The particle in a box (PiB) model can be applied to electrons which move freely in a molecule such as π electrons. 1,3-butadiene CH2=CH-CH=CH2 has an absorption peak in the UV-Vis spectrum at 290 nm. This peaks is assigned to the π → π* transition of the lowest energy. This transition is also called the HOMO → LUMO transition. As a simple approximation, let’s consider molecule of butadiene as being potential 1D box of length 3 * 1.4 Å = 4.2 Å, when counting three carbon-carbon bonds each 1.4 Å long. Also let’s consider the four π electrons occupy molecular orbitals MOs and energy of MOs is calculated according to the PiB model. a)
The particle in a box (PiB) model can be applied to electrons which move freely in a molecule such as π electrons. 1,3-butadiene CH2=CH-CH=CH2 has an absorption peak in the UV-Vis spectrum at 290 nm. This peaks is assigned to the π → π* transition of the lowest energy. This transition is also called the HOMO → LUMO transition. As a simple approximation, let’s consider molecule of butadiene as being potential 1D box of length 3 * 1.4 Å = 4.2 Å, when counting three carbon-carbon bonds each 1.4 Å long. Also let’s consider the four π electrons occupy molecular orbitals MOs and energy of MOs is calculated according to the PiB model. a)
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter4: Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10P: Use the data in Figure 4.8 to estimate the ratio of radiation intensity at 10,000 Å (infrared) to...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Atomic Structure
The basic structure of an atom is defined as the component-level of atomic structure of an atom. Precisely speaking an atom consists of three major subatomic particles which are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Many theories have been stated for explaining the structure of an atom.
Shape of the D Orbital
Shapes of orbitals are an approximate representation of boundaries in space for finding electrons occupied in that respective orbital. D orbitals are known to have a clover leaf shape or dumbbell inside where electrons can be found.
Question
The particle in a box (PiB) model can be applied to electrons which move freely in a molecule such as π electrons.
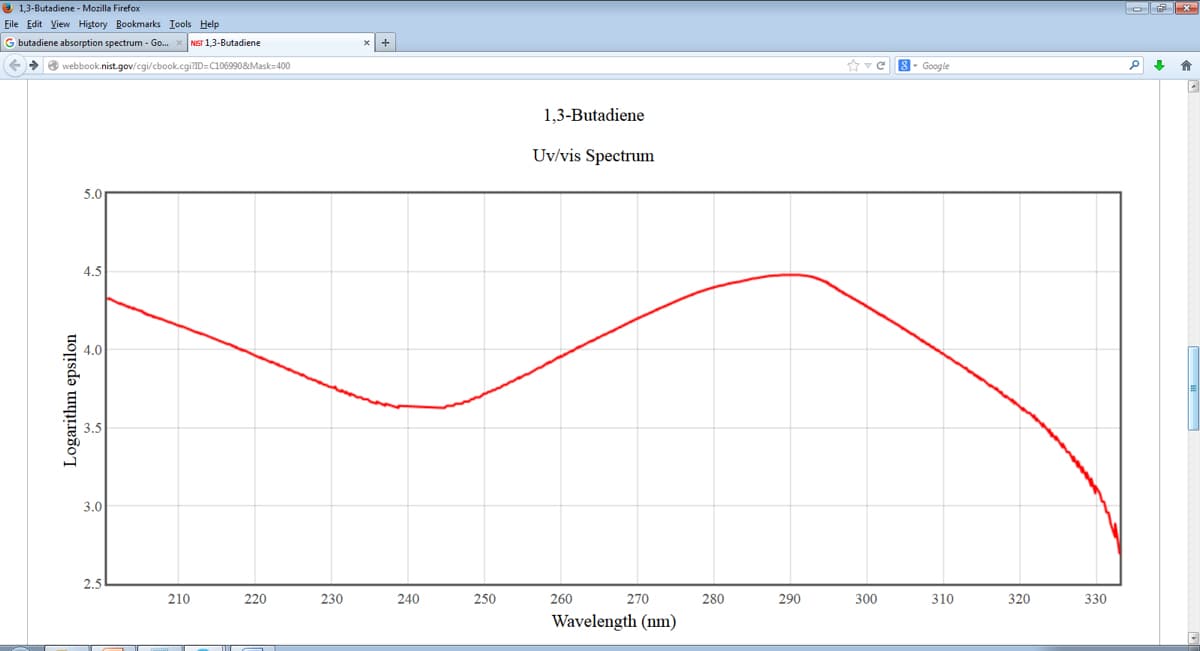
1,3-butadiene CH2=CH-CH=CH2 has an absorption peak in the UV-Vis spectrum at 290 nm. This peaks is assigned to the π → π* transition of the lowest energy.
This transition is also called the HOMO → LUMO transition.
As a simple approximation, let’s consider molecule of butadiene as being potential 1D box of length 3 * 1.4 Å = 4.2 Å, when counting three carbon-carbon bonds each 1.4 Å long.
Also let’s consider the four π electrons occupy molecular orbitals MOs and energy of MOs is calculated according to the PiB model.
a) Sketch the scheme of MOs of butadiene molecule and populate them with electrons.
b) Calculate the wavelength of light λcalc which corresponds to absorption of light and excitation of π electron from the HOMO to the LUMO in the molecule of butadiene.
c) Compare this calculated λcalc with experimental value of λexp = 290 nm provided above, and explain the difference (at least two reasons).
Transcribed Image Text:1,3-Butadiene - Mozilla Firefox
File Edit View History Bookmarks Tools Help
G butadiene absorption spectrum - Go... XNIST 1,3-Butadiene
webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C106990&Mask=400
Logarithm epsilon
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
||
210
220
ILAT
230
x +
240
250
1,3-Butadiene
Uv/vis Spectrum
260
270
Wavelength (nm)
280
290
☆ C 8- Google
300
310
320
330
P
會
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning