
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
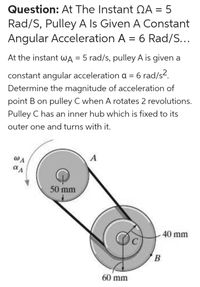
Transcribed Image Text:Question: At The Instant QA = 5
Rad/S, Pulley A Is Given A Constant
Angular Acceleration A = 6 Rad/S...
At the instant wA = 5 rad/s, pulley A is given a
%3D
constant angular acceleration a = 6 rad/s?.
Determine the magnitude of acceleration of
point B on pulley C when A rotates 2 revolutions.
Pulley C has an inner hub which is fixed to its
outer one and turns with it.
WA
A
50 mm
40 mm
B
60 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A four-bar linkage is shown in the figure (the ground "link" OC is considered the fourth bar). If the angular velocity and angular acceleration of drive link OA are 6.1 rad/s and 6.6 rad/s² respectively, both counterclockwise, determine the angular accelerations of bars AB and BC for the instant represented. The angular accelerations are positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. The answers are not 2.356 and 11.327, or 390.82 and 465.7arrow_forwardThe disk is moving to the left such that it has an angular acceleration cx=9 rad/s² and angular velocity w=2 rad/s at the instant shown. It does not slip at A Suppose that r=0.3 m (Figure 1) Figure 6) < 1 of 1 ar A ▼ Y Part A Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ag= Submit Part B 0= μA Submit Value 3 Request Answer → Determine the direction of the acceleration of point B measured clockwise from the positive z axis. Express your answer using three significant figures. ΠΕΙ ΑΣΦ m/s² Request Answer 11 vec 3 ? → ?arrow_forwardA four-bar linkage is shown in the figure (the ground "link" OC is considered the fourth bar). If the angular velocity and angular acceleration of drive link OA are 6.1 rad/s and 6.6 rad/s² respectively, both counterclockwise, determine the angular accelerations of bars AB and BC for the instant represented. The angular accelerations are positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. The answers are not 2.356 and 11.327.arrow_forward
- answer quicklyarrow_forward4. A weight, attached to a cord, is travelling on a smooth circular table. A cord is pulling the weight radially inward with a constant velocity of 5 cm/s. There are no forces in the 8-direction, so a = 0. 0 = 10 rad/s r=20cm 5 cm/s a. At the time shown on the figure, what is the radial component of acceleration? b. What is the angular acceleration, ö, of the block? (Hint: a = 0, but 0 +0)arrow_forward4. 4) The hydraulic cylinder Dextends, moves the rigid rod ABC, and causes the collar A to move with velocity and acceleration both to the left. If the dimensions/₁ 1.0 ft, and /2 = 2.0 ft, vµ = 5.5 ft/s, aµ = 2.1 ft/s², and the angle 0 = 30°, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) of rod ABC. Negative sign must be included if the angular acceleration is clockwise. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Your Answer: 1₁ Answer B 12 ÏÏ a =arrow_forward
- A portion of a steam locomotive is shown below. If the locomotive is moving to the right at a constant speed of 45 mph, (a) what is the linear and angular velocity of point B, and (b) what is the linear and angular acceleration of point B, given that the wheels are 50 inches in diameter, length AC = 10 in, length AD = 55 in, and B is half way between A and D.arrow_forward2. The gear A on the drive shaft of an outboard motor has a radius of ½ inch while the meshed pinion gear on B has a radius of 1% inches. If the drive starts from rest and is accelerated at a constant a = 200 rad/s², what is the speed, tangential acceleration, and normal acceleration at point P on the propeller after 3 seconds. 2.20 inarrow_forwardFor the following mechanism, rod AB is pinned to the two disks at point A and point B, and the two disks roll to the left without slipping. if the length of rod AB, I= 2.4 m, and its angular velocity @ = 6.2 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the linear velocity of point B. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point and proper unit. (0.5 m 0.5 m No slipping No slipping Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forward
- The following figure shows how a mechanical actuator works. Determine the angular acceleration of bars AB and BC.arrow_forwardA cylinder of radius 7 = 0.2 m is about to start rolling down an inclined plane. The acceleration of the center of the cylinder is 9.81 sin(0) m/s?. The angular acceleration is 9.81 sin(0)/r rad/s?. Assume 0 = 0.8 rad. What is the magnitude of acceleration of the point on the cylinder furthest from the inclined plane in m/s?. Hint: Since it is about to start rolling, the velocity of the center of the cylinder and angular velocity of the cylinder are still zero at that instant. You Answered 0.2739 Correct Answer 14.075 margin of error +/- 2%arrow_forwardAdvanced Applied Mathematics - Circular Motion 1. When an airplane touches down at 1 = 0, a stationary wheel is subjected to a constant angu- lar acceleration a = 110 rad/s until / = 1 s. (a) What is the wheel's angular velocity at t = 1 s? (b) At 1 = 0, the angle 0 = 0. Determine 9 in radians and in revolutions at / = 1 s. 2. A small box B of mass mkg is placed on a rough horizontal rotating disc. B is metres from the centre of rotation as shown in Fig. 1 below. The coefficient of friction between the disc and B is u. Find, in terms of u, r and g, the maximum speed v that can be given to B without it slipping. 3. One end of a light inextensible string of length L metres is attached to a fixed point C. A small brass hall Roarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY