
Determine the required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium of the linkage at θ = 60°. Each link has a mass of 20 kg.
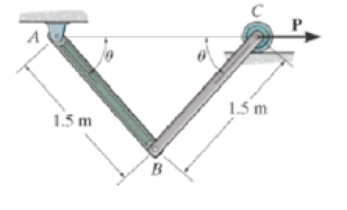
The required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 1FP
The required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of each link
The given angle
Show the free body diagram of the forces acting on the link as in Figure (1).
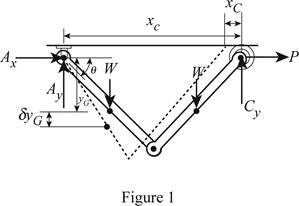
Observation:
The weight W and the horizontal component of P do positive work, when the position coordinates
Virtual displacement:
Write the position coordinate about x axis at point C.
Here, the length of the link AB is
Write the position coordinate about y axis about the center of the link.
Determine the weight of the link W.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Virtual work equation:
Write the virtual work equation to determine the magnitude of force P.
Here, the angle of force
Conclusion:
Differentiate Equation (I) with respect to
Substitute 1.5 m for
Differentiate Equation (II) with respect to
Substitute 1.5 m for
Substitute 20 kg for m and
Substitute 196.2 N for W,
Here, the value of
Modify the Equation,
Thus, the required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Aerodynamics
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
- The weightless bars AB and CE, together with the 5-lb weight BE, form a parallelogram linkage. The ideal spring attached to D has a free length of 2 in. and a stiffness of 7.5 lb/in. Find the two equilibrium positions that are in the range 0/2, and determine their stability. Neglect the weight of slider F.arrow_forwardThe 1200-lb homogeneous block is placed on rollers and pushed up the 10 incline at constant speed. Determine the force P and the roller reactions at A and B.arrow_forwardDetermine the vertical force P that must be applied at G to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage.arrow_forward
- The ring weighs 5 N and is in equilibrium. The force F1 = 4.5 N. Determine the force F2 and the angle ∝.arrow_forwardQ (4): The 11 Kg lamp fixture is suspended from the two springs, each having an unstretched length of 6 m. Determine stiffness of k for equilibrium.arrow_forwardThe crate has a mass of 130 kg. 1. Determine the tension developed in cable DA for equilibrium. 2. Determine the tension developed in cable DB for equilibrium. 3. Determine the tension developed in cable DC for equilibrium.arrow_forward
- In each case, determine the force P required to maintain equilibrium. The block weighs 100 lb.arrow_forwardIf the block is held in the equilibrium position shown, determine the mass of the block D. The unextended length of the spring AB is 9 m.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the force P required to hold the 300-kg crate in equilibriumarrow_forward
- The uniform block having a mass m rests on the top surface of the halfcylindershown. Show that this is a condition of unstable equilibrium if h > 2R.arrow_forwardDetermine the vertical force P that must be applied at ABC to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage.arrow_forwardBoth pulleys are fixed to the shaft and as the shaft turns with constant angular velocity, the power of pulley A is transmitted to pulley B. Determine the horizontal tension T in the belt on pulley B and the x, y, z components ofreaction at the journal bearing C and thrust bearing D if θ = 0°. The bearings are in proper alignment and exert only force reactions on the shaft.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
