Three steel bars have a diameter of 25 mm and carbon contents of 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8%, respectively. The specimens were subjected to tension until rupture. The load versus deformation results were as shown in Table P3.19. If the gauge length is 50 mm, determine the following: a. The tensile stresses and strains for each specimen at each load increment. b. Plot stresses versus strains for all specimens on one graph. TABLE P3.19 Specimen No. Carbon Content (%) 1 3 0.2 0.5 0.8 Deformation (mm) Load (kN) 0.00 0.07 133 133 133 0.10 137 191 191 0.15 142 196 285 0.50 147 201 324 1.00 140 199 383 2.50 155 236 447 5.00 196 295 491 (Rupture) 7.50 226 336 10.00 241 341 12.50 218 304 (Rupture) 13.75 196 (Rupture) c. The proportional limit for each specimen. d. The 0.2% offset yield strength for each specimen. e. The modulus of elasticity for each specimen. f. The strain at rupture for each specimen. g. Comment on the effect of increasing the carbon content on the following: Yield strength ii. Modulus of elasticity iii. Ductility i.
Three steel bars have a diameter of 25 mm and carbon contents of 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8%, respectively. The specimens were subjected to tension until rupture. The load versus deformation results were as shown in Table P3.19. If the gauge length is 50 mm, determine the following: a. The tensile stresses and strains for each specimen at each load increment. b. Plot stresses versus strains for all specimens on one graph. TABLE P3.19 Specimen No. Carbon Content (%) 1 3 0.2 0.5 0.8 Deformation (mm) Load (kN) 0.00 0.07 133 133 133 0.10 137 191 191 0.15 142 196 285 0.50 147 201 324 1.00 140 199 383 2.50 155 236 447 5.00 196 295 491 (Rupture) 7.50 226 336 10.00 241 341 12.50 218 304 (Rupture) 13.75 196 (Rupture) c. The proportional limit for each specimen. d. The 0.2% offset yield strength for each specimen. e. The modulus of elasticity for each specimen. f. The strain at rupture for each specimen. g. Comment on the effect of increasing the carbon content on the following: Yield strength ii. Modulus of elasticity iii. Ductility i.
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337094740
Author:Segui, William T.
Publisher:Segui, William T.
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.5.6P: The data in Table 1.5.3 were obtained from a tensile test of a metal specimen with a rectangular...
Related questions
Question
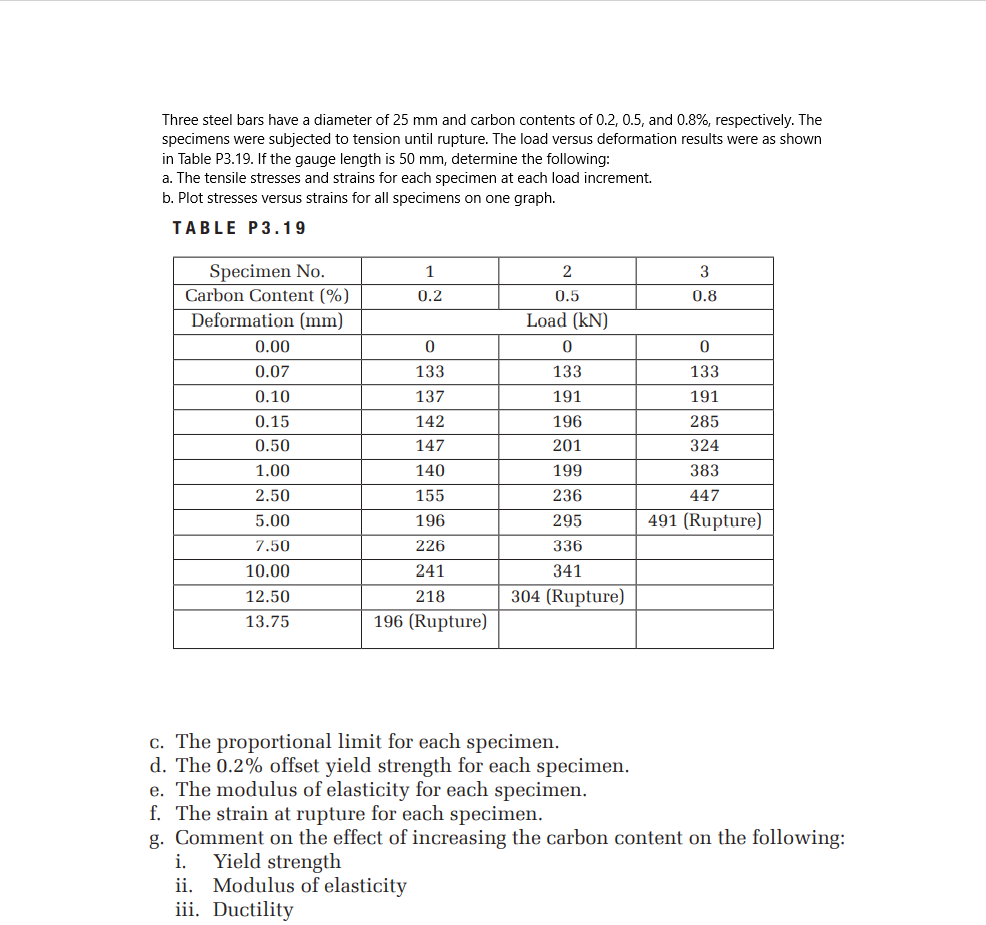
Transcribed Image Text:Three steel bars have a diameter of 25 mm and carbon contents of 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8%, respectively. The
specimens were subjected to tension until rupture. The load versus deformation results were as shown
in Table P3.19. If the gauge length is 50 mm, determine the following:
a. The tensile stresses and strains for each specimen at each load increment.
b. Plot stresses versus strains for all specimens on one graph.
TABLE P3.19
Specimen No.
Carbon Content (%)
1
3
0.2
0.5
0.8
Deformation (mm)
Load (kN)
0.00
0.07
133
133
133
0.10
137
191
191
0.15
142
196
285
0.50
147
201
324
1.00
140
199
383
2.50
155
236
447
5.00
196
295
491 (Rupture)
7.50
226
336
10.00
241
341
12.50
218
304 (Rupture)
13.75
196 (Rupture)
c. The proportional limit for each specimen.
d. The 0.2% offset yield strength for each specimen.
e. The modulus of elasticity for each specimen.
f. The strain at rupture for each specimen.
g. Comment on the effect of increasing the carbon content on the following:
Yield strength
ii. Modulus of elasticity
iii. Ductility
i.
Expert Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 9 steps with 14 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305086272
Author:
William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:
Cengage Learning