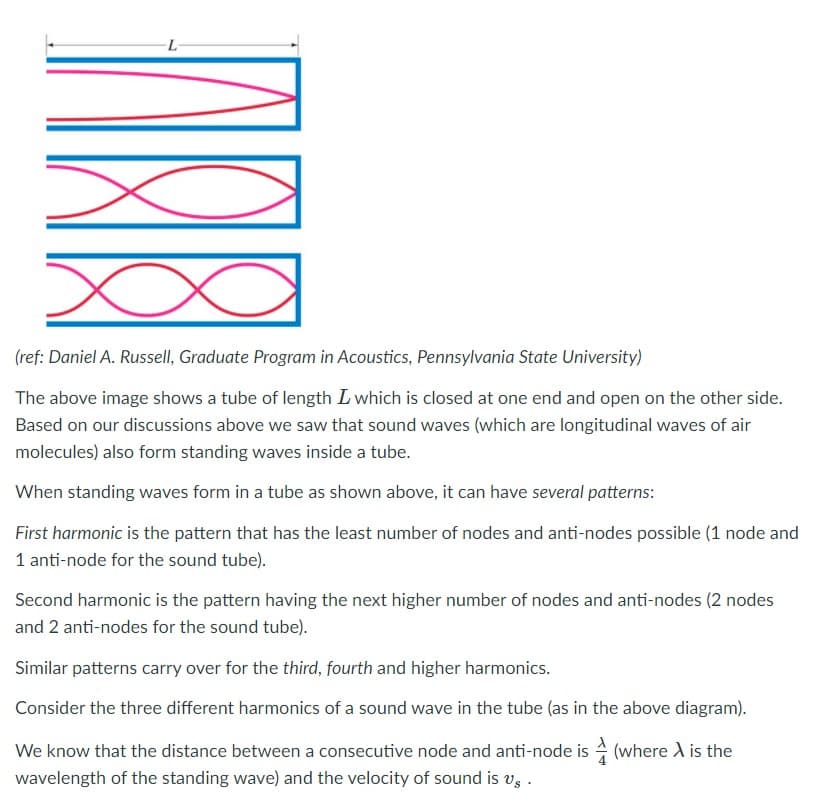
The above image shows a tube of length L which is closed at one end and open on the other side. Based on our discussions above we saw that sound waves (which are longitudinal waves of air molecules) also form standing waves inside a tube. When standing waves form in a tube as shown above, it can have several patterns: First harmonic is the pattern that has the least number of nodes and anti-nodes possible (1 node and 1 anti-node for the sound tube). Second harmonic is the pattern having the next higher number of nodes and anti-nodes (2 nodes and 2 anti-nodes for the sound tube).
The above image shows a tube of length L which is closed at one end and open on the other side. Based on our discussions above we saw that sound waves (which are longitudinal waves of air molecules) also form standing waves inside a tube. When standing waves form in a tube as shown above, it can have several patterns: First harmonic is the pattern that has the least number of nodes and anti-nodes possible (1 node and 1 anti-node for the sound tube). Second harmonic is the pattern having the next higher number of nodes and anti-nodes (2 nodes and 2 anti-nodes for the sound tube).
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter27: Wave Optics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17P: A riverside warehouse has several small doors facing the river. Two of these doors are open as shown...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:(ref: Daniel A. Russell, Graduate Program in Acoustics, Pennsylvania State University)
The above image shows a tube of length L which is closed at one end and open on the other side.
Based on our discussions above we saw that sound waves (which are longitudinal waves of air
molecules) also form standing waves inside a tube.
When standing waves form in a tube as shown above, it can have several patterns:
First harmonic is the pattern that has the least number of nodes and anti-nodes possible (1 node and
1 anti-node for the sound tube).
Second harmonic is the pattern having the next higher number of nodes and anti-nodes (2 nodes
and 2 anti-nodes for the sound tube).
Similar patterns carry over for the third, fourth and higher harmonics.
Consider the three different harmonics of a sound wave in the tube (as in the above diagram).
We know that the distance between a consecutive node and anti-node is (where A is the
wavelength of the standing wave) and the velocity of sound is v, .

Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following gives the wavelength of the third harmonic of the sound wave as in the
above diagram ?
O A = -4L
4L
4L
O A =
%3D
X = 4L
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning