
Concept explainers
Gruman Company purchased a machine for $220,000 on January 2, 2016. It made the following estimates:
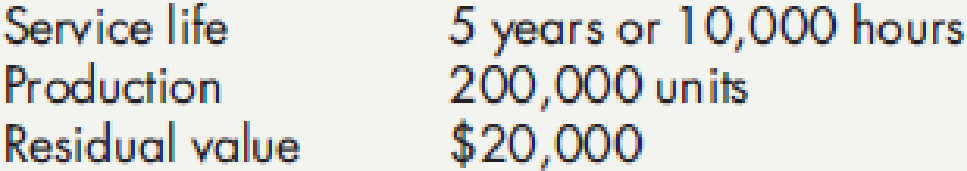
In 2016, Gruman uses the machine for 1,800 hours and produces 44,000 units. In 2017, Gruman uses the machine for 1,500 hours and produces 35,000 units.
Required:
- 1. Compute the
depreciation expense for 2016 and 2017 under each of the following methods:- a. straight-line
- b. sum-of-the-years’-digits (round to the nearest dollar)
- c. double-declining-balance
- d. activity method based on hours worked
- e. activity method based on units of output
- 2. For each method, what is the book value of the machine at the end of 2016? At the end of 2017?
- 3. Next Level If Gruman used a service life of 8 years or 15,000 hours and a residual value of $10,000, what would be the effect on (a) depreciation expense and (b) book value under the straight-line, sum-of-the-years’digits, and double-declining-balance depreciation methods?
1.
Compute the depreciation expense of Company G for 2016 and 2017 under the given depreciation method.
Explanation of Solution
Depreciation: Depreciation is a method of reducing the capitalized cost of long-lived operating assets or plant assets for the period the asset is used.
Straight-line depreciation method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset could be distributed equally throughout the useful life of the asset is referred to as straight-line method.
Activity method: In this method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is charged based on the units of production or hours worked each year. When the usefulness of an asset is related to the production cost of a unit, this method is more appropriate to use.
Sum-of- the-years’ digits method: Sum-of-the years’ digits method determines the depreciation by multiplying the depreciable base and declining fraction.
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
a. Straight line method:
2016:
2017:
b. Sum-of- the-years’ digits method:
| Year |
Depreciable Base ($) (1) |
Depreciation rate per year |
Depreciation expense ($) | ||
| 2016 | 200,000 | = | 66,667 | ||
| 2017 | 200,000 | = | 53,333 |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate the depreciable base of asset.
Working note (2):
Calculate the denominator of the fraction for sum-of-the-year’s digit.
c. Double-declining-balance method:
2016:
2017:
Working note (3):
Compute the depreciation rate:
Useful life = 5 years
d. Activity method (hours worked):
2016:
2017:
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost per hour.
e. Activity method (unit of output):
2016:
2017:
Working note (5):
Calculate the cost per unit.
2.
Calculate the book value of the machine at the end of 2016 and 2017 under each depreciation method.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the book value of the machine at the end of 2016 and 2017 under each depreciation method as follows:
| Year |
Book Value (A) |
Depreciation (B) |
Ending Book Value |
| a. Straight-line Method | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $40,000 | $180,000 |
| 2017 | $180,000 | $40,000 | $140,000 |
| b. Sum-of-the-years’-digits | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $66,667 | $153,333 |
| 2017 | $153,333 | $53,333 | $100,000 |
| c. Double-declining-balance | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $88,000 | $132,000 |
| 2017 | $132,000 | $52,800 | $79,200 |
| d. Activity based method on hours worked | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $36,000 | $184,000 |
| 2017 | $184,000 | $30,000 | $154,000 |
| e. Activity based method on units of output | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $44,000 | $176,000 |
| 2017 | $176,000 | $35,000 | $141,000 |
Table (2)
Note: Ending book value for 2016 is considered as the beginning book value for 2017.
3.
Identify the effect of (a) the depreciation expense and (b) book value under the straight line, sum of the year’s digit, and double-declining balance method, assume that Company G used a service life of 8 years, or 15,000 hours and residual value of $10,000.
Explanation of Solution
(a) Identify the effect of the depreciation expense under the straight line, sum of the year’s digit, and double-declining balance method as follows:
Straight line method:
2016:
2017:
Sum-of- the-years’ digits method:
| Year |
Depreciable Base ($) (6) |
Depreciation rate per year |
Depreciation expense ($) | ||
| 2016 | 210,000 | = | 46,667 | ||
| 2017 | 210,000 | = | 40,833 |
Table (3)
Working note (6):
Calculate the depreciable base of asset.
Working note (7):
Calculate the denominator of the fraction for sum-of-the-year’s digit.
Double-declining-balance method:
2016:
2017:
Working note (8):
Compute the depreciation rate:
Useful life = 5 years
b) Identify the effect of the book value under the straight line, sum of the year’s digit, and double-declining balance method as follows:
| Year |
Book Value (A) |
Depreciation (B) |
Ending Book Value |
| Straight-line Method | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $26,250 | $193,750 |
| 2017 | $193,750 | $26,250 | $167,500 |
| Sum-of-the-years’-digits | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $46,667 | $173,333 |
| 2017 | $173,333 | $40,833 | $132,500 |
| Double-declining-balance | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $55,000 | $165,000 |
| 2017 | $165,000 | $41,250 | $123,750 |
Table (4)
Note: Ending book value for 2016 is considered as the beginning book value for 2017.
When the service life of an asset increases, the depreciation expense gets decreased under straight line, sum of year’s digit, and double-declining balance method, and this decreased depreciation expense increases the ending book value of machinery.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis
- Utica Machinery Company purchases an asset for 1,200,000. After the machine has been used for 25,000 hours, the company expects to sell the asset for 150,000. What is the depreciation rate per hour based on activity?arrow_forwardMontello Inc. purchases a delivery truck for $25,000. The truck has a salvage value of $6,000 and is expected to be driven for 125,000 miles. Montello uses the units-of-production depreciation method, and in year one it expects to use the truck for 26,000 miles. Calculate the annual depreciation expense.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2014, Klinefelter Company purchased a building for 520,000. The building had an estimated life of 20 years and an estimated residual value of 20,000. The company has been depreciating the building using straight-line depreciation. At the beginning of 2020, the following independent situations occur: a. The company estimates that the building has a remaining life of 10 years (for a total of 16 years). b. The company changes to the sum-of-the-years-digits method. c. The company discovers that it had ignored the estimated residual value in the computation of the annual depreciation each year. Required: For each of the independent situations, prepare all journal entries related to the building for 2020. Ignore income taxes.arrow_forward
- Kam Company purchased a machine on January 2, 2019, for 20,000. The machine had an expected life of 8 years and a residual value of 300. The double-declining-balance method of depreciation is used. Required: 1. Compute the depreciation expense for each year of the assets life and book value at the end of each year. 2. Assuming that the company has a policy of always changing to the straight-line method at the midpoint of the assets life, compute the depreciation expense for each year of the assets life. 3. Assuming that the company always changes to the straight-line method at the beginning of the year when the annual straight-line amount exceeds the double-declining-balance amount, compute the depreciation expense for each year of the assets life.arrow_forwardColquhoun International purchases a warehouse for $300,000. The best estimate of the salvage value at the time of purchase was $15,000, and it is expected to be used for twenty-five years. Colquhoun uses the straight-line depreciation method for all warehouse buildings. After four years of recording depreciation, Colquhoun determines that the warehouse will be useful for only another fifteen years. Calculate annual depreciation expense for the first four years. Determine the depreciation expense for the final fifteen years of the assets life, and create the journal entry for year five.arrow_forwardOn May 10, 2019, Horan Company purchased equipment for 25,000. The equipment has an estimated service life of 5 years and zero residual value. Assume that the straight-line depreciation method is used. Required: Compute the depreciation expense for 2019 for each of the following four alternatives: 1. Horan computes depreciation expense to the nearest day. (Use 12 months of 30 days each and round the daily depreciation rate to 2 decimal places.) 2. Horan computes depreciation expense to the nearest month. Assets purchased in the first half of the month are considered owned for the whole month. 3. Horan computes depreciation expense to the nearest whole year. Assets purchased in the first half of the year are considered owned for the whole year. 4. Horan records one-half years depreciation expense on all assets purchased during the year.arrow_forward
- Hathaway Company purchased a copying machine for 8,700 on October 1, 2019. The machines residual value was 500 and its expected service life was 5 years. Hathaway computes depreciation expense to the nearest whole month. Required: 1. Compute depredation expense (rounded to the nearest dollar) for 2019 and 2020 using the: a. straight-line method b. sum-of-the-years-digits method c. double-declining-balance method 2. Next Level Which method produces the highest book value at the end of 2020? 3. Next Level Which method produces the highest charge to income in 2020? 4. Next Level Over the life of the asset, which method produces the greatest amount of depreciation expense?arrow_forwardMontello Inc. purchases a delivery truck for $25,000. The truck has a salvage value of $6,000 and is expected to be driven for 125,000 miles. Montello uses the units-of-production depreciation method, and in year one the company expects the truck to be driven for 26,000 miles; in year two, 30,000 miles; and in year three, 40,000 miles. Consider how the purchase of the truck will impact Montellos depreciation expense each year and what the trucks book value will be each year after depreciation expense is recorded.arrow_forwardMontello Inc. purchases a delivery truck for $15,000. The truck has a salvage value of $3,000 and is expected to be driven for eight years. Montello uses the straight-line depreciation method. Calculate the annual depreciation expense.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning





