
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
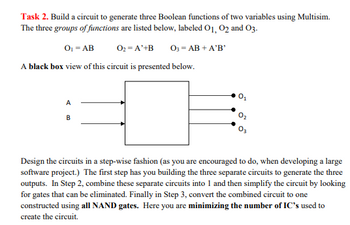
Transcribed Image Text:Task 2. Build a circuit to generate three Boolean functions of two variables using Multisim.
The three groups of functions are listed below, labeled O1, O2 and 03.
0₁ = AB
O₂ = A'+B 03 = AB + A'B'
A black box view of this circuit is presented below.
A
B
Design the circuits in a step-wise fashion (as you are encouraged to do, when developing a large
software project.) The first step has you building the three separate circuits to generate the three
outputs. In Step 2, combine these separate circuits into 1 and then simplify the circuit by looking
for gates that can be eliminated. Finally in Step 3, convert the combined circuit to one
constructed using all NAND gates. Here you are minimizing the number of IC's used to
create the circuit.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
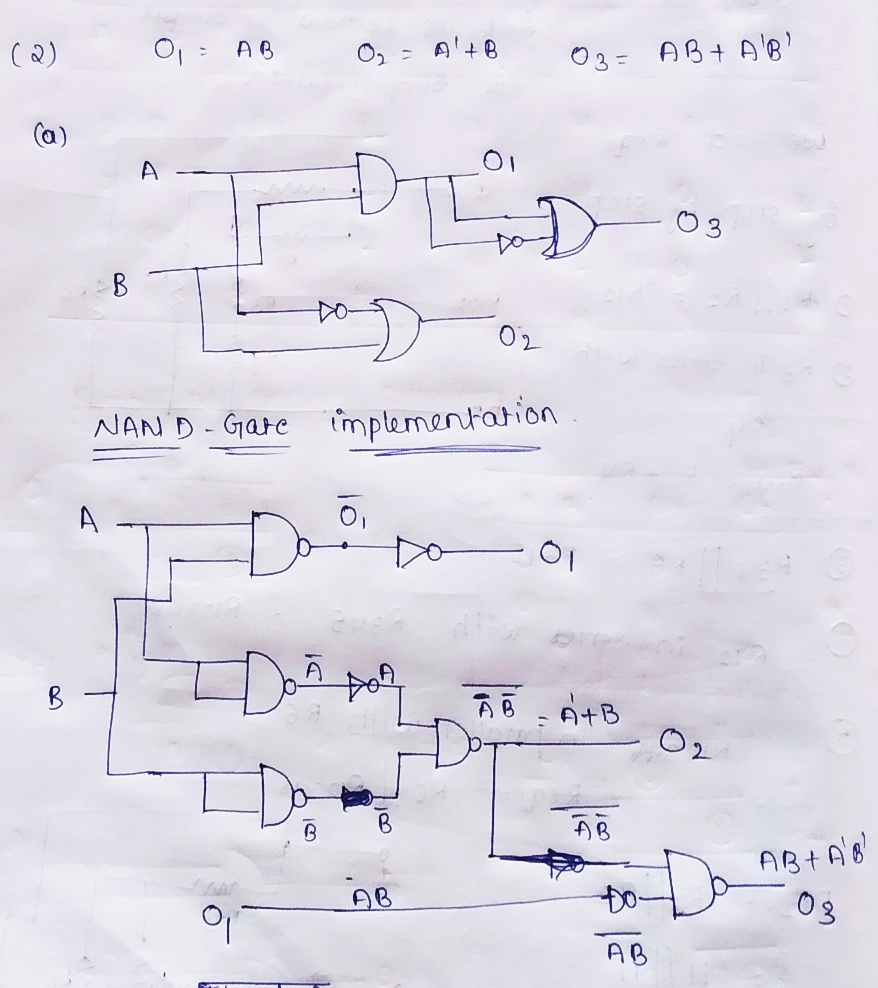
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- ISP-Java Taking what you learned over the last 8 weeks, it is now your turn to create a program of your choosing. If you are not sure where to begin, think of a task that you repeat often in your major that would benefit from a program. For example, chemistry unit conversions, finding the area for geometric shapes, etc. You can also create an interactive story that changes based on the user input/decisions. The possibilities are endless. The program must include instructions for the user. Be in the mindset that the program you develop will be used by anyone. You will not receive any assistance from the instructor. It is up to you to figure out your program. Your program must include (but not limited to) the following: • Comments • Input(s) and output(s) • Decision structures • Loops Be as creative as possible!arrow_forwardImplement the counter increment before returning to the loop's beginning. After completing these stages, your code should resemble the following, implementing the counter control loop's fundamental structure: .text li $s0, 0 lw $s1, n start_loop: sle $t1, $s0, $s1 beqz $t1, end_loop # code block addi $s0, $s0, 1 b start_loop end_loop:.data n: .word 5arrow_forwarddon't want the step i want the answers. Also this is not quiz but homeworkarrow_forward
- Active buzzer project: Write an algorithm for the below code for all steps. Then write a conclusion (test&debug) for the code. Also, write comments for the code explaining each line.arrow_forwardBuilding Arena models: A few years ago, I was in a group involved with building industrial facilities. A team of consultants visited us to make a presentation about improving the building process. They had a demonstration in the form of a game. We were divided into two teams of four and sat four in a row at a table. Person 1 was given 100 poker chips. The game process was Person 1 would roll a single die. Whatever the number was, he or she would pass that number of chips to Person 2. Person 2 would roll the die, and • If the number of the roll is less than or equal to the chips in front of Person 2, the number of the die roll is passed to the next person. Any remaining chips stay in place, to be passed on another turn when possible.• If the roll on the die is greater than the number of the chips in front of Person 2, all the chips are passed, but the difference in what could be passed is lost on that turn. For example, if Person 2 has 3 chips and rolls a “1,” then one chip is passed.…arrow_forwardThe Goal: Like the title suggests, this project involves writing a program that simulates rolling dice. When the program runs, it will randomly choose a number between 1 and 6. (Or whatever other integer you prefer — the number of sides on the die is up to you.) The program will print what that number is. It should then ask you if you’d like to roll again. For this project, you’ll need to set the min and max number that your dice can produce. For the average die, that means a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 6. You’ll also want a function that randomly grabs a number within that range and prints it. Concepts to keep in mind: Random, Integer, Print, While Loopsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY