The structural steel column is fixed at its base and free at its upper end. Assume L = 13.0 ft, a = 0.99 in., b = 7.5 in., c = 9.48 in., d = 9.48 in., and t = 0.79 in. At the top of the column, a load Pis applied to the stiffened seat support at an eccentricity of e from the centroidal axis of the wide-flange shape. Using the allowable stress method, determine the maximum allowable eccentricity e if (a) P = 18 kips and (b) P = 32 kips. Apply the AISC equations given in Section 16.5 and assume that E = 29,000 ksi and oy = 50 ksi.
The structural steel column is fixed at its base and free at its upper end. Assume L = 13.0 ft, a = 0.99 in., b = 7.5 in., c = 9.48 in., d = 9.48 in., and t = 0.79 in. At the top of the column, a load Pis applied to the stiffened seat support at an eccentricity of e from the centroidal axis of the wide-flange shape. Using the allowable stress method, determine the maximum allowable eccentricity e if (a) P = 18 kips and (b) P = 32 kips. Apply the AISC equations given in Section 16.5 and assume that E = 29,000 ksi and oy = 50 ksi.
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter11: Columns
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.4.14P
Related questions
Question
PLEASE ANSWER
(STRESS)e = ?
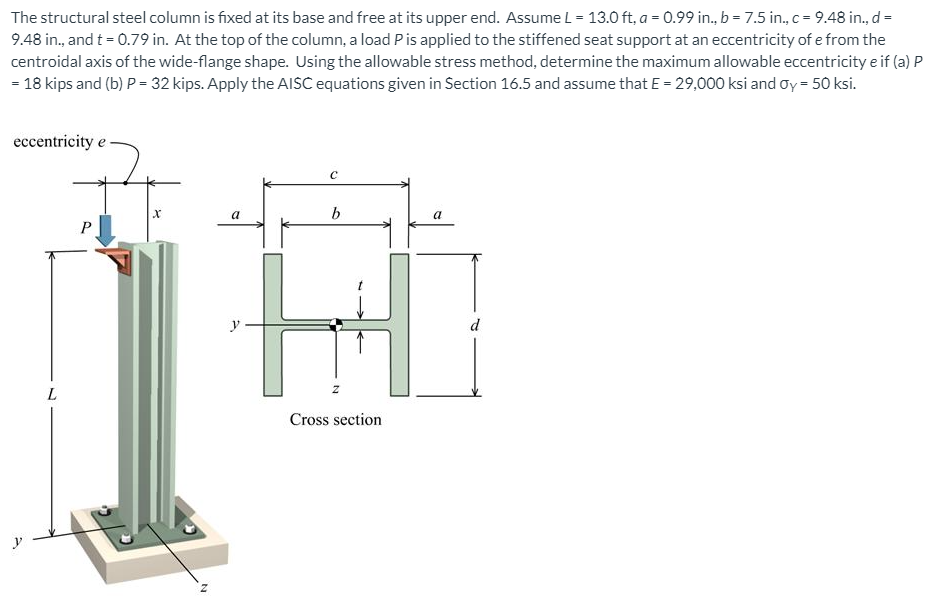
Transcribed Image Text:The structural steel column is fixed at its base and free at its upper end. Assume L = 13.0 ft, a = 0.99 in., b = 7.5 in., c = 9.48 in., d =
9.48 in., and t = 0.79 in. At the top of the column, a load Pis applied to the stiffened seat support at an eccentricity of e from the
centroidal axis of the wide-flange shape. Using the allowable stress method, determine the maximum allowable eccentricity e if (a) P
= 18 kips and (b) P = 32 kips. Apply the AISC equations given in Section 16.5 and assume that E = 29,000 ksi and oy = 50 ksi.
eccentricity e
b
y
d
Cross section
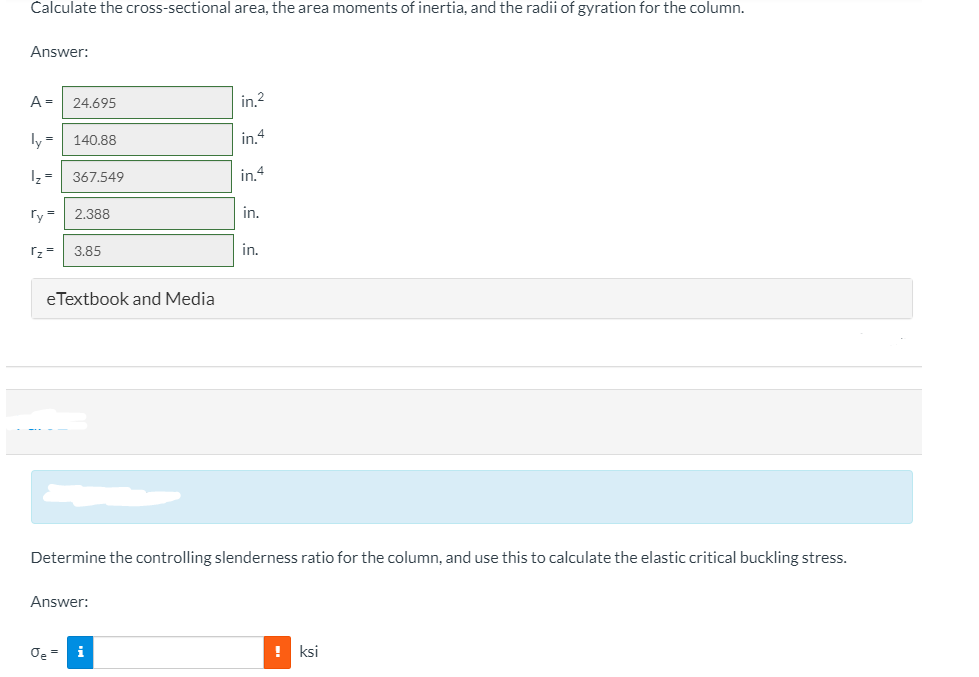
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate the cross-sectional area, the area moments of inertia, and the radii of gyration for the column.
Answer:
A =
24.695
in.2
ly =| 140.88
in4
1z =
367.549
in.4
ry =
2.388
in.
rz =
3.85
in.
eTextbook and Media
Determine the controlling slenderness ratio for the column, and use this to calculate the elastic critical buckling stress.
Answer:
! ksi
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning