Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point: sodium bromide (NaBr), methane (CH4), and formaldehyde (CH,O) Rank from highest to lowest boiling point. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. > View Available Hint(s) Reset Help formaldehyde ( CH20 sodium bromide (NaBr ) methane ( CH,) Lowest boiling point
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point: sodium bromide (NaBr), methane (CH4), and formaldehyde (CH,O) Rank from highest to lowest boiling point. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. > View Available Hint(s) Reset Help formaldehyde ( CH20 sodium bromide (NaBr ) methane ( CH,) Lowest boiling point
Chapter10: Liquids And Solids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: What are intermolecular forces? How do they differ from intramolecular forces? What are...
Related questions
Question
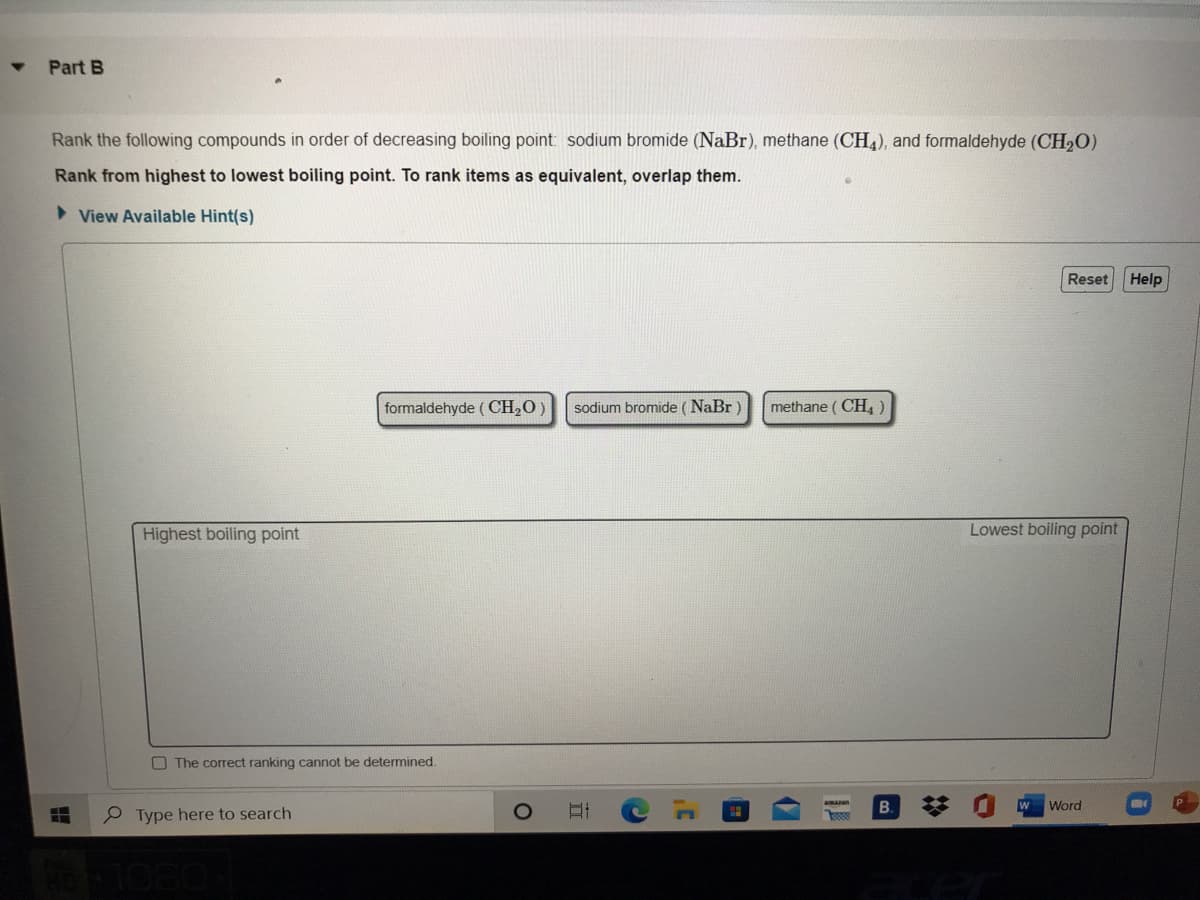
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point: sodium bromide (NaBr), methane (CH,), and formaldehyde (CH,O)
Rank from highest to lowest boiling point. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
> View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
formaldehyde ( CH2O
sodium bromide (NaBr
methane ( CH,)
Highest boiling point
Lowest boiling point
O The correct ranking cannot be determined.
B.
%23
W Word
P Type here to search

Transcribed Image Text:Activity 7
ntermolecular Forces in Liquids
4 of 6
Applying intermolecular forces to properties
A dipole moment tends to stabilize the liquid state of the compound as molecules align to form attractive molecular interactions. A liquid state that is more stable, that is one that is held together by stronger dipole forces, will have a higher boiling point
since it takes more energy to break these intermolecular forces.
Part B
i decreasing boiling point: sodium bromide (NaBr), methane (CH,), and formaldehyde (CH2O)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning