
Concept explainers
A truck is moving north at a speed of 70 km/h. The exhaust pipe above the truck cab
sends out a trail of smoke that makes an angle of
the wind is blowing directly toward the east, what is the wind speed at that location?
[Hint: The smoke reveals the direction of the truck with-respect-to the air.]
The speed of wind at the location considering the wind is blowing toward east and if the truck moves north at a speed of
Answer to Problem 44SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The speed of truck is
The exhaust pipe sends smoke at an angle
The wind is blowing toward the east.
Formula used:
Consider two vectors
The magnitude of vector
Here,
The angle of vector
Here,
The scalar components of vector
Here,
Vector
The resultant vector of two vectors represented by adjacent sides of a parallelogram is expressed as
Here,
Explanation:
Understand that the smoke is emitted from the truck in a direction exactly opposite to the direction of motion of truck. According to the problem, the truck moves north, therefore the smoke is initially emitted in the south direction.
Draw a diagram for the problem considering north as +y direction, south as –y direction, east as +x direction, and west as –x direction:
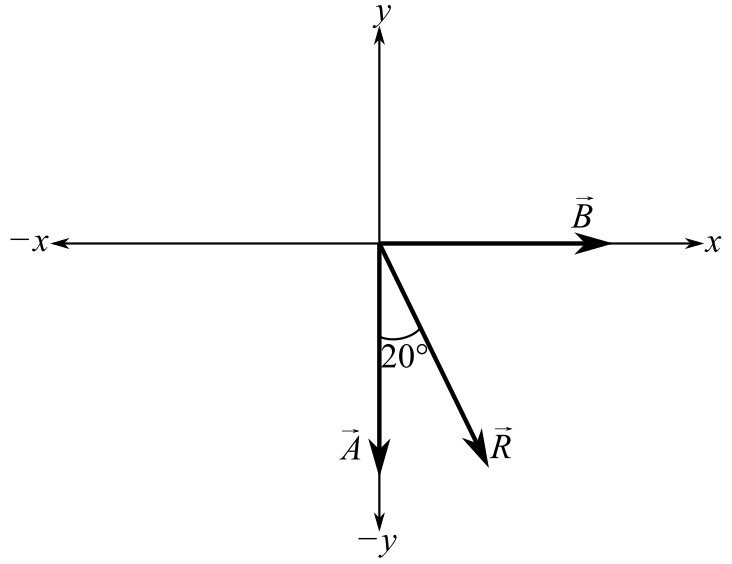
Here,
Consider the expression for angle with the horizontal:
Here,
Substitute
Consider the expression for horizontal scalar component of the velocity vector of air through the exhaust pipe:
Here,
The angle is measured anticlockwise from the horizontal, therefore, consider the angle as negative.
Substitute
Consider the expression for vertical scalar component of the velocity vector of air through the exhaust pipe.
Here,
Substitute
Consider the Cartesian form of resultant velocity of air:
Here,
Substitute
Consider the velocity of smoke of truck, which is equal to magnitude of the velocity of truck, that is,
The velocity vector
The resultant velocity of the wind is in the east direction. Therefore, the vertical component of
According to the problem, the truck moves in north direction, therefore, it doesn’t have any horizontal velocity. Therefore, the velocity of wind is equal to the horizontal component of resultant smoke velocity. The horizontal component of vector
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The speed of wind at the location is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- a fireman d=31.0 m away from a burning building directs a stream of water from a ground-level hose at an angle of 0i=26.0 degrees above the horizontal. if the speed of the stream as it leaves the hose is vi=40.0 m/s, at what height will the stream of water strike the building?arrow_forwardA fireman d = 32.0 m away from a burning building directs a stream of water from a ground-level fire hose at an angle of θi = 31.0° above the horizontal as shown in the figure. If the speed of the stream as it leaves the hose is vi = 40.0 m/s, at what height will the stream of water strike the building?arrow_forwardA plane is headed due east with air speed 240kph. If a wind of 40kph is blowing from the north, find the ground speed of the plane.arrow_forward
- A small airplane is flying due north at 150 km/h when it encounters a wind of 80 km/h from the east. What is the resultant ground velocity of the plane? (Answer: 170km/h; 62 degree)arrow_forwardA strong wind blows to the west at a speed of 38.7 mi/h relative to the ground causing a commercial plane to change course What should be the plane's velocity in order to maintain a southward direction at a constant speed of 452 mi/h relative to the ground?arrow_forwardA jetliner with an airspeed of 1000 km/hr sets out on a 1500 km flight due south. To maintain a southward direction, however, the plane must be pointed fifteen degrees west of south. If the flight takes 100 min, what is the wind velocity?arrow_forward
- At what altitude must a military plane flying horizontally at 175 m/s be in order to deliver relief goods to evacuees? The evacuees are in an evacuation centre 1750m away from where the plane is.arrow_forwardIf you are standing on the free-throw line on a basketball court, the basket is about 4.5 m horizontally from you and it is located around 3m above the floor. What initial velocity vector is required to successfully throw the ball into the basket?arrow_forwardA hose lying on the ground shoots a stream of water upward at an angle of 40° to the horizontal. The speed of the water is 15 m/s as it leaves the hose. How high will it strike a wall which is 8 m away?arrow_forward
- The engine of a boat drives it across a river that is 238 m wide. The velocity of the boat relative to the water is 14.2 m/s. The velocity of the water with respect to the shore is 2.7 m/s @ East. The driver of the boat wants to travel straight across the river (north). At what angle should the boat’s velocity be directed so that the boat goes straight across the river (with respect to the +x-axis)? (Use as many sig figs as possible even though its an angle.)arrow_forwardA boat crosses a river of width 225 m in whichthe current has a uniform speed of 1.35 m/s.The pilot maintains a bearing (i.e., the direction in which the boat points) perpendicularto the river and a throttle setting to give aconstant speed of 2.92 m/s relative to the water.What is the magnitude of the speed of theboat relative to a stationary shore observer?Answer in units of m/s. How far downstream from the initial positionis the boat when it reaches the opposite shore?Answer in units of marrow_forwardWhen a projectile is fired with a velocity of 815 m/s at angle of 37 degrees above the horizontal, the maximum height reached by the projectile is about?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
