
a.
Introduction: A contract or agreement laid between two parties for buying and selling of an asset at a specific rate and on a specific future date is known as forward contract. This is a contract or an agreement between a buyer and a seller to trade an asset at a future date whose price is set when contract is drawn and such agreements settle at the end of the contract on that specific date.
To prepare:
a.
Explanation of Solution
Use of forward contract to manage the foreign currency risk of exposed foreign currency position, not designated as a hedge.
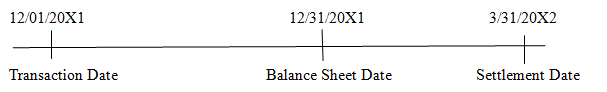
-Purchase of furniture - Settle forward exchange
resulting in foreign contract and receive
currency payable 100,000 Australian
Dollars
-Sign foreign exchange - Pay foreign currency
contract to receive payable
Australian Dollars on
March 31st
Forward Rate:
A$1 = $0.609 A$1 = $0.612
Spot Rate:
A$1 = $0.600 A$1 = $0.610 A$1 = $ 0.602
| Journal entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X1 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Inventory | 60,000 | ||
| Dec 1st | Accounts Payable (1) | 60,000 | |
| 20X1 | (To record Accounts payable.) | ||
| Foreign Currency receivable from Exchange Broker (A$) | 60,900 | ||
| Dollars Payable to Exchange Broker (2) | 60,900 | ||
| (To record forward contract to manage foreign currency risk.) | |||
| Dec 31st | Foreign Currency Transaction Loss (3) | 1,000 | |
| 20X1 | Accounts Payable (A$) | 1,000 | |
| (To record foreign currency transaction loss.) | |||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) (4) | 300 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 300 | ||
| (To record foreign currency transaction gain.) | |||
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X2 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Foreign Currency Transaction Loss (5) | 1,000 | ||
| March 31st | Foreign Currency receivable from Exchange Broker (A$) | 1,000 | |
| 20X2 | (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable.) | ||
| Account Payable (A$) (6) | 800 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 800 | ||
| (To record revalue of foreign currency payable.) | |||
| Dollars payable to Exchange broker | 60,900 | ||
| Cash | 60,900 | ||
| (To record cash payment required by forward contract.) | |||
| Foreign Currency Units (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Accounts Payables (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign Currency Units (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| (To record payment to creditor.) | |||
Working Notes:
1.Accounts Payable =
2.Foreign currency receivable =
6.Accounts Payable =
b.
Introduction: A contract or agreement laid between two parties for buying and selling of an asset at a specific rate and on a specific future date is known as forward contract. This is a contract or an agreement between a buyer and a seller to trade an asset at a future date whose price is set when contract is drawn and such agreements settle at the end of the contract on that specific date.
To prepare: Journal entries for forward contract as fair value of hedge of foreign currency firm commitment.
b.
Explanation of Solution
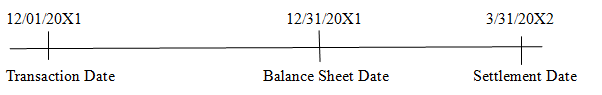
-Sign foreign exchange -Purchase of furniture - Settle forward exchange
contract to hedge foreign resulting in foreign contract and receive
currency payable firm currency payable. 100,000 Australian
commitment dollars.
-Pay foreign currency
Forward Rate:
A$1 = $0.609 A$1 = $0.612 A$1 = $0.605
Spot Rate:
A$1 = $0.600 A$1 = $0.610 A$1 = $0.608A$1 = $ 0.602
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X1 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Dec 1st | Foreign Currency receivable from Exchange Broker (A$) | 60,900 | |
| 20X1 | Dollars Payable to Exchange Broker (1) | 60,900 | |
| (To record forward contract to manage foreign currency risk.) | |||
| Dec 31st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 300 | |
| 20X1 | Foreign currency transaction gain (2) | 300 | |
| (To record foreign currency transaction gain.) | |||
| Foreign currency transaction loss (3) | 300 | ||
| Firm commitment | 300 | ||
| (To record the loss on the financial instrument.) | |||
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X2 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Foreign Currency Transaction Loss (4) | 700 | ||
| Jan 30th | Foreign Currency receivable from Exchange Broker (A$) | 700 | |
| 20X2 | (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable.) | ||
| Firm commitment (5) | 700 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 700 | ||
| (To record the gain on the financialinstrument.) | |||
| Inventory (purchases) | 61,200 | ||
| Accounts payable (A$) (6) | 60,800 | ||
| Firm Commitment | 400 | ||
| (To record acquirement of furniture initially.) | |||
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X2 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| March 31st | Foreign Currency transaction loss (A$) (7) | 300 | |
| 20X2 | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 300 | |
| (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable.) | |||
| Accounts Payable (A$) (8) | 600 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 600 | ||
| (To record revalue of foreign currency payable.) | |||
| Dollars payable to exchange broker (A$) | 60,900 | ||
| Cash | 60,900 | ||
| (to record the delivery of US dollars to exchange broker.) | |||
| Foreign Currency units (A$) (9) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| (To record the delivery of US dollars from exchange broker.) | |||
| Accounts Payable (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign currency unit (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| (To record the payment of A$ 100,000 to foreign creditor.) | |||
Working Notes:
1. Foreign currency receivable
=
3. Foreign currency transaction loss =
6.Accounts Payable =
8.Accounts Payable =
9 Foreign Currency Units =
c.
Introduction: A contract or agreement laid between two parties for buying and selling of an asset at a specific rate and on a specific future date is known as forward contract. This is a contract or an agreement between a buyer and a seller to trade an asset at a future date whose price is set when contract is drawn and such agreements settle at the end of the contract on that specific date.
To prepare: Journal entries for forward contract as cash flow hedge of
c.
Explanation of Solution
Use of forward contract as cash flow hedge of forecasted foreign currency transaction.
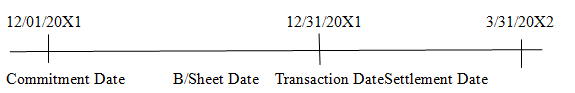
-Sign foreign exchange-Purchase of furniture - Settle forward exchange
Contract to hedge resulting in foreign contract and receive
Forecasted foreign Currency Payable 100,000 Australian
Currency transaction. Dollars.
- Pay foreign currency
payable.
Forward Rate:
A$1 = $0.609 A$1 = $0.612 A$1 = $0.605
Spot Rate:
A$1 = $0.600 A$1 = $0.610 A$1 = $0.608 A$1 = $ 0.602
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X1 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Dec 1st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,900 | |
| 20X1 | Dollars payable to exchange broker | 60,900 | |
| (To record forward contract to manage foreign currency risk | |||
| Dec 31st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 300 | |
| 20X1 | Other comprehensive income | 300 | |
| (To record OCI for effective portion of change in fair value) | |||
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X2 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Other comprehensive income (OCI) | 700 | ||
| Jan 30th | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 700 | |
| 20X2 | (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable and OCI) | ||
| Inventory (Purchases) | 60,800 | ||
| Account payable (A$) | 60,800 | ||
| (To record furniture acquired and value at spot rate) | |||
| March 31st | Other comprehensive income | 300 | |
| 20X2 | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 300 | |
| (To record revalue of foreign currency and OCI) | |||
| Accounts Payable (A$) | 600 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 600 | ||
| (To record change in current earning as specified by FASB 52) | |||
| Foreign currency transaction loss | 600 | ||
| Other comprehensive income | 600 | ||
| (To record reclassify amount from OCI to offset foreign currency transaction gain) | |||
| Dollars payable to exchange brokers (A$) | 60900 | ||
| Cash | 60900 | ||
| (To record the delivery of US dollars to exchange broker) | |||
| Foreign currency units (A$) | 60200 | ||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60200 | ||
| (To receive $100,000 from broker in accordance with forward contract signed on December 1st) | |||
| Accounts payable (A$) | 60200 | ||
| Foreign currency units (A$) | 60200 | ||
| (To deliver $100,000 to foreign creditor) | |||
Working Notes:
1. Foreign currency receivable =
A$ 100,000 × 0.612 (Spot Rate) 31st Dec 20X1 − $60,900
4.Accounts Payable =
7 Foreign Currency Units =
d.
Introduction: A contract or agreement laid between two parties for buying and selling of an asset at a specific rate and on a specific future date is known as forward contract. This is a contract or an agreement between a buyer and a seller to trade an asset at a future date whose price is set when contract is drawn and such agreements settle at the end of the contract on that specific date.
To prepare: Journal entries for forward contract used for speculative purpose only.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Use of forward contract for speculative purpose only
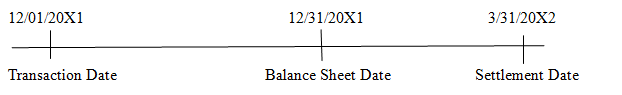
-Sign 120 day speculative - Settle forward exchange
Contract to purchasecontract and receive
100,000 Australian 100,000 Australian Dollar. Dollar.
Forward Rate:
A$1 = $0.609 A$1 = $0.612
Spot Rate:
A$1 = $0.600 A$1 = $0.610 A$1 = $ 0.602
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X1 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Dec 1st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,900 | |
| 20X1 | Dollars payable to exchange broker | 60,900 | |
| (To record 120 forward contracts for speculation) | |||
| Dec 31st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 300 | |
| 20X1 | Foreign currency transaction gain | 300 | |
| (To record foreign currency transaction gain) | |||
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X2 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Foreign currency transaction loss | 1,000 | ||
| March 31st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 1,000 | |
| 20X2 | (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable) | ||
| Dollars payable to exchange broker | 60,900 | ||
| Cash | 60,900 | ||
| (To record delivery of US $ to forward exchange broker) | |||
| Foreign currency units (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| (To receive A$ 100,000 from exchange broker) | |||
Working Notes:
- Foreign currency receivable =
7 Foreign Currency Units =
e.
Introduction: A contract or agreement laid between two parties for buying and selling of an asset at a specific rate and on a specific future date is known as forward contract. This is a contract or an agreement between a buyer and a seller to trade an asset at a future date whose price is set when contract is drawn and such agreements settle at the end of the contract on that specific date.
To prepare: Journal entries for forward contract to manage the foreign currency position, considering time value of money.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Use of forward contract to manage the exposed foreign currency positionconsidering the time value of money at a 12% annual rate. Forward contract not designed as a hedge.
-Purchase of Furniture - Settle forward exchange
resulting in Foreign contract and receive
currency payable. 100,000 Australian
Dollar.
-Sign hedging foreign - Pay foreign Currency
exchange contract to Payable
receive Australian Dollars
on March 31st.
Forward Rate:
A$1 = $0.609 A$1 = $0.612
Spot Rate:
A$1 = $0.600 A$1 = $0.610 A$1 = $ 0.602
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X1 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Inventory (purchases) | 60,000 | ||
| Dec 1st | Accounts payable (A$) | 60,000 | |
| 20X1 | (To record foreign currency payable) | ||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,900 | ||
| Dollars payable to exchange broker | 60,900 | ||
| (To record forward contract to hedge foreign currency) | |||
| Dec 31st | Foreign currency transaction loss | 1,000 | |
| 20X1 | Accounts payable (A$) | 1,000 | |
| (To record foreign currency transaction loss) | |||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 291 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 291 | ||
| (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable) | |||
| Journal Entries in the books of M CompFor the year Dec 31st20X2 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Debit$ | Credit$ |
| Foreign currency transaction loss | 991 | ||
| March 31st | Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 991 | |
| 20X2 | (To record revalue of foreign currency receivable) | ||
| Account payable (A$) | 800 | ||
| Foreign currency transaction gain | 800 | ||
| (To record revalue of foreign currency payable) | |||
| Dollars payable to exchange broker | 60,900 | ||
| Cash | 60,900 | ||
| (To record cash payment required by forward contract) | |||
| Foreign currency units (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign currency receivable from exchange broker (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| (to receive $100,000 from exchange broker as per forward contract) | |||
| Accounts payables (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| Foreign currency units (A$) | 60,200 | ||
| (To record payment to creditor) | |||
Working Notes:
1.Accounts Payable =
2. Foreign currency receivable =
3.Foreign currency transaction loss =
4.Foreign currency transaction Gain = Foreign currency receivable Dec 31st (forward rate) − foreign currency receivable Dec 1st (forward rate)
5 Foreign Currency Transaction Loss
6. Accounts Payable =
7 Foreign Currency Units =
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ADVANCED FIN.ACCT.(LL)-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- On August 1, Ling-Harvey Corporation (a U.S.-based importer) placed an order to purchase merchandise from a foreign supplier at a price of 400,000 ringgits. Ling-Harvey will receive and make payment for the merchandise in three months on October 31. On August 1, Ling-Harvey entered into a forward contract to purchase 400,000 ringgits in three months at a forward rate of $0.60. It properly designates the forward contract as a fair value hedge of a foreign currency firm commitment. The fair value of the firm commitment is measured by referring to changes in the forward rate. Relevant exchange rates for the ringgit are as follows: Date Spot rate Forward rate ( to October 31) August 1 $0.60 $0.60 September30 0.63 0.66 October 31 0.68 N/A Ling-Harvey’s incremental borrowing rate is 12 percent. The present value factor for one month at an annual interest rate of 12 percent (1 percent per month) is 0.9901. Ling-Harvey must close its books and prepare its third-quarter financial…arrow_forwardOn August 1, Ling-Harvey Corporation (a U.S.-based importer) placed an order to purchase merchandise from a foreign supplier at a price of 400,000 ringgits. Ling-Harvey will receive and make payment for the merchandise in three months on October 31. On August 1, Ling-Harvey entered into a forward contract to purchase 400,000 ringgits in three months at a forward rate of $0.60. It properly designates the forward contract as a fair value hedge of a foreign currency firm commitment. The fair value of the firm commitment is measured by referring to changes in the forward rate. Relevant exchange rates for the ringgit are as follows:Ling-Harvey’s incremental borrowing rate is 12 percent. The present value factor for one month at an annual interest rate of 12 percent (1 percent per month) is 0.9901. Ling-Harvey must close its books and prepare its third-quarter financial statements on September 30.a. Prepare journal entries for the forward contract and firm commitment through October 31.b.…arrow_forward1. On September 1, 20X1, Cano & Company, a U.S. corporation, sold merchandise to a foreign firm for 250,000 euros. Terms of the sale require payment in euros on February 1, 20X2. On September 1, 20X1, the spot exchange rate was $1.30 per euro. At Cano’s year-end on December 31, 20X1, the spot rate was $1.28, but the rate increased to $1.33 by February 1, 20X2, when payment was received. Required: What foreign currency transaction gain or loss should be recorded in 20X1? What foreign currency transaction gain or loss should be recorded in 20X2? Amount Gain / Loss 1. Foreign currency transaction gain (loss) 20X1 2. Foreign currency transaction gain (loss) - 20X2arrow_forward
- On December 12, year 11, Imp Co. entered into three forward exchange contracts, each to purchase 100,000 LCU's in 90 days. The relevant exchange rates are as follows:Spot rate Forward rate(for March 12, year 12)December 12, year 11 $0.88 $0.90December 31, year 11 $0.98 $0.93Imp entered into the second forward contract to hedge a commitment to purchase equipment being manufactured to Imp specifications. At December 31, 2022, what amount of foreign currency transaction gain should Imp include in income from this forward contract?a. $0b. $3,000c. $5,000d. $10,000arrow_forwardOn November 2, 201*, Sade entered into firm commitment with Singaporean firm to acquire an equipment, delivery andpassage of title on February 28, 201* at a price of 5,000 Singapore Dollar (SGD). On the same date, to hedge againstunfavorable changes in exchange rate of SGD, Sade entered into a 120-day forward contract with Andy Bank for 5,000SGD. The relevant exchange rates were as follows:11/2/201*12/31/201* 02/28/201*Spot Rate 34 36 37Forward Rate 35 38 37How much is the recognized derivative liability as of December 31, 201* as a result of the above transactions?arrow_forwardOn December 12, 20X5, Dahl Company entered into three forward exchange contracts, each to purchase 100,000 francs in 90 days. The relevant exchange rates are as follows: Spot Rate Forward Rate for March 12, 20X6 December 12, 20X5 $ 0.88 $ 0.90 December 31, 20X5 0.98 0.93 3. Dahl entered into the first forward contract to manage the foreign currency risk from a purchase of inventory in November 20X5, payable in March 20X6. The forward contract is not designated as a hedge. At December 31, 20X5, what amount of foreign currency transaction gain should Dahl include in income from this forward contract? multiple choice $10,000 $0 $5,000 $3,000 4. Dahl entered into the second forward contract to hedge a commitment to purchase equipment being manufactured to Dahl’s specifications. At December 31, 20X5, what amount of foreign currency transaction gain should Dahl include in income from this forward contract? multiple choice $10,000 $0 $5,000…arrow_forward
- On December 1, 20X8, Denizen Corporation entered into a 120-day forward contract to purchase 200,000 Canadian dollars (C$). Denizen's fiscal year ends on December 31. The forward contract was to hedge a firm commitment agreement made on December 1, 20X8, to purchase electronic goods on January 30, with payment due on March 31, 20X8. The derivative is designated as a fair value hedge. The direct exchange rates follow: Spot Rate Forward Rate for March 1, 20X9 December 1, 20X8 $ 0.940 $ 0.944 December 31, 20X8 $ 0.945 $ 0.947 January 30, 20X9 $ 0.942 $ 0.943 March 31, 20X9 $ 0.941 Required: Prepare all journal entries for Denizen Corporation.arrow_forwardThe spot foreign exchange rate for the US dollar is 0.69056 Euros. Yourcompany agrees to pay a bank 63,694 Euros in 3 months in exchange for 100,000US dollars. This is a foreign currency forward contract. No cash is exchanged upfront. Give the underlying asset, the maturity date, and the forward rate (for theUS dollar). Compare to the spot forward rate. Concludearrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. Note: Items 3 through 5 are based on the following: On December 12, 20X5, Dahl Company entered into three forward exchange contracts, each to purchase 100,000 francs in 90 days. The relevant exchange rates are as follows: Spot Rate Forward Rate for March 12, 20X6 December 12, 20X5 $ 0.88 $ 0.90 December 31, 20X5 0.98 0.93 3. Dahl entered into the first forward contract to manage the foreign currency risk from a purchase of inventory in November 20X5, payable in March 20X6. The forward contract is not designated as a hedge. At December 31, 20X5, what amount of foreign currency transaction gain should Dahl include in income from this forward contract? multiple choice $10,000 $0 $5,000 $3,000arrow_forward
- On March 1, Laton Products (a U.S. firm) purchased manu-facturing inputs from a Mexican supplier for 20,000 pesos, payable on June 1. The exchange rate for pesos on March 1was $0.17. If the exchange rate increases to $0.19 on June 1,what amount of gain or loss would be reported by Latonrelated to the currency exchange?a. $400 gain.b. $200 loss.c. $400 loss.d. $200 gain.arrow_forwardForward exchange contract designated as a fair value hedge of a foreign-currency-denominated accounts payable, strengthening $US On October 20, 2018, our company purchased from a company located in Slovenia 100,000 units of a product at a purchase price of €7.00 per unit. Our company is required to pay for the merchandise in Euros (€). The exchange rate on the date of purchase is $1.48:€1, and the due date for our payment is January 20, 2019. To mitigate the risk of exchange rate fluctuations between the purchase date and the payment date, on October 20, 2018, our company enters into a forward contract with an exchange broker. The contract obligates our company to buy €700,000 on January 20, 2019, while we lock in the $US we will pay for the Euros on that date at the forward rate of $1.45:€1 (i.e., the forward rate on October 20, 2018, for settlement on January 20, 2019). Assume this derivative qualifies as a fair value hedge, and our company’s functional currency and reporting…arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. Note: Items 3 through 5 are based on the following: On December 12, 20X5, Dahl Company entered into three forward exchange contracts, each to purchase 100,000 francs in 90 days. The relevant exchange rates are as follows: Spot Rate Forward Rate for March 12, 20X6 December 12, 20X5 $ 0.88 $ 0.90 December 31, 20X5 0.98 0.93 2. On September 1, 20X5, Johnson Incorporated entered into a foreign exchange contract for speculative purposes by purchasing €50,000 for delivery in 60 days. The rates to exchange U.S. dollars for euros follow: 9/1/X5 9/30/X5 Spot rates $ 0.75 $ 0.70 30-day forward rate 0.73 0.72 60-day forward rate 0.74 0.73 In its September 30, 20X5, income statement, what amount should Johnson report as foreign exchange loss? multiple choice $2,500 $500 $1,500 $1,000arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning



