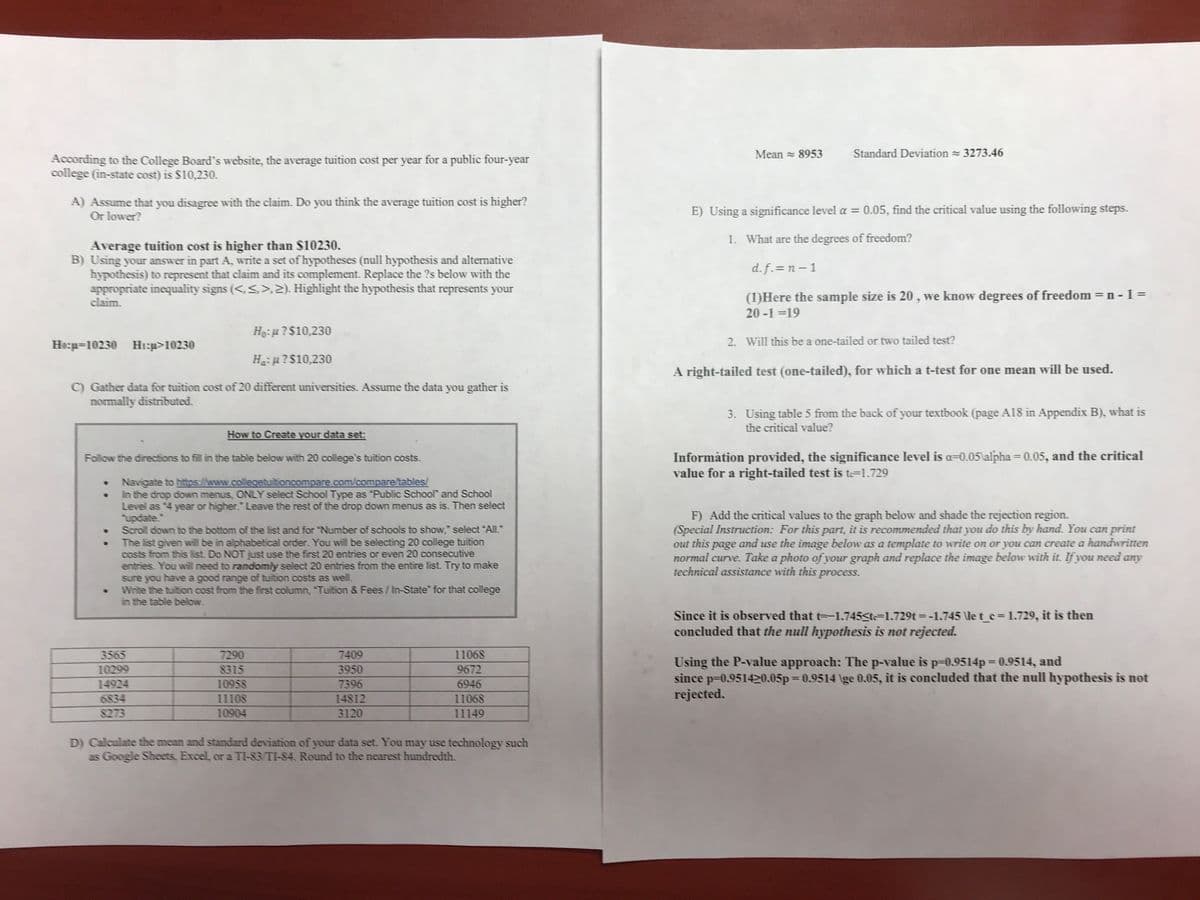
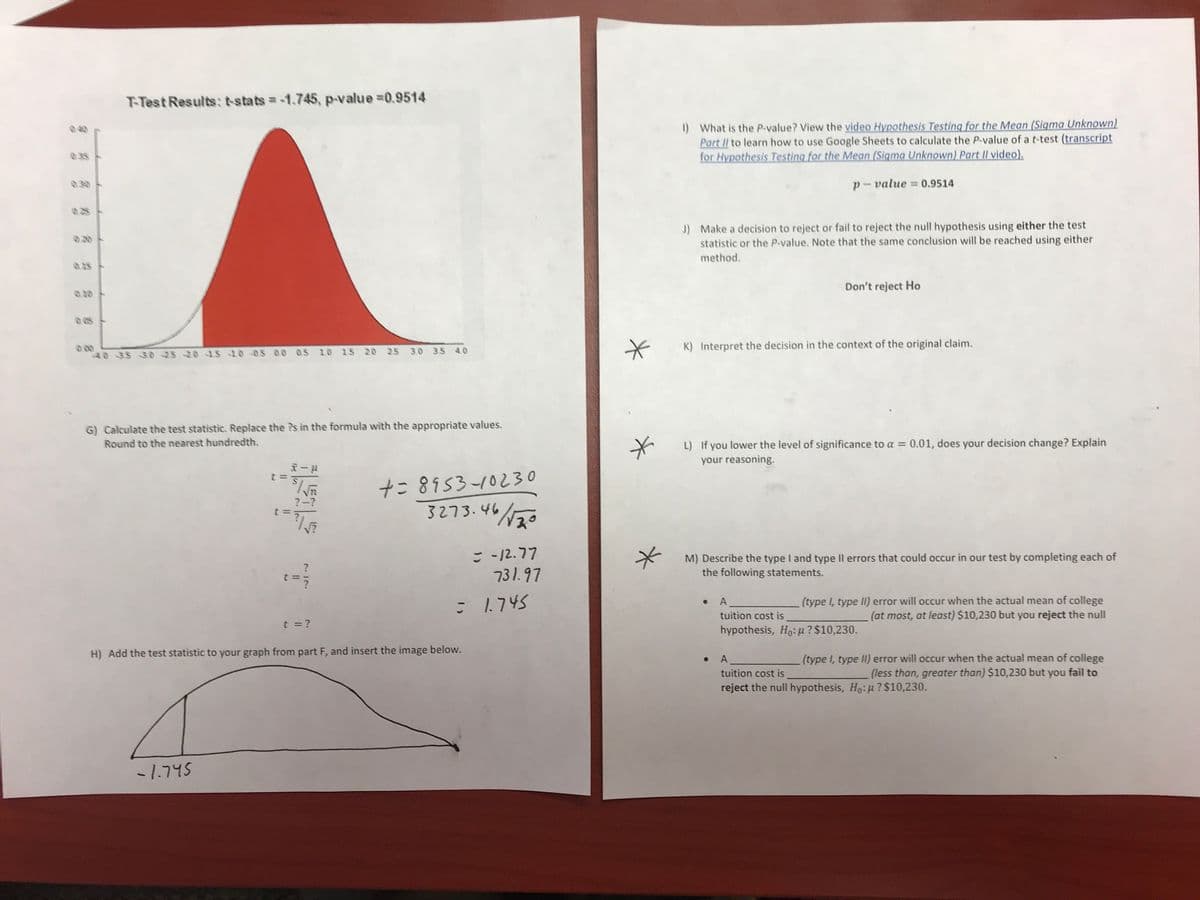
K L M
Percentage
A percentage is a number indicated as a fraction of 100. It is a dimensionless number often expressed using the symbol %.
Algebraic Expressions
In mathematics, an algebraic expression consists of constant(s), variable(s), and mathematical operators. It is made up of terms.
Numbers
Numbers are some measures used for counting. They can be compared one with another to know its position in the number line and determine which one is greater or lesser than the other.
Subtraction
Before we begin to understand the subtraction of algebraic expressions, we need to list out a few things that form the basis of algebra.
Addition
Before we begin to understand the addition of algebraic expressions, we need to list out a few things that form the basis of algebra.
K
L
M
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









