
Concept explainers
1.
Cost Classification and Cost Behavior: The relationship between costs and activity is known as cost behaviour. The costs which are expensed for the period and which cannot be directly attributed to the goods produced are period costs, while those costs which relates directly to the goods produced are product costs.
To classify the given cost items as period cost or product cost and determine its cost behavior as variable or fixed respectively.
1.
Answer to Problem 26C
Solution:
Statement showing classification of cost items as period cost or product cost and determine its cost behavior:
| Cost Item | Cost Behavior | Period (Selling or Administrative) Cost | Product Cost | ||
| Variable | Fixed | Direct | Indirect | ||
| Direct labor | $118,000 | $118,000 | |||
| Advertising | $50,000 | $50,000 | |||
| Factory supervision | $40,000 | $40,000 | |||
| Property taxes, factory building | $3,500 | $3,500 | |||
| Sales commissions | $80,000 | $80,000 | |||
| Insurance, factory | $2,500 | $2,500 | |||
| $4,000 | $4,000 | ||||
| Lease cost, factory equipment | $12,000 | $12,000 | |||
| Indirect materials, factory | $6,000 | $6,000 | |||
| Depreciation, factory building | $10,000 | $10,000 | |||
| Administrative office supplies (billing) | $3,000 | $3,000 | |||
| Administrative office salaries | $60,000 | $60,000 | |||
| Direct materials used (wood, bolts, etc.) | $94,000 | $94,000 | |||
| Utilities, factory | $20,000 | $20,000 | |||
Explanation of Solution
The above solution classifies various cost items into the given categories. However, the cost items such as sales commissions and administrative office supplies (billing) are classified as direct product costs as such costs will be incurred only if selling activity takes place. Thus, the variable nature of such costs makes it directly related to the number of units sold and we have classified accordingly.
The explanation to above cost items classified as period or product costs and determine its cost behavior are as-
- Direct labor cost will be incurred in relation to the production of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Advertising cost is an expense incurred to increase the sales of a company. However, it is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period respectively. Thus, it is a fixed and period cost.
- Factory supervision cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable to such factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Property taxes cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable to the factory building which is a factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Sales commissions will be incurred in relation to the production and sales of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and sold and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Insurance,
factory cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable as factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively. - Depreciation charged for administrative office equipment. It is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is expensed for the period respectively. Thus, it is a fixed and period cost.
- Lease cost incurred for the factory equipment which cannot be directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable as factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Indirect materials cost isnot directly attributable to the goods produced. However, such cost is incurred for the goods produced but cannot be traced easily within such factory. Thus, such cost is variable in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Depreciation charged for the factory buildingis not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is charged for the period. However, such cost is attributable as factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Administrative office supplies (billing) costwill be incurred in relation to the production and sales of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and sold and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Administrative office salariesis not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period respectively. Thus, it is a fixed and period cost.
- Direct materials used (wood, bolts, etc.)will be incurred in relation to the production of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Utilities, factory cost will be incurred in relation to the production of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
The above given cost items are classified as product cost or period cost and the nature of cost behavior is identified.
2.
Cost Classification and Cost Behavior: The relationship between costs and activity is known as cost behaviour. The costs which are expensed for the period and which cannot be directly attributed to the goods produced are period costs, while those costs which relates directly to the goods produced are product costs.
To compute the average product cost of one patio set for the given cost items as classified above.
Answer to Problem 26C
Solution:
Statement showing total cost incurred as period cost or product cost and determine its cost behavior:
| Cost Item | Cost Behavior | Period (Selling or Administrative) Cost | Product Cost | ||
| Variable | Fixed | Direct | Indirect | ||
| Direct labor | $118,000 | $118,000 | |||
| Advertising | $50,000 | $50,000 | |||
| Factory supervision | $40,000 | $40,000 | |||
| Property taxes, factory building | $3,500 | $3,500 | |||
| Sales commissions | $80,000 | $80,000 | |||
| Insurance, factory | $2,500 | $2,500 | |||
| Depreciation, administrative office equipment | $4,000 | $4,000 | |||
| Lease cost, factory equipment | $12,000 | $12,000 | |||
| Indirect materials, factory | $6,000 | $6,000 | |||
| Depreciation, factory building | $10,000 | $10,000 | |||
| Administrative office supplies (billing) | $3,000 | $3,000 | |||
| Administrative office salaries | $60,000 | $60,000 | |||
| Direct materials used (wood, bolts, etc.) | $94,000 | $94,000 | |||
| Utilities, factory | $20,000 | $20,000 | |||
| Total | $321,000 | $182,000 | $114,000 | $315,000 | $74,000 |
The average product cost of one patio set is $194.50 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
The explanation to above cost items classified as period or product costs and determine its cost behavior are as-
- Direct labor cost will be incurred in relation to the production of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Advertising cost is an expense incurred to increase the sales of a company. However, it is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period respectively. Thus, it is a fixed and period cost.
- Factory supervision cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable to such factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Property taxes cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable to the factory building which is a factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Sales commissions will be incurred in relation to the production and sales of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and sold and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Insurance, factory cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable as factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Depreciation charged for administrative office equipment. It is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is expensed for the period respectively. Thus, it is a fixed and period cost.
- Lease cost incurred for the factory equipment which cannot be directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period. However, such cost is attributable as factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Indirect materials cost is not directly attributable to the goods produced. However, such cost is incurred for the goods produced but cannot be traced easily within such factory. Thus, such cost is variable in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Depreciation charged for the factory building is not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is charged for the period. However, such cost is attributable as factory overhead cost. Thus, such cost is fixed in nature and it is an indirect product cost respectively.
- Administrative office supplies (billing) cost will be incurred in relation to the production and sales of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and sold and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Administrative office salariesis not directly attributable to the goods produced and a lump-sum amount is incurred for the period respectively. Thus, it is a fixed and period cost.
- Direct materials used (wood, bolts, etc.) will be incurred in relation to the production of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
- Utilities, factory cost will be incurred in relation to the production of goods. Thus, it is a variable cost. Also, such cost is directly attributable to such goods produced and, therefore, it is a direct product cost.
The product cost consists of direct as well as indirect product cost which is $389,000 (direct product cost $315,000 and indirect product cost $74,000). The total number of patio furniture consisting of a table and four chairs are 2,000 sets per year. Therefore, the average product cost of one patio set is $194.50 ($389,000/2,000 sets).
Formula:
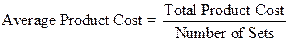
The above calculations show the average product cost of one patio set respectively.
3.
Cost Classification and Cost Behavior: The relationship between costs and activity is known as cost behaviour. The costs which are expensed for the period and which cannot be directly attributed to the goods produced are period costs, while those costs which relates directly to the goods produced are product costs.
To determine whether the average product cost per set will increase, decrease or remain unchanged, if the production drops to 1,000 sets annually.
Answer to Problem 26C
Solution:
The average product cost per set, consisting of direct and indirect product cost, will increase if the production drops to 1,000 sets annually.
Explanation of Solution
As the production drops to 1,000 sets annually, the fixed costs assigned to 1,000 sets will increase in comparison with assignment of such costs to 2,000 sets estimated. This happens because the fixed costs lump-sum amount remains unchanged for the period. The variable costs will remain same for production of 1,000 sets respectively.
We have considered direct as well as indirect product costs for computing the average product cost for one patio set. Therefore, the fixed cost behavior items will increase the average product cost respectively.
Thus, we conclude that the average product cost per set, consisting of direct and indirect product cost, will increase if the production drops to 1,000 sets annually.
4.
Cost Classification and Cost Behavior: The relationship between costs and activity is known as cost behaviour. The costs which are expensed for the period and which cannot be directly attributed to the goods produced are period costs, while those costs which relates directly to the goods produced are product costs.
Todetermine the price to be charged by the president of the company to his brother-in-law for making a patio set for himself from the company.
Answer to Problem 26C
Solution:
As the company is operating at its full capacity, the president would be charging the total cost incurred and assigned to such patio set, while the brother-in-law would be expecting to pay the variable costs incurred for such patio set respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Yes, ideally there would be disagreement between the two for the price quotations as explained above. As the company is operating at its full capacity, the president of such company would also charge the fixed cost assigned to such patio set. The brother-in-law would be expecting to pay for only the variable costs portion of such patio set.
As the major cost items, such as direct materials used, direct labor etc., are variable costs upon which there is no disagreement for price quotations between the two; the president of the company would more likely negotiate the price and still be selling such patio set at cost price respectively.
Thus, we have shown the price quotations both would be having in their minds for a patio set from the Dorilane Company.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCT.(LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





