is as follows: Zn (s) + Cl2 (g, 1 atm.) →ZNCI2 (aq) a) Write the reaction that takes place in each half-cell. E and Zn"/Zn = -0.763 V %3! EvzCı,/cr =1.36 V calculate the standard potential, E°cell, b) Being and AGº. c) It the molality of the electrolyte ZnCl2 is of 0.1 m, employ the Debye-Hückel law for calculating the average ionic activity coefficient (y+), the average ionic activity (a±) and the electrolyte's activity (a2) d) Calculate the cell potential (Ecell), at 25 °C, using the values obtained in the previous section.
is as follows: Zn (s) + Cl2 (g, 1 atm.) →ZNCI2 (aq) a) Write the reaction that takes place in each half-cell. E and Zn"/Zn = -0.763 V %3! EvzCı,/cr =1.36 V calculate the standard potential, E°cell, b) Being and AGº. c) It the molality of the electrolyte ZnCl2 is of 0.1 m, employ the Debye-Hückel law for calculating the average ionic activity coefficient (y+), the average ionic activity (a±) and the electrolyte's activity (a2) d) Calculate the cell potential (Ecell), at 25 °C, using the values obtained in the previous section.
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter17: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14P
Related questions
Question
The Zn-Cl battery has been suggested as an energy generator in transportation. The reaction
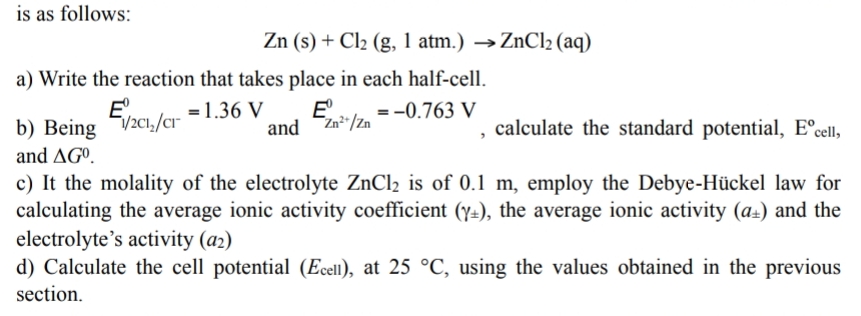
is as follows:
Zn (s) + Cl2 (g, 1 atm.) ZnCl2 (aq)
a) Write the reaction that takes place in each half-cell.
b) Being and , calculate the standard potential, Eºcell,
and ∆G0.
c) It the molality of the electrolyte ZnCl2 is of 0.1 m, employ the Debye-Hückel law for calculating the average ionic activity coefficient (γ±), the average ionic activity (a±) and the
electrolyte’s activity (a2)
d) Calculate the cell potential (Ecell), at 25 °C, using the values obtained in the previous section.
Transcribed Image Text:is as follows:
Zn (s) + Cl2 (g, 1 atm.) →ZnCl2 (aq)
a) Write the reaction that takes place in each half-cell.
E'.
b) Being V2C1,/cr
and AGº.
=1.36 V
E
= -0.763 V
Zn²"/Zn
calculate the standard potential, E°cell,
and
c) It the molality of the electrolyte ZnCl2 is of 0.1 m, employ the Debye-Hückel law for
calculating the average ionic activity coefficient (y=), the average ionic activity (a±) and the
electrolyte's activity (a2)
d) Calculate the cell potential (Ecell), at 25 °C, using the values obtained in the previous
section.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning