Run the simulation twice with default settings, and make sure the "stop when fixed" button is ON. For each simulation trials, take note of how many populations are fixed for the bw allele, and in which populations (i.e., population #1-10) the bw allele became fixed. To determine the generation where 50% of the populations are fixed, find the point where the fifth population is fixed for one of the two alleles (either bw or non-bw). Place your cursor on the line on the graph where the population becomes fixed (i.e., is at 1 or 0 on the y-axis), and the number of generations that have occurred at that point will appear on the x-axis. All of the data has been filled for you, but you need to try and do this on your own so you are familiar with the program for lab this week. Trial Total # of Which Generation where Generation where Generation where populations populations are fixed for the first five of the all populations fixed for bw population is fixed for bw or populations are fixed bw or non- are fixed bw or bw? non-bw non-bw bw N=10 1 3 3, 8, 10 20 56 N=10 3 4, 7, 10 14 59 26 N=20 1, 3, 7, 8, 10 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10 1,3,4,5,9,10 1 15 43 106 94 N=20 2 6. 11 26 N=80 6. 51 107 338 N=80 2 3,4,5,6,7,8 58 118 280 1. What was the effect of increasing population size on time to fixation? Explain your results. 2. Since the simulation starts with 50% of the bw allele, what is the average number of populations that would become fixed for this allele? Explain your answer. 3. What is the effect of changing initial bw allele frequency on time to fixation? Explain your answer including data (either in table or figure format) collected from the simulation. You need to decide what parameters to change and what to use as a control in order to answer this question.
Run the simulation twice with default settings, and make sure the "stop when fixed" button is ON. For each simulation trials, take note of how many populations are fixed for the bw allele, and in which populations (i.e., population #1-10) the bw allele became fixed. To determine the generation where 50% of the populations are fixed, find the point where the fifth population is fixed for one of the two alleles (either bw or non-bw). Place your cursor on the line on the graph where the population becomes fixed (i.e., is at 1 or 0 on the y-axis), and the number of generations that have occurred at that point will appear on the x-axis. All of the data has been filled for you, but you need to try and do this on your own so you are familiar with the program for lab this week. Trial Total # of Which Generation where Generation where Generation where populations populations are fixed for the first five of the all populations fixed for bw population is fixed for bw or populations are fixed bw or non- are fixed bw or bw? non-bw non-bw bw N=10 1 3 3, 8, 10 20 56 N=10 3 4, 7, 10 14 59 26 N=20 1, 3, 7, 8, 10 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10 1,3,4,5,9,10 1 15 43 106 94 N=20 2 6. 11 26 N=80 6. 51 107 338 N=80 2 3,4,5,6,7,8 58 118 280 1. What was the effect of increasing population size on time to fixation? Explain your results. 2. Since the simulation starts with 50% of the bw allele, what is the average number of populations that would become fixed for this allele? Explain your answer. 3. What is the effect of changing initial bw allele frequency on time to fixation? Explain your answer including data (either in table or figure format) collected from the simulation. You need to decide what parameters to change and what to use as a control in order to answer this question.
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter19: Population Genetics And Human Evolution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7QP: How Can We Measure Allele Frequencies in Populations? Drawing on your newly acquired understanding...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
#2 and #3
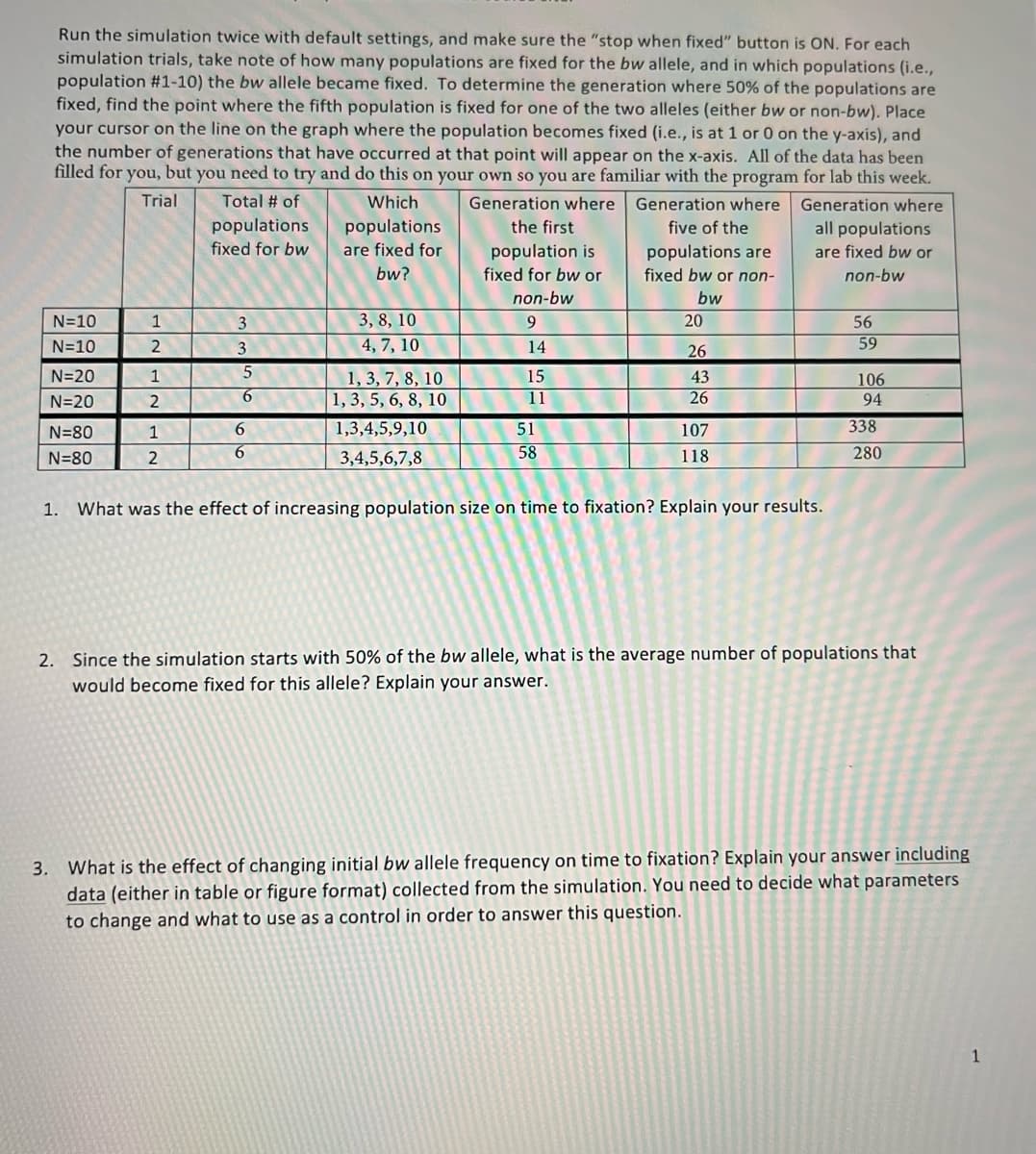
Transcribed Image Text:Run the simulation twice with default settings, and make sure the "stop when fixed" button is ON. For each
simulation trials, take note of how many populations are fixed for the bw allele, and in which populations (i.e.,
population #1-10) the bw allele became fixed. To determine the generation where 50% of the populations are
fixed, find the point where the fifth population is fixed for one of the two alleles (either bw or non-bw). Place
your cursor on the line on the graph where the population becomes fixed (i.e., is at 1 or 0 on the y-axis), and
the number of generations that have occurred at that point will appear on the x-axis. All of the data has been
filled for you, but you need to try and do this on your own so you are familiar with the program for lab this week.
Trial
Total # of
Which
Generation where Generation where
Generation where
populations
populations
the first
five of the
all populations
fixed for bw
are fixed for
population is
fixed for bw or
populations are
fixed bw or non-
are fixed bw or
bw?
non-bw
non-bw
bw
N=10
3
3, 8, 10
20
56
N=10
2
3
4, 7, 10
14
26
59
N=20
1
15
1, 3, 7, 8, 10
1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10
43
106
N=20
6
11
26
94
N=80
1
6
1,3,4,5,9,10
51
107
338
N=80
2
3,4,5,6,7,8
58
118
280
1. What was the effect of increasing population size on time to fixation? Explain your results.
2. Since the simulation starts with 50% of the bw allele, what is the average number of populations that
would become fixed for this allele? Explain your answer.
3. What is the effect of changing initial bw allele frequency on time to fixation? Explain your answer including
data (either in table or figure format) collected from the simulation. You need to decide what parameters
to change and what to use as a control in order to answer this question.
1
Expert Solution
Answer-2.
50% of the population will be fixed for the allele this is because genetic drift is random.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning