
Concept explainers
Scenes A-D represent atomic-scale views of different samples of substances:
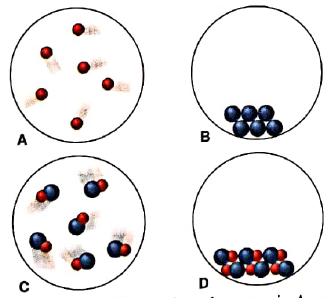
- Under one set of conditions, the substances in A and B mix, and the result is depicted in C. Does this represent a chemical or a physical change?
- Under a second set of conditions, the same substances mix, and the result is depicted in D. Does this represent a chemical or a physical change?
- Under a third set of conditions, the same substances mix, and the result is depicted in D. Does this represent a chemical or a physical change?
- After the change in part(c) has occurred, does the sample have different chemical properties? Physical properties?
a)
Interpretation: Whether combination of A and B to form C is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction: Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
Substances that are present in A and B have completely different properties than those formed in C. So when A and B are mixed to form C, it refers to chemical change.
b)
Interpretation: Whether combination of A and B to form D is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction:Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
Substances that are present in A and B have completely different properties than those formed in D. So when A and B are mixed to form D, a completely different substance is formed. Therefore combination of A and B to form D is chemical change.
c)
Interpretation: Whether conversion of C to D is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction: Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
When sample in C is converted to D, there occurs difference in arrangement of particles only while substances remain same. Therefore it is physical change.
d)
Interpretation: Whether conversion of C to D is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction: Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
When sample in C is converted to D, only arrangement of particles is changed while substances remain same. Therefore it is physical change and physical properties are changed in conversion of C to D.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Principles of General Chemistry
- You have learned the basic way in which scientists analyze problems, propose models to explain the systems under consideration, and then experiment to test their models. Suppose you have a sample of a liquid material. You are not sure whether the liquid is a purecompound(for example, water or alcohol) or asolution. How could you apply the scientific method to study the liquid and to determine which type of material the liquid is?arrow_forwardWhich substance can be separated by filtration? A. Compound B. Element C. Mixture D. Solution Which is an example of physical property of matter? * A. Baking a cake B. Cooking of gelatin C. Melting of ice D. Rusting of metal Which is an example of chemical property of matter? A. Digestion of food B. Evaporation of water C. Sublimation of moth balls D. Condensation of water vapor Which is a physical property of matter? A. Combustibility B. Corrosiveness C. Density D. Reactivityarrow_forward1.) Which macroscopic characteristics differentiate solids, liquids, and gases? (List as many as possible.) 2.) In what types of technology do the elements designated as critical materials generally play important roles? 3.) When a scientist looks at an experiment and then predicts the results of other related experiments, which type of reasoning is she using? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- In a dry test tube, put enough cane sugar to make a layer about 1⁄4 inch deep. heat the tube in the flame while holding a cool inverted beaker near the mouth of the test tube. Observations: What is collected in the beaker? Where did this come from? What are the elements present in this substance? What is left behind in the test tube? What element is it? What elements therefore are present in combination in sugar?arrow_forwardTwo beakers contain clear, colorless liquids. When the contentsof the beakers are mixed a white solid is formed. (a) Isthis an example of a chemical or a physical change? (b) Whatwould be the most convenient way to separate the newlyformed white solid from the liquid mixture—filtration, distillation,or chromatography.arrow_forwardIs boiling water a physical or chemical change? Provide evidence from the pictures. When______changes occur, Written excerpt-The water being boiled is pure water. When the water is heated the kinetic energy of the water molecules increases, meaning that the molecules begin to move faster. As the speed increases they begin to overcome their attractions to the other molecules. This eventually allows the water to change from a liquid to a gas as molecules escape out of the liquid and into the air. In the written excerpt it indicates that? The chemical equations shows?arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is false? a. Matter may be a pure substance or it may be a mixture b. A pure substance may either be an element or a compound c. Mixtures may be composed of two or more elements, two or more compounds, or a combination of both d. a mixture may be either homogenous or heterogenous e. all of the above statements are truearrow_forwardWhich of the following figures represents (a) a pure element,(b) a mixture of two elements, (c) a pure compound, (d) amixture of an element and a compound? (More than onepicture might fit each description.) [Section 1.2]arrow_forwardWhich of the following are chemical changes? Which are physical changes? a. the cutting of food b. interaction of food with saliva and digestive enzymes c. proteins being broken down into amino acids d. complex sugars being broken down into simple sugars e. making maple syrup by heating maple sap to remove water through evaporation f. DNA unwindingarrow_forward
- Based on the information in Figure 1.1, which three elements would you argue are the most critical among the “critical materials”? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardA white, crystalline material that looks like table salt gives off a gas when heated under certain conditions. There is no change in the appearance of the solid that remains, but it does not taste the same as it did originally. Was the beginning material an element or a compound? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardParacelsus, a sixteenth-century alchemist and healer, adopted as his slogan: "The patients are your textbook, the sickbed is your study. Is this view consistent with using the scientific method?arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





