Problem 3: A shaft is to have a semicircular grove machined around the circumference at a specified location. The shaft diameter and reduced cross-sectional diameter are known as well as the torsion that the shaft will experience and the material's yield strength. Using the stress concentration figures given the textbook as Fig. A-15-15 (p. 1046) and the equations given as Eq. 4.21, determine minimum radius of the groove (r). Using the both of the following failure criteria: (use a safety factor of n = 2) d = 0.05 m, D = 0.055 m, T = 2500 Nm, Sy = 500 MPa, n = 2 (a) Using the maximum distortional energy failure theory (b) Using the maximum shear stress failure theory 5 T D MEC₁ d r T
Problem 3: A shaft is to have a semicircular grove machined around the circumference at a specified location. The shaft diameter and reduced cross-sectional diameter are known as well as the torsion that the shaft will experience and the material's yield strength. Using the stress concentration figures given the textbook as Fig. A-15-15 (p. 1046) and the equations given as Eq. 4.21, determine minimum radius of the groove (r). Using the both of the following failure criteria: (use a safety factor of n = 2) d = 0.05 m, D = 0.055 m, T = 2500 Nm, Sy = 500 MPa, n = 2 (a) Using the maximum distortional energy failure theory (b) Using the maximum shear stress failure theory 5 T D MEC₁ d r T
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter3: Torsion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.7.10P: What is the maximum power that can be delivered by a hollow propeller shaft (outside diameter 50 mm,...
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Using the maximum distortional energy failure theory
(b) Using the maximum shear stress failure theory
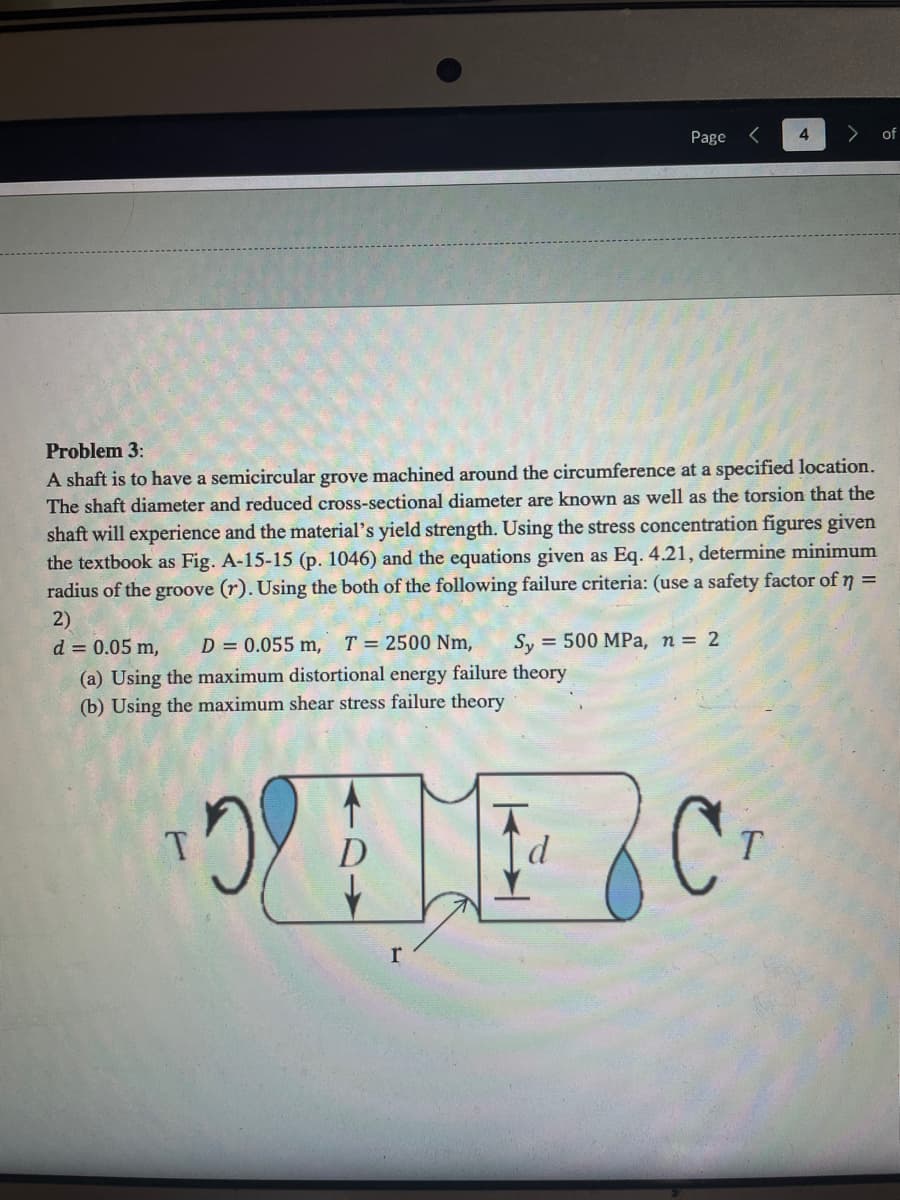
Problem 3:
A shaft is to have a semicircular grove machined around the circumference at a specified location.
The shaft diameter and reduced cross-sectional diameter are known as well as the torsion that the
shaft will experience and the material's yield strength. Using the stress concentration figures given
the textbook as Fig. A-15-15 (p. 1046) and the equations given as Eq. 4.21, determine minimum
radius of the groove (r). Using the both of the following failure criteria: (use a safety factor of n =
2)
d = 0.05 m, D = 0.055 m, T = 2500 Nm, Sy 500 MPa, n = 2
T
OME C
H
D
T
Page
r
d
4
of
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning