
a.
Create worksheet for the restatement of income and
a.
Explanation of Solution
Income:
Net income is the profit for the business. It is obtained by subtracting all the expenses and losses incurred from revenue.
Retained earnings:
Retained earnings are that part of profit which is taken out to meet unexpected expenses and losses. It can also be taken out for reinvestment.
Worksheet for restatement of income and retained earnings to U.S, GAAP for the year ended December 31, year 1:
| Items |
Local GAAP (in $m) |
U.S. GAAP (in $m) |
| Sales | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ||
| Gross profit | ||
| Less: Operating expenses | ||
| Operating income | 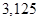 | |
| Less: Interest expense | ||
| Less: other expense | ||
| Income before income taxes | ||
| Provision for income taxes | ||
| Net income | ||
| Retained earnings (Jan 1) | - | - |
| Dividends | - | - |
| Retained earnings (Dec 31 |
Table (1)
Worksheet for restatement of balance sheet to U.S. GAAP for the year ended December 31, Year 1:
| Items |
Local GAAP (in $m) |
U.S. GAAP (in $m) |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | ||
| Cash | ||
| Accounts receivable | ||
| Inventories | ||
| Total current assets(A) | ||
| Fixed and long-term assets: | ||
| Property, plant and equipment | ||
| Long-term investments | ||
| Deferred charges | ||
| Total fixed and long-term assets (B) | ||
| Total assets (A+B) | ||
| Liabilities and stockholder’s equity | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | ||
| Accrued expenses | ||
| Short-term debt | ||
| Other current liabilities | ||
| Total current liabilities (C) | ||
| Long term liabilities: | ||
| Long-term debt | ||
| Deferred income tax | ||
| Other long term liabilities | ||
| Total long-term liabilities (D) | ||
| Total liabilities (E) (C+D) | ||
| Stockholder’s equity: | ||
| Capital | ||
| Capital surplus | ||
| Retained earnings | ||
| Revaluation reserve | - | |
| Unrealized gains (losses) | - | |
| Total stockholder’s equity (F) | ||
| Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity (E+F) |
Table (2)
b.
Prepare reconciling entries for each Year 1 reconciliation item included in the reconciliation from Local GAAP to U.S. GAAP in Exhibit 10.11.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Journalizing:
Journalizing is the process of recording the transactions of an organization in the order of happening of events Based on these
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To increase balance of the account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To decrease balance of the account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
To record inventory indirect costs:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Inventories | |||
| Cost of goods sold | ||||
| (to record inventory indirect costs) |
Table (3)
- Since inventories is an asset and assets increased. Hence, inventories is debited.
- Since cost of goods sold is a revenue and revenues increased. Hence, COGS is credited.
To record revaluation of property, plant and equipment:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Revaluation reserve | |||
| Property, plant and equipment | ||||
| (to record revaluation ) |
Table (4)
- Since revaluation reserve is a liability and liabilities decreased. Hence, revaluation reserve is debited.
- Since property, plant and equipment is an asset and assets decreased. Hence, property, plant and equipment is credited.
To record capitalized interest:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Property, plant and equipment | |||
| Interest expense | ||||
| (to record capitalized interest) |
Table (5)
- Since property, plant and equipment is an asset and assets are increased. Hence, property, plant and equipment is debited.
- Since interest expense is a gain and gains are increased. Hence, interest expense is credited.
To record deferred charges:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Operating expense | |||
| Deferred charges | ||||
| (to record deferred charges) |
Table (6)
- Since operating expense is an expense and expenses are increased. Hence, operating expense is debited.
- Since deferred charges are an asset and assets are decreased. Hence, deferred charges is credited.
Recording government grants:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Revenue | |||
| Property, plant and equipment | ||||
| Operating expense | ||||
| (to record government grants) |
Table (7)
- Since revenue is a revenue and revenue is decreased. Hence, revenue is debited.
- Since property, plant and equipment is an asset and assets are decreased. Hence, property, plant and equipment is credited.
- Since operating expense is an expense and expenses are decreased. Hence, operating expense is credited.
To record unrealized loss:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Unrealized loss | |||
| Other expenses | ||||
| (to record unrealized loss) |
Table (8)
- Since unrealized loss is a loss and losses are increased. Hence, unrealized loss is debited.
- Since other expenses are an expense and expenses are decreased. Hence, other expenses is credited.
To record deferred tax effect of U.S. GAAP adjustments:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Y1 | Provision for income taxes | |||
| Deferred income taxes | ||||
| (to record adjustment to deferred tax) |
Table (9)
- Since provision for income taxes is a liability and liabilities decreased. Hence, provision for income taxes is debited.
- Since deferred income taxes is an asset and assets decreased. Hence, deferred income taxes is credited.
c.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet for restatement of income and retained earnings to U.S, GAAP for the year ended December 31, year 1:
| Items |
Local GAAP (in $m) |
U.S. GAAP (in $m) |
| Sales | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ||
| Gross profit | ||
| Less: Operating expenses | ||
| Operating income | ||
| Less: Interest expense | ||
| Less: other expense | ||
| Income before income taxes | ||
| Provision for income taxes | ||
| Net income | ||
| Retained earnings (Jan 1) | - | - |
| Dividends | - | - |
| Retained earnings (Dec 31 |
Table (10)
d.
Calculate
d.
Explanation of Solution
On Local GAAP basis:
Calculation of current ratio:
The formula to calculate current ratio is,
Substitute
Thus, current ratio is
Calculation of total asset turnover:
The formula to calculate total asset turnover is,
Substitute
Thus, total asset turnover is
Calculation of debt/equity ratio:
The formula to calculate debt/equity ratio is,
Substitute
Thus, debt/equity ratio is
Calculation of times interest earned:
Substitute
Thus, times interest earned is
Calculation of net profit margin:
The formula to calculate net profit margin is,
Substitute
Thus, net profit margin is
Calculation of return on equity:
The formula to calculate return on equity is,
Substitute
Thus, return on equity is
Calculation of operating profit margin:
The formula to calculate operating profit margin is,
Substitute
Thus, operating profit margin is
Calculation of income as percent of total stockholders’ equity:
The formula to calculate IPTSE is,
Substitute
Thus, IPTSE is
On U.S. GAAP basis:
Calculation of current ratio:
The formula to calculate current ratio is,
Substitute
Thus, current ratio is
Calculation of total asset turnover:
The formula to calculate total asset turnover is,
Substitute
Thus, total asset turnover is
Calculation of debt/equity ratio:
The formula to calculate debt/equity ratio is,
Substitute
Thus, debt/equity ratio is
Calculation of times interest earned:
Substitute
Thus, times interest earned is
Calculation of net profit margin:
The formula to calculate net profit margin is,
Substitute
Thus, net profit margin is
Calculation of return on equity:
The formula to calculate return on equity is,
Substitute
Thus, return on equity is
Calculation of operating profit margin:
The formula to calculate operating profit margin is,
Substitute
Thus, operating profit margin is
Calculation of income as percent of total stockholders’ equity:
The formula to calculate IPTSE is,
Substitute
Thus, IPTSE is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK INTERNATIONAL ACCOUNTING

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





