pan atom will gain or loose electrons to becone stable. stable an atom LWith a full valere shell #protons. =# electrons m geall charge Neutral 231Na 35,„CI #p'=_|| + #p'= charge |구 #e=. #e= llt 0 |- #n°=_I 2 How do I make Sodium and Chlorine Stable?????? neutral chage neixtral. 22„Na 35,„CI #p°= _|\ + 10- (llpt Nano 17 18 18 17t 18- #p'= electrostohi attraction He=_lO - #e= It #n°= 12 0 anion Cation #n°= Based on what you have just seen above, explain why the Alkali Metals are the MOST reactive metals in the periodic table?_ Based on what you have just learned above, explain why the Noble Gases are NOT a reactive group in the periodic table? HOMEWORK - Consolidating my learning....write the ionic charges above each group (I-VIII) from the workbook page with Bohr-Rutherford diagrams. Then-write the ionic charges above each group on your "coloured" periodic table. Below, explain WHY each group has the ionic charge you stated: IS Group V Group1- Group II- Group VI Group IV- Group VII Group VIII
pan atom will gain or loose electrons to becone stable. stable an atom LWith a full valere shell #protons. =# electrons m geall charge Neutral 231Na 35,„CI #p'=_|| + #p'= charge |구 #e=. #e= llt 0 |- #n°=_I 2 How do I make Sodium and Chlorine Stable?????? neutral chage neixtral. 22„Na 35,„CI #p°= _|\ + 10- (llpt Nano 17 18 18 17t 18- #p'= electrostohi attraction He=_lO - #e= It #n°= 12 0 anion Cation #n°= Based on what you have just seen above, explain why the Alkali Metals are the MOST reactive metals in the periodic table?_ Based on what you have just learned above, explain why the Noble Gases are NOT a reactive group in the periodic table? HOMEWORK - Consolidating my learning....write the ionic charges above each group (I-VIII) from the workbook page with Bohr-Rutherford diagrams. Then-write the ionic charges above each group on your "coloured" periodic table. Below, explain WHY each group has the ionic charge you stated: IS Group V Group1- Group II- Group VI Group IV- Group VII Group VIII
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter6: The Periodic Table And Periodic Law
Section6.3: Periodic Trends
Problem 21SSC
Related questions
Question
100%
PLEASE ANSWER THE CIRCLED SECTION ONLY (HOMEWORK - Consolidating my learning)
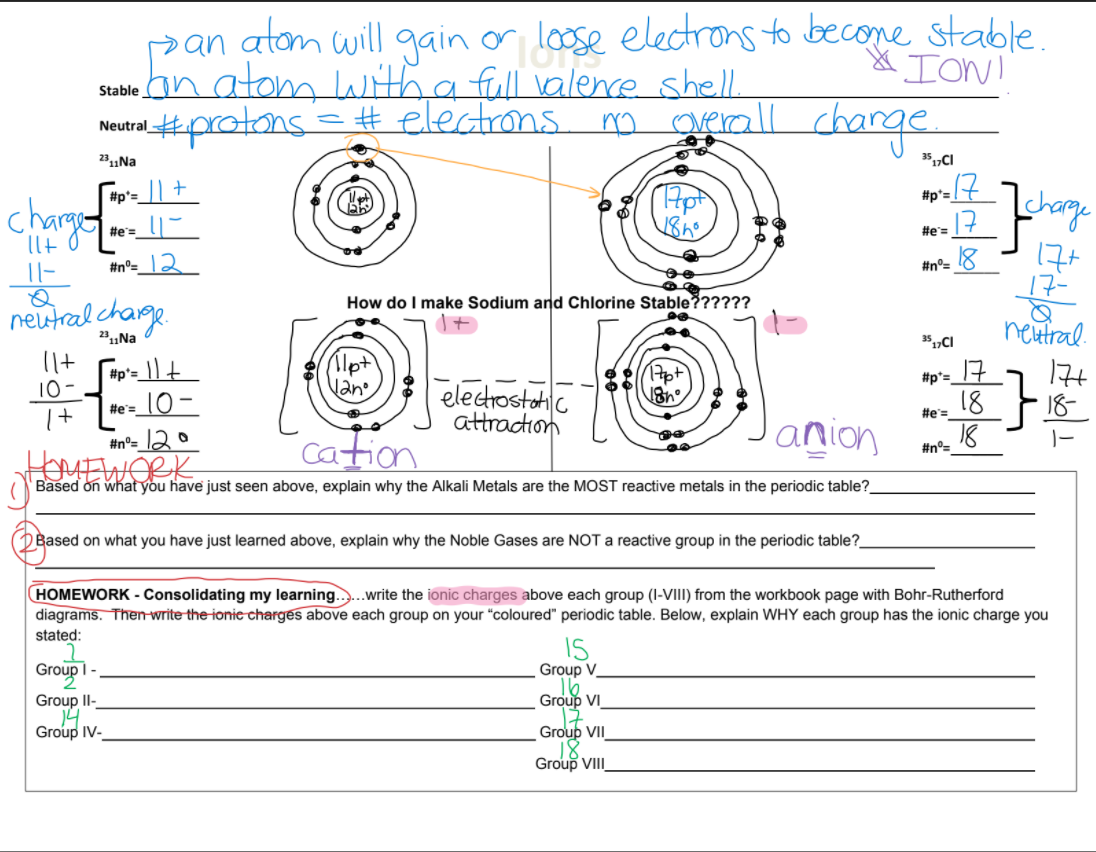
Transcribed Image Text:pan atam will gain or loose
Stable an atom Lwith a full valenre shell
#protons
electrons to becone stable.
& IOW!
=#electrons mo greall chare
Neutral
23„Na
35„CI
17
17
chage
#p's +
#p*=
charge
#e=
#e=
llt
#n°= l2
#n°=
17-
Q
neutral charge.
How do I make Sodium and Chlorine Stable??????
neitral.
7t
18
23„Na
35„CI
#p'= |+
10-
lpt
Vano
17
18
18
#p*=_
- 10-
electrostoatc
attraction
#e=
#e=
It
cation
anion
#n°= 12
#n°=
リー
Based on what you have just seen above, explain why the Alkali Metals are the MOST reactive metals in the periodic table?
Based on what you have just learned above, explain why the Noble Gases are NOT a reactive group in the periodic table?
HOMEWORK - Consolidating my learning....write the ionic charges above each group (I-VIII) from the workbook page with Bohr-Rutherford
diagrams. Then-write the ionie charges above each group on your "coloured" periodic table. Below, explain WHY each group has the ionic charge you
stated:
Group1-
IS
Group V
Group VI
Group II-
14
Group IV-
Group VII
Group VIII
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning