of a reaction is
calculated from the standard heats of formation (
AH) (subscript "f" for formation) of its reactants
and products. Therefore, the standard enthalpy
AHn of any reaction can be mathematically
determined, as long as the standard heats of
formation (AH:) of its reactants and products are
AH = cAH¿ (C) + dAH; (D) -aAH; (A) – bAH (B)
Notice that the stoichiometric coefficients, a, b, c, d, are an important part of this equation. This formula is often
generalized as follows, where the first sum on the right-hand side of the equation is a sum over the products and
the second sum is over the reactants:
AHn =Eoroducts nAH – Eactants mAH
where m and n represent the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients for each substance.
known.
Part A
What is AHn for the following
tion?
Assignments
P i 1:30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning