
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS
6th Edition
ISBN: 8220103146609
Author: Anderson
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.6P
Consider an NACA 2412 airfoil (the meaning of the number designations for standard NACA airfoil shapes is discussed in Chapter 4). The following is a tabulation of the lift, drag, and moment coefficients about the quarter chord for this airfoil, as a function of angle of attack.
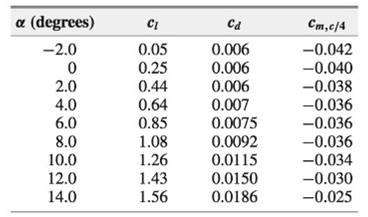
From this table, plot on graph paper the variation of
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
a)What is the impact of increasing Reynolds number on skin friction and pressure drags over an airfoil? What can be happened for separation in this case?
b) What is an adverse pressure gradient and where does it occur on an airfoil (show that on a sketch)?
c) Why lift-to-drag ratio is an important parameter for an aircraft?
d)How can changing in altitude affect the aircraft power required, PR? Show thatmathematically and graphically?
The airfoil section of the wing of the British Spitfire of World War II fame is an NACA 2213 at the wing root, tapering to an NACA 2205 at the wing tip. The root chord is 8.33 ft. The measured profile drag coefficient of the NACA 2213 airfoil is 0.006 at a Reynolds number of 9 × 106. Consider the Spitfire cruising at an altitude of 19000 ft. Assume that μ varies as the square root of temperature.
At this velocity and altitude, assuming completely turbulent flow, estimate the skin-friction drag coefficient for the NACA 2213 airfoil, and compare this with the total profile drag coefficient. Calculate the percentage of the profile drag coefficient that is due to pressure drag. (Round the final answer to three decimal places.)
The skin-friction drag coefficient for the NACA 2213 airfoil is .
Consider the NACA 2412 airfoil, data for which is given in 4.10 and 4.11. The data are given for two values of the Reynolds number based on chord length. For the case where Rec = 3.1×106, estimate: (a) the laminar boundary layer thickness at the trailing edge for a chord length of 1.5 m and (b) the net laminar skin-friction drag coefficient for the airfoil.
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS
Ch. 1 - For most gases at standard or near standard...Ch. 1 - Starting with Equations (1.7),(1.8), and (1.11),...Ch. 1 - Consider an infinitely thin flat plate of chord c...Ch. 1 - Consider an infinitely thin flat plate with a 1 m...Ch. 1 - Consider an airfoil at 12 angle of attack. The...Ch. 1 - Consider an NACA 2412 airfoil (the meaning of the...Ch. 1 - The drag on the hull of a ship depends in part on...Ch. 1 - The shock waves on a vehicle in supersonic flight...Ch. 1 - Consider two different flows over geometrically...Ch. 1 - Consider a Lear jet flying at a velocity of 250...
Ch. 1 - A U-tube mercury manometer is used to measure the...Ch. 1 - The German Zeppeins of World War I were dirigibles...Ch. 1 - Consider a circular cylinder in a hypersonic flow,...Ch. 1 - Derive Archimedes principle using a body of...Ch. 1 - Consider a light, single-engine, propeller-driven...Ch. 1 - Consider a flat plate at zero angle of attack in a...Ch. 1 - Consider the Space Shuttle during its atmospheric...Ch. 1 - The purpose of this problem is to give you a feel...Ch. 1 - For the design of their gliders in 1900 and 1901,...Ch. 1 - Consider the existence of a forward-facing axial...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Compute the hydraulic radius for a circular drain pipe running half full if its inside diameter is 300 mm.
Applied Fluid Mechanics (7th Edition)
A 20-lb force is applied to the control rod AB as shown. Knowing that the length of the rod is 9 in. and that t...
Statics and Mechanics of Materials
The triple jump is a track-and-field event in which an athlete gets a running start and tries to leap as far as...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
5.1 through 5.9
Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.
Fig. P5.1
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Kindly give me both right solutions with clear calculations The drag polar of a glider is given by CD=0.01+0.022CL2 . If it is launched from a height of 400m in still air. Please determine:(a) the maximum lift to drag ratio ??;(b) the greatest possible ground distance it can cover.arrow_forwardThe airfoil section of the wing of the British Spitfire of World War II fame is an NACA 2213 at the wing root, tapering to an NACA 2205 at the wing tip. The root chord is 8.33 ft. The measured profile drag coefficient of the NACA 2213 airfoil is 0.006 at a Reynolds number of 9 × 106. Consider the Spitfire cruising at an altitude of 19000 ft. Assume that μ varies as the square root of temperature. At what velocity is it flying for the root chord Reynolds number to be 9 × 106? (Round the final answer to the nearest whole number.) The velocity at which the spitfire is flying for the root chord Reynolds number to be 9 × 106 is ..........ft/s.arrow_forwardConsider an infinite wing with a NACA 1412 airfoil section and a chord length of 3 ft. The wing is at an angle of attack of 5° in an airflow velocity of 100 ft/s at standard sea-level conditions. Calculate the Reynold’s number, lift, drag, and moment about the quarter-chord per unit span. Cl = 0.67, Cmc/4 = -0.025 and Cd = 0.007Detailed solution plsarrow_forward
- Air flows at Ma = 2.5 past a half-wedge airfoil whoseangles are 4°, as in Fig. Compute the lift and dragcoefficient at α equal to (a) 0° and (b) 6°.arrow_forwardA Mitsubishi A6M Zero which has a wing area of 22.44 square meters with a lift generated of 6,000 N. If the wingspan is 12 meters, Calculate the velocity at minimum thrust required at standard sea level conditions. Assume wing is an elliptical planform and parasite drag is 0.045.arrow_forward19) You're flying a plane with a max speed of 267 ft/s and a wing area of 175ft^2 and a lift coefficient of 0.205, your plane weighs 2000lbs. What is the smallest radius turn you can make at 5000ft of altitude(where the air is 0.002048 slug/ft^3) at a constant speed without loosing altitude?arrow_forward
- Alight aircraft with a wing area of 114 m^2 and a span of 29 m is flying at an altitude of 3,550 m when the engine suddenly fails. If the parasite drag coefficient is 0.0325, determine the maximum distance over the ground that the aircraft can cover. Assume elliptical lift distribution. Provide answer in km, nearest hundredths.arrow_forwardThe NACA 64(l)–412 airfoil has a lift-to-drag ratio of 50 at 0° angle of attack. At what angle of attack does this ratio increase to 80?arrow_forwardConsider the NACA 2412 airfoil discussed . The airfoil is flying at a velocity of 60 m/s at a standard altitude of 3 km . The chord length of the airfoil is 2 m. Calculate the lift per unit span when the angle of attack is 4◦.arrow_forward
- Air is flowing past a symmetrical airfoil at an angle of attack of 5°. Is the (a) lift and (b) drag acting on the airfoil zero or nonzero?arrow_forwardAn airplane with a NACA 23012 airfoil cruises at 150 m/s at an altitude of 6000 m. The airfoil has an aspect ratio of 10 with a span of 36 m. Using the airfoil data as in Fig. 3, determine the lift and drag forces. Then determine the power required to overcome drag. Consider the airplane flying at an angle of attack equal to 2.arrow_forwardAn airfoil generates a 1200 N/m sectional lift when traveling at 75 m/s at sea level. What is the circulation generated by this airfoil?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Ficks First and Second Law for diffusion (mass transport); Author: Taylor Sparks;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c3KMpkmZWyo;License: Standard Youtube License