Place the following steps of the bacterial protein synthesis in their correct order? Peptide bond formation at the peptidyl-transferase center. Binding of MRNA and initiator formyl-methionyl-IRNAMet to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Aminoacylation and formylation of the initiator tRNAMet Joining of the 30S and the 50S ribosomal subunits Release Factor (RF) dependent hydrolysis of the peptidyl tRNA and release of the fully synthesized polypeptide from the ribosome Elongation Factor G (EF-G) dependent translocation of the nibosome by one codon along the MRNA
Place the following steps of the bacterial protein synthesis in their correct order? Peptide bond formation at the peptidyl-transferase center. Binding of MRNA and initiator formyl-methionyl-IRNAMet to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Aminoacylation and formylation of the initiator tRNAMet Joining of the 30S and the 50S ribosomal subunits Release Factor (RF) dependent hydrolysis of the peptidyl tRNA and release of the fully synthesized polypeptide from the ribosome Elongation Factor G (EF-G) dependent translocation of the nibosome by one codon along the MRNA
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Chapter15: Genes And Proteins
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3VCQ: Figure 15.16 Many antibiotics inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. For example, tetracycline blocks...
Related questions
Question
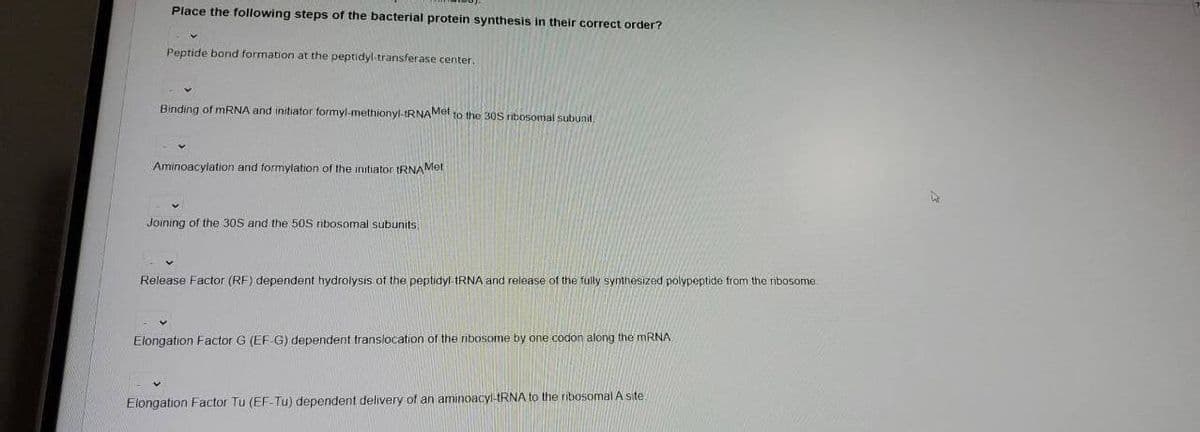
Transcribed Image Text:Place the following steps of the bacterial protein synthesis in their correct order?
Peptide bond formation at the peptidyl-transferase center.
Binding of MRNA and initiator formyl-methionyl-IRNAMet to the 30S ribosomal subunit,
Aminoacylation and formylation of the initiator tRNAMet
Joining of the 30S and the 50S ribosomal subunits,
Release Factor (RF) dependent hydrolysis of the peptidyl RNA and release of the fully synthesized polypeptide from the ribosome.
Elongation Factor G (EF G) dependent translocation of the ribosome by one codon along the MRNA
Elongation Factor Tu (EF-Tu) dependent delivery of an aminoacyl-IRNA to the ribosomal A site
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax