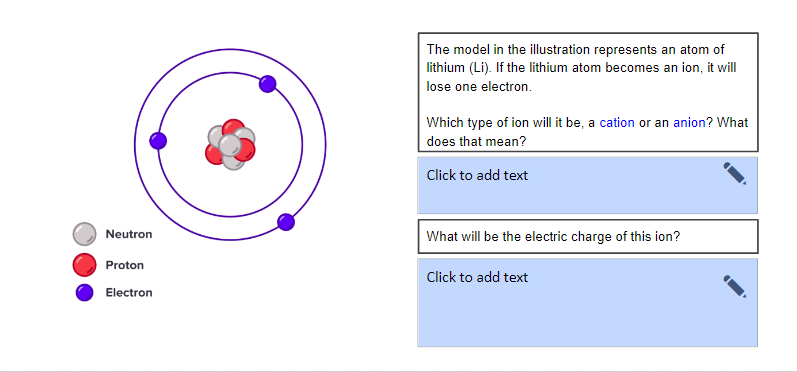
The model in the illustration represents an atom of lithium (Li). If the lithium atom becomes an ion, it will lose one electron. Which type of ion will it be, a cation or an anion? What does that mean? Click to add text Neutron What will be the electric charge of this ion? Proton Click to add text Electron
Electron Affinity
When an element undergoes a chemical reaction, it either gains energy or loses energy. This gain or loss of energy is due to the phenomena that occur at atomic level. During reaction, atoms either gain electrons from other atoms or lose electrons to other atoms, and in that process, energy is produced.
P-Block Elements
Elements which are present on the right side of the periodic table are called p-block elements. In addition to the noble gases, they include the families of boron, mercury, nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine. These elements have diverse real-life implementations that we regularly experience around us.
Metals and Non-metals
The periodic table is composed of metals, semi-metals and nonmetal elements. The physical and chemical properties of metals and nonmetals differ from each other. The study of metals and nonmetals will help one to understand the appropriate application of the particular element.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









