The eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules with free 3'-OH and 5'-PO3- ends. DNA free ends are signals of double strand breaks, which are highly detrimental for the cell. Using the diagram below as a reference, describe structurally how telomeres resolve this problem. Make sure to highlight the interactions involved, the nature of the telomeric sequences and the correct nomenclature for the structure formed. 5' Telomeric DNA TTGGGGTTGGGGTTGGGG 3' TGGGGז AACCCC AACCCCAACCCC AACCCCAACCCC Non-telomeric DNA TTGGGG 3' TGGזGG AACCCC. 5' AACCCC AACCCC TTGGGG TTGGGG TTGGGGTTGGGGTTGGGG AACCCCAACCCCAAC C AACCCC TGGGGז
The eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules with free 3'-OH and 5'-PO3- ends. DNA free ends are signals of double strand breaks, which are highly detrimental for the cell. Using the diagram below as a reference, describe structurally how telomeres resolve this problem. Make sure to highlight the interactions involved, the nature of the telomeric sequences and the correct nomenclature for the structure formed. 5' Telomeric DNA TTGGGGTTGGGGTTGGGG 3' TGGGGז AACCCC AACCCCAACCCC AACCCCAACCCC Non-telomeric DNA TTGGGG 3' TGGזGG AACCCC. 5' AACCCC AACCCC TTGGGG TTGGGG TTGGGGTTGGGGTTGGGG AACCCCAACCCCAAC C AACCCC TGGGGז
Biology (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Chapter14: Gene Regulation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8TYU: Through alternative splicing, eukaryotes (a) reinforce gene inactivation (b) prevent transcription...
Related questions
Question
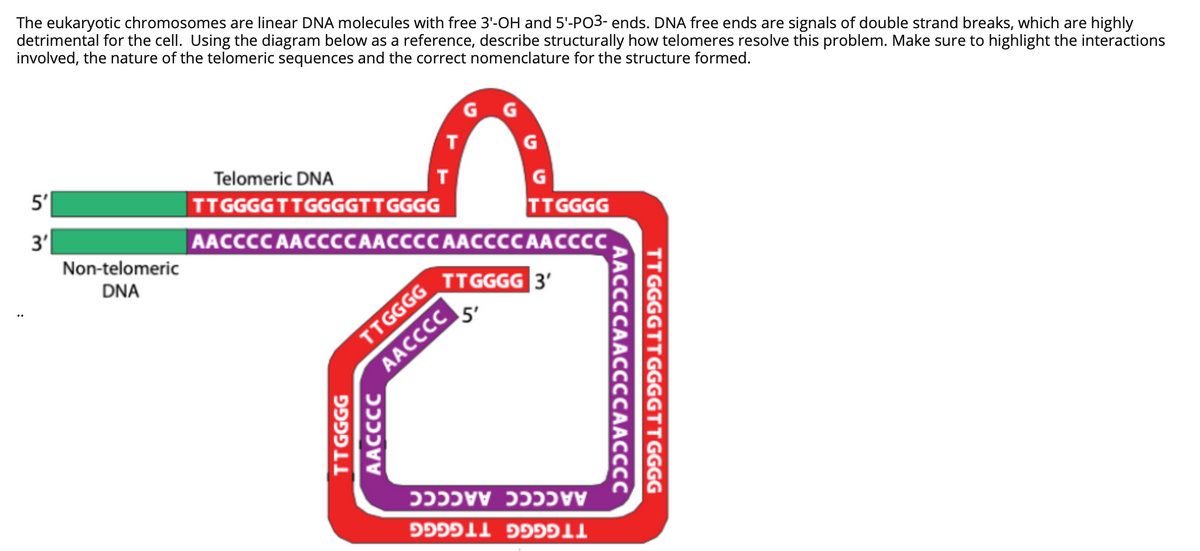
Transcribed Image Text:The eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules with free 3'-OH and 5'-PO3- ends. DNA free ends are signals of double strand breaks, which are highly
detrimental for the cell. Using the diagram below as a reference, describe structurally how telomeres resolve this problem. Make sure to highlight the interactions
involved, the nature of the telomeric sequences and the correct nomenclature for the structure formed.
G G
Telomeric DNA
5'
т
GCGGזזTTGGGGTTGG6
G
TTGGGG
AACCCC AACCCCAACCCC AACCCCAACCCC.
3'
Non-telomeric
DNA
TTGGGG 3'
TTGGGG
5'
AACCCC
AACCCC AACCCC
LL פפפ llככפפ
TT GGGGTTGGGGTTGGGG
AACCCCAACCCCAACCCC
vvככככ
llפכפפ
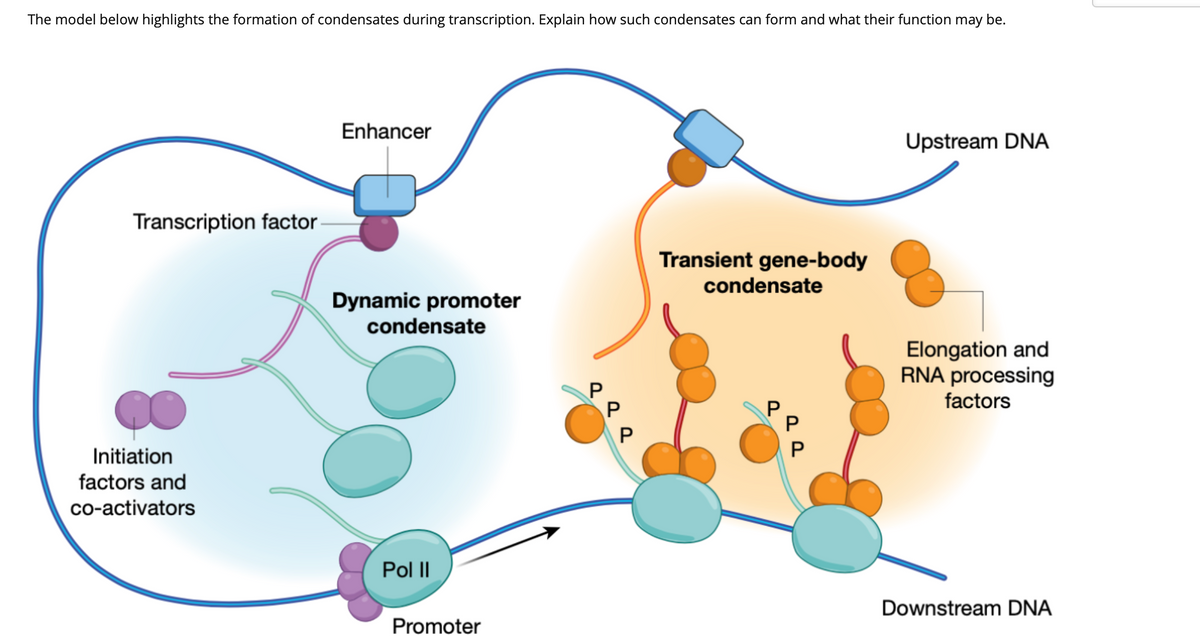
Transcribed Image Text:The model below highlights the formation of condensates during transcription. Explain how such condensates can form and what their function may be.
Enhancer
Upstream DNA
Transcription factor
Transient gene-body
condensate
Dynamic promoter
condensate
Elongation and
RNA processing
factors
Initiation
factors and
co-activators
Pol II
Downstream DNA
Promoter
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning