The president of Hill Enterprises, Terri Hill, projects the firm's aggregate demand requirements over the next 8 months as follows: 1200 January February May June 2,100 1,500 2,100 March 1,700 1.800 July August 1,900 1,300 April Her operations manager is considering a new plan, which begins in January with 200 units on hand and ends with zero inventory. Stockout cost of lost sales is $125 per unit Inventory holding cost is $20 per unit per month. Ignore any idle-time costs. The plan is called plan B. Plan B: Produce at a constant rate of 1,200 units per month, which will meet minimum demands. Then use subcontracting, with additional units at a premium price of $75 per unit Subcontracting capacity is limited to 900 units per month. Evaluate this plan by computing the costs for January through Augusi In order to arrive at the costs, first compute the ending inventory and subcontracting units for each month by filing in the table below (enter your responses as whole numbers). Ending Inventory 200 Subcontract Period Month O December 1 January 2 February 3 March 4 April 5 May 6 June 7 July 8 August Demand Production Units 1.200 1,200 1.500 1,200 1,700 1,200 1,800 1,200 5 2,100 1,200 2.100 1,200 1,900 1,200 1,300 1,200 The total subcontracting cost S (Enter your response as a whole number.) The total inventory carrying cost = S (Enter your response as a whole number.) The total cost, excluding normal time labor costs, is = $ (Enter your response as a whole number)
The president of Hill Enterprises, Terri Hill, projects the firm's aggregate demand requirements over the next 8 months as follows: 1200 January February May June 2,100 1,500 2,100 March 1,700 1.800 July August 1,900 1,300 April Her operations manager is considering a new plan, which begins in January with 200 units on hand and ends with zero inventory. Stockout cost of lost sales is $125 per unit Inventory holding cost is $20 per unit per month. Ignore any idle-time costs. The plan is called plan B. Plan B: Produce at a constant rate of 1,200 units per month, which will meet minimum demands. Then use subcontracting, with additional units at a premium price of $75 per unit Subcontracting capacity is limited to 900 units per month. Evaluate this plan by computing the costs for January through Augusi In order to arrive at the costs, first compute the ending inventory and subcontracting units for each month by filing in the table below (enter your responses as whole numbers). Ending Inventory 200 Subcontract Period Month O December 1 January 2 February 3 March 4 April 5 May 6 June 7 July 8 August Demand Production Units 1.200 1,200 1.500 1,200 1,700 1,200 1,800 1,200 5 2,100 1,200 2.100 1,200 1,900 1,200 1,300 1,200 The total subcontracting cost S (Enter your response as a whole number.) The total inventory carrying cost = S (Enter your response as a whole number.) The total cost, excluding normal time labor costs, is = $ (Enter your response as a whole number)
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
100%
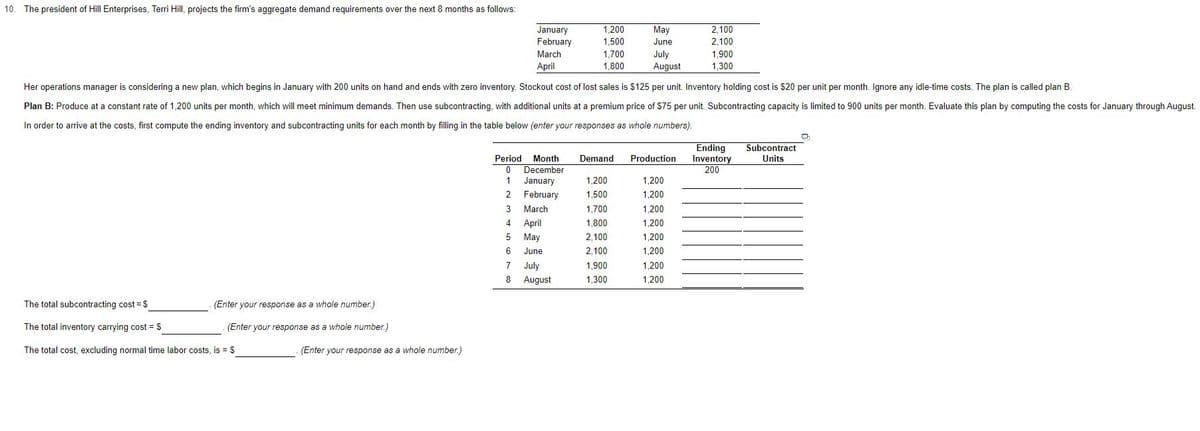
Transcribed Image Text:10. The president of Hill Enterprises, Terri Hill, projects the firm's aggregate demand requirements over the next 8 months as follows:
2,100
January
February
1,200
May
1,500
June
2,100
1,700
1,800
March
July
August
1,900
April
1,300
Her operations manager is considering a new plan, which begins in January with 200 units on hand and ends with zero inventory. Stockout cost of lost sales is $125 per unit. Inventory holding cost is $20 per unit per month. Ignore any idle-time costs. The plan is called plan B.
Plan B: Produce at a constant rate of 1,200 units per month, which will meet minimum demands. Then use subcontracting, with additional units at a premium price of $75 per unit. Subcontracting capacity is limited to 900 units per month. Evaluate this plan by computing the costs for January through August.
In order to arrive at the costs, first compute the ending inventory and subcontracting units for each month by filling in the table below (enter your responses as whole numbers).
Ending
Inventory
200
Subcontract
Period Month
O December
January
Demand
Production
Units
1
1,200
1,200
February
1,500
1,200
3
March
1,700
1,200
April
1,800
1,200
5
May
2,100
1,200
6
June
2,100
1,200
7
July
1,900
1,200
8
August
1,300
1,200
The total subcontracting cost = $
(Enter your response as a whole number.)
The total inventory carrying cost = S
(Enter your response as a whole number.)
The total cost, excluding normal time labor costs, is = $
(Enter your response as a whole number.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.