
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
The fatty acid can react with glycerol to form triglyceride with the formation of ester linkages. The reaction between acid and alcohol gives an ester as a major product. The ester group is derived by a carboxylic acid group in which the acidic hydrogen is replaced by an alkyl group.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: A triglyceride _______
The triglyceride is formed by the reaction of glycerol and fatty acids. It is characterized by the presence of ester linkages. Box C contains a triglyceride.
Thus, A triglyceride Box C.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Final oxidation product of a primary alcohol Box G.
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an aldehyde or to ketone. Product obtained may depend on the oxidising agent used. Therefore, in presence of mild oxidising agent, one gets aldehyde or ketone. In the presence of strong oxidizing agent, carboxylic acid is obtained.
Thus, final oxidation product of a primary alcohol Box G.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Condensation polymerization monomer _____.
Box G contains a compound in which two carboxylic groups are present. These two carboxylic groups can undergo condensation polymerization which is characterized by the loss of water molecule.
Thus, Condensation polymerization monomer Box G.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Polymers are the high molecular mass compounds. The small monomers units joined together to form large molecule, this reaction is known as polymerization reaction. Addition polymerization is the polymerization in which monomer units are linked together with no side product formation. Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Segment of an
Addition polymers are formed by the addition reaction of two monomer units. There is no by product formed in addition polymerization reaction. The given polymer is formed by the addition polymerization reaction of dichloroethene molecule.
Thus, Segment of an addition polymer molecule Box F.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. To get an aldehyde or ketone, oxidation of acohol must takes place in the presence of mild oxidising agent such as copper at 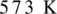 . Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
. Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Initial oxidation product of a primary alcohol _____.
The initial oxidation of a primary alcohol results in the formation of an aldehyde. Compound in Box D is an aldehyde.
Thus, initial oxidation product of a primary alcohol Box D.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
An amide bond is formed between a carboxylic acid and an
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Contains an amide bond _____.
An amide bond is formed between a carboxylic acid and an amine. The carboxylic acid group of one amino acid reacts with an amino group of another amino acid to form an amide bond by removing a water molecule. Compound in Box B contains an amide bond.
Thus, Contains an amide bond Box B.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Addition polymerization is the polymerization in which monomer units are linked together with no side product formation. Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Addition polymerization monomer _____.
Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond. Compounds in Boxes A and H contain a double bond.
Thus, Addition polymerization monomers are Box A and Box H.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
The reaction between acid and alcohol gives an ester as a major product. The ester is derived by a carboxylic acid group in which the acidic hydrogen is replaced by an alkyl group.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Contains an ester linkage _____.
The triglyceride is formed by the reaction of glycerol and fatty acids. It is characterized by the presence of ester linkages. Box C contains a triglyceride.
Thus, contains an ester linkage Box C.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. To get an aldehyde or ketone, oxidation of acohol must takes place in the presence of mild oxidizing agent such as copper at 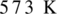 . Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
. Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Final oxidation product of a secondary alcohol _____.
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. Secondary alcohols undergo oxidation to form ketons. Compound in Box I is a ketone.
Thus, final oxidation product of a secondary alcohol is Box I.
(j)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of alcohols: primary, secondary and tertiary. The type of alcohols depends upon the carbon atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: A tertiary alcohol _____.
The compound given in Box E is a tertiary alcohol. The hydroxyl group is attached with a carbon atom that is attached with three other carbon atoms.
Thus, a tertiary alcohol Box E.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science, Hybrid Edition (with OWLv2 24-Months Printed Access Card)
- Identify the buffer system(s)the conjugate acidbase pair(s)present in a solution that contains equal molar amounts of the following: a. HF, KC2H3O2, NaC2H3O2, and NaF b. HNO3, NaOH, H3PO4, and NaH2PO4arrow_forwardAn important component of blood is the buffer combination of dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion. Consider blood with a pH of 7.44. a What is the ratio of [H2PO4] to [HPO42]? b What does the pH become if 25% of the hydrogen phosphate ions are converted to dihydrogen phosphate ion? c What does the pH become if 15% of the dihydrogen phosphate ions are converted to hydrogen phosphate ions?arrow_forwardFollow the directions of Question 64. Consider two beakers: Beaker A has a weak acid(K a=1105). Beaker B has HCI. The volume and molarity of each acid in the beakers are the same. Both acids are to be titrated with a 0.1 M solution of NaOH. (a) Before titration starts (at zero time), the pH of the solution in Beaker A is the pH of the solution in Beaker B. (b) At half-neutralization (halfway to the equivalence point), the pH of the solution in Beaker A the pH of the solution in Beaker B. (c) When each solution has reached its equivalence point, the pH of the solution in Beaker A the pH of the solution in Beaker B. (d) At the equivalence point, the volume of NaOH used to titrate HCI in Beaker B the volume of NaOH used to titrate the weak acid in Beaker A.arrow_forward
- Does the pH of the solution increase, decrease, or stay the same when you (a) Add solid sodium oxalate, Na2C2O4, to 50.0 mL of 0.015-M oxalic acid? (b) Add solid ammonium chloride to 100. mL of 0.016-M HCl? (c) Add 20.0 g NaCl to 1.0 L of 0.012-M sodium acetate, NaCH3COO?arrow_forwardWrite the net ionic equation in which the slightly soluble salt barium fluoride, BaF2, dissolves in dilute hydrochloric acid.arrow_forwardThe buffer capacity indicates how much OH- or H+ ions a buffer can react with. What is the buffer capacity of the buffers in Problem 10?arrow_forward
- Phenol, C6H5OH, is a weak organic acid. Suppose 0.515 g of the compound is dissolved in enough water to make 125 mL of solution. The resulting solution is titrated with 0.123 M NaOH. C6H5OH(aq) + OH(aq) C6H5O(aq) + H2O() (a) What is the pH of the original solution of phenol? (b) What are the concentrations of all of the following ions at the equivalence point: Na+, H3O+, OH, and C6H5O? (c) What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point?arrow_forwardA solution is 1.5 104 M Zn2 and 0.20 M HSO4. The solution also contains Na2SO4. What should be the minimum molarity of Na2SO4 to prevent the precipitation of zinc sulfide when the solution is saturated with hydrogen sulfide (0.10 M H2S)?arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of a 0.072 M aqueous solution of aluminum chloride, AlCl3. The acid ionization of hydrated aluminum ion is Al(H2O)63+(aq)+H2O(l)Al(H2O)5OH2+(aq)+H3O+(aq) and K4 is 1.4 103.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





