
Analyze Pacific Airways
Pacific Airways provides air travel services between Los Angeles and Seattle. Cost information per flight is as follows:
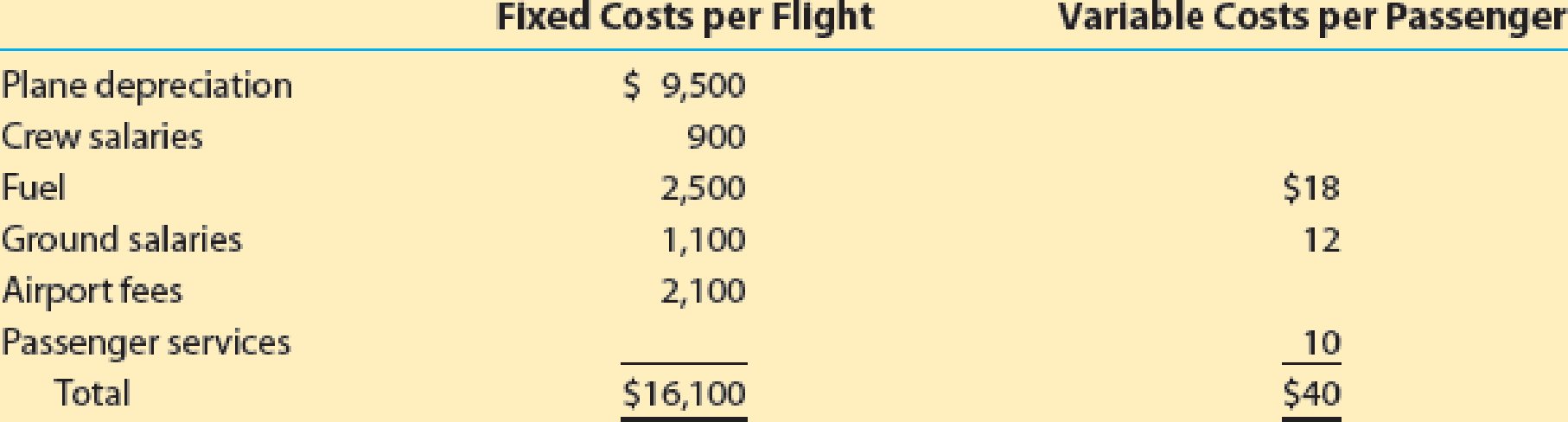
Each flight has a capacity of 150 seats, with an average of 125 seats sold per flight at an average ticket price of $180. Assume Pacific Airways is considering a new service that would provide tickets at half price. Passengers would need to fly standby to receive the discount, but would be provided a flight for a given day of travel. An analysis revealed that an average of 8 existing passengers would use the new discounted tickets for travel. In addition, 15 new passengers would be attracted to the offer.
- a. Determine the contribution margin per passenger for the full-priced ticket.
- b. Determine the break-even number of seats sold per flight.
- c. Determine the contribution margin per passenger for discounted tickets.
- d. Should Pacific Airways offer the discounted ticket plan? Answer the question by computing the incremental contribution margin per flight for the plan.
a.
Compute the contribution margin per passenger for the full-priced ticket.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin: The amount of sales revenue remained after the variable costs are incurred is called contribution margin. In other words, contribution margin is the surplus amount of revenue over variable costs.
The following is the formula to calculate the contribution margin:
Contribution Margin = Sales – Variable cost
Calculate the contribution margin per passenger.
The contribution margin per passenger at full fare is $140.
b.
Compute the break-even number of seats sold per flight.
Explanation of Solution
Break-even: Break even refers to the point where the production can yield all the costs involved and any further production contributes to the profit.
Calculate the break even seats per flight.
The break even seats per flight are 115 seats.
c.
Compute the contribution margin per passenger for the discounted tickets.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin: The amount of sales revenue remained after the variable costs are incurred is called contribution margin. In other words, contribution margin is the surplus amount of revenue over variable costs.
Calculate the contribution margin per passenger.
The contribution margin per passenger at discounted fare is $50.
d.
Compute the incremental contribution margin per flight to decide on the proposal to allow discount.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin: The amount of sales revenue remained after the variable costs are incurred is called contribution margin. In other words, contribution margin is the surplus amount of revenue over variable costs.
Calculate the incremental contribution margin per flight.
The incremental contribution margin per flight is $30.
Working Note (1):
Calculate the lost contribution margin from customers switching tickets.
Working Note (2):
Calculate the gained contribution margin from discount customers.
Differential Analysis: Differential analysis refers to the analysis of differential revenue which a company could gain or differential cost which a company could incur based on the available alternative options of business.
Prepare the differential analysis table to analyze the effect of the new plan:
| Differential Analysis of Company PA | |||
| Continue with No Change (Alt. 1) or Offer the Discount Plan (Alt. 2) | |||
| February 5 | |||
| Particulars | No Change (Alternative 1) | Discount Plan (Alternative 2) | Differential Effect (Alternative 2) |
| Revenues per flight | (3) $22,500 | (4) $23,130 | $630 |
| Costs per flight: | |||
| Plane depreciation | ($9,500) | ($9,500) | $0 |
| Crew salaries | ($900) | ($900) | $0 |
| Fuel | (5) ($4,750) | (6) ($5,020) | ($270) |
| Ground salaries | (7) ($2,600) | (8) ($2,780) | ($180) |
| Airport fees | ($2,100) | ($2,100) | $0 |
| Passenger services | (9) ($1,250) | (10) ($1,400) | ($150) |
| Income per flight | $1,400 | $1,430 | $30 |
Table (1)
The differential analysis of Company PA shows that the offer of Discount plan, has a greater differential income of $30.
Working Note (3):
Calculate the revenue per flight for existing plan.
Working Note (4):
Calculate the revenue per flight for new plan.
Working Note (5):
Calculate the fuel price for existing plan.
Working Note (6):
Calculate the fuel price for new plan.
Working Note (7):
Calculate the ground salaries for existing plan.
Working Note (8):
Calculate the ground salaries for new plan.
Working Note (9):
Calculate the passenger services cost for existing plan.
Working Note (10):
Calculate the passenger services cost for new plan.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Myrtle Air Express decided to offer direct service from Cleveland to Myrtle Beach. Management must decide between a full-price service using the companys new fleet of jet aircraft and a discount service using smaller-capacity commuter planes. It is clear that the best choice depends on the market reaction to the service Myrtle Air offers. Management developed estimates of the contribution to profit for each type of service based on two possible levels of demand for service to Myrtle Beach: strong and weak. The following table shows the estimated quarterly profits (in thousands of dollars): a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence for this problem? How many decision alternatives are there? How many outcomes are there for the chance event? b. If nothing is known about the probabilities of the chance outcomes, what is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches? c. Suppose that management of Myrtle Air Express believes that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3. Use the expected value approach to determine an optimal decision. d. Suppose that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2. What is the optimal decision using the expected value approach? e. Use sensitivity analysis to determine the range of demand probabilities for which each of the decision alternatives has the largest expected value.arrow_forwardAble Transport operates a tour bus that they lease with terms that involve a fixed fee each month plus a charge for each mile driven. Able Transport drove the bus 7,000 miles and paid a total of $1,360 in June. In October. Able Transport paid $1,280 for the 5,000 miles driven. If Able Transport uses the high-low method to analyze costs, how much would Able Transport pay in December, if they drove 6,000 miles?arrow_forwardAble Transport operates a tour bus that they lease with terms that involve a fixed fee each month plus a charge for each mile driven. Able Transport drove the tour bus 4,000 miles and paid a total of $1,250 in March. In April, they paid $970 for 3.000 miles. What is the variable cost per mile if Able Transport uses the high-low method to analyze costs?arrow_forward
- Assume Intervale Railway is considering hiring a reservations agency to handle passenger reservations. The agency would charge a flat fee of $13,000 per month, plus $3 per passenger reservation. What is the total reservation cost if 200,000 passengers take the trip next month? $613,000 $3.07 $600,000 $13,000arrow_forwardPassenger load on a flight Eastern Skies Airlines has three flights that depart from New York City and arrive in Chicago every day. The three flights are as follows: Flight Number Flight Departure Time Flight Frequency 57 8:00 AM 7 days per week 85 10:00 AM 7 days per week 94 11:30 AM 7 days per week Each flight uses a jet with a capacity of 180 seats. The airline measures the utilization of the aircraft by passenger load. Passenger load is the number of seats sold divided by the number of available seats on a flight for a time period. The following operating data are available for June: Flight Number Number of Seats Sold 57 5,130 85 2,592 94 2,376 a. Determine the available seat capacity for each flight number for June.fill in the blank 1 b. Determine the passenger load for each flight number for June. Flight Number Passenger Load 57 % 85 94 c. What recommendations could you provide Eastern Skies…arrow_forwardPassenger load on a flight Eastern Skies Airlines has three flights that depart from New York City and arrive in Chicago every day. The three flights are as follows: Flight Number Flight Departure Time Flight Frequency 57 8:00 AM 7 days per week 85 10:00 AM 7 days per week 94 11:30 AM 7 days per week Each flight uses a jet with a capacity of 180 seats. The airline measures the utilization of the aircraft by passenger load. Passenger load is the number of seats sold divided by the number of available seats on a flight for a time period. The following operating data are available for June: Flight Number Number of Seats Sold 57 5,130 85 2,592 94 2,376 a. Determine the available seat capacity for each flight number for June.fill in the blank 1 b. Determine the passenger load for each flight number for June. Flight Number Passenger Load 57 fill in the blank 2 % 85 fill in the blank 3 94 fill in the blank 4 c.…arrow_forward
- Assume Intervale Railway is considering hiring a reservations agency to handle passenger reservations. The agency would charge a flat fee of $13,000 per month, plus $3 per passenger reservation. What is the total reservation cost if 200,000 passengers take the trip next month? a. $613,000 b. $3.07 c. $600,000 d. $13,000arrow_forwardSuper Cruiseline offers nightly dinner cruises departing from several cities on the eastern coast of the United States including Charleston, Baltimore, and Alexandria. Dinner cruise tickets sell for $80 per passenger. Super Cruiseline's variable cost of providing the dinner is $40 per passenger, and the fixed cost of operating the vessels (depreciation, salaries, docking fees, and other expenses) is $240,000 per month. The company's relevant range extends to 14,000 monthly passengers. Use this information to compute the following: a. What is the contribution margin per passenger? b. What is the contribution margin ratio? c. Use the unit contribution margin to project operating income if monthly sales total11,000 passengers. d. Use the contribution margin ratio to project operating income if monthly sales revenue totals $515,000.arrow_forwardAnalyze Cityscape Hotels Cityscape Hotels has 200 rooms available in a major metropolitan city. The hotel is able to attract business customers during the weekdays and leisure customers during the weekend. However, the leisure customers on weekends occupy fewer rooms than do business customers on weekdays. Thus, Cityscape plans to provide special weekend pricing to attract additional leisure customers. A hotel room is priced at $180 per room night. The cost of a hotel room night includes the following: Line Item Description Cost Per Room Night(at normal occupancy) Housekeeping service $23 Utilities 7 Amenities 3 Hotel depreciation 55 Hotel staff (excluding housekeeping) 42 Total $130 The special weekend price is proposed for $120 per room night. At this price, it is anticipated that average occupancy for the weekend (Friday, Saturday, and Sunday) will increase from 30% to 50% of available rooms. Question Content Area a. What is the contribution margin for a…arrow_forward
- Analyze Cityscape Hotels Cityscape Hotels has 200 rooms available in a major metropolitan city. The hotel is able to attract business customers during the weekdays and leisure customers during the weekend. However, the leisure customers on weekends occupy fewer rooms than do business customers on weekdays. Thus, Cityscape plans to provide special weekend pricing to attract additional leisure customers. A hotel room is priced at $180 per room night. The cost of a hotel room night includes the following: Cost Per Room Night(at normal occupancy) Housekeeping service $23 Utilities 7 Amenities 3 Hotel depreciation 55 Hotel staff (excluding housekeeping) 42 Total $130 The special weekend price is proposed for $120 per room night. At this price, it is anticipated that average occupancy for the weekend (Friday, Saturday, and Sunday) will increase from 30% to 50% of available rooms.arrow_forwardAnalyze Cityscape Hotels Cityscape Hotels has 200 rooms available in a major metropolitan city. The hotel is able to attract business customers during the weekdays and leisure customers during the weekend. However, the leisure customers on weekends occupy fewer rooms than do business customers on weekdays. Thus, Cityscape plans to provide special weekend pricing to attract additional leisure customers. A hotel room is priced at $180 per room night. The cost of a hotel room night includes the following: Cost Per Room Night(at normal occupancy) Housekeeping service $23 Utilities 7 Amenities 3 Hotel depreciation 55 Hotel staff (excluding housekeeping) 42 Total $130 The special weekend price is proposed for $120 per room night. At this price, it is anticipated that average occupancy for the weekend (Friday, Saturday, and Sunday) will increase from 30% to 50% of available rooms. a. What is the contribution margin for a…arrow_forwardSunset Travel Agency specializes in flights between Toronto and Jamaica. It books passengers on Hamilton Air. Sunset’s fixed costs are $23,500 per month. Hamilton Air charges passengers $1,500 per round-trip ticket. Calculate the number of tickets Sunset must sell each month to (a) break even and (b) make a target operating income of $10,000 per month in each of the following independent cases. Q1. Sunset’s variable costs are $43 per ticket. Hamilton Air pays Sunset 6% commission on ticket price. Q2. Sunset’s variable costs are $40 per ticket. Hamilton Air pays Sunset 6% commission on ticket price. Q3. Sunset’s variable costs are $40 per ticket. Hamilton Air pays $60 fixed commission per ticket to Sunset. Comment on the results. Q4. Sunset’s variable costs are $40 per ticket. It receives $60 commission per ticket from Hamilton Air. It charges its customers a delivery fee of $5 per ticket. Comment on the results.arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College



