
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
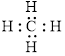
The structural formula for
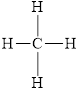
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
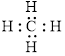
Figure 1
All electron pair are involved in bonding. Therefore, there is no lone pair. The structural formula for
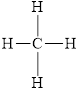
Figure 2
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
![]()
The structural formula for
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
![]()
Figure 3
Out of ten electron pairs, only two electron pairs are involved in bonding. Therefore, there are eight lone pairs. The structural formula for
![]()
Figure 4
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
![]()
The structural formula for
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
![]()
Figure 5
Out of seven electron pairs, three electron pairs are involved in bonding. Therefore, there are four lone pairs. The structural formula for
![]()
Figure 6
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
(d)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
![]()
The structural formula for
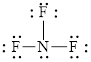
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
![]()
Figure 7
Out of thirteen electron pairs, only three electron pairs are involved in bonding. Therefore, there are ten lone pairs. The structural formula for
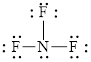
Figure 8
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY
- in the molecule PCI3 given the phosphorus has the electronegativity of 2.1 and the chlorine has an electronegativity of three point no we can conclude that this molecule isarrow_forwardWhat is the formula for a hypochlorite ion?(including charges)arrow_forwardWrite the chemical formula of the following. A. Calcium chloride B. Calcium chloratearrow_forward
- Give a cation isoelectronic with fluoride ion______________________ 3.Arrange in increasingsize: sodiumion, nitride ion, magnesium ion, oxide ion, neon. (explain your rationale)______<______<______<_____<_____ Arrange in decreasingsize: sulfide ion, argon, potassium ion, calcium ion, chloride ion. (explain your rationale)______>______>______>_____>___arrow_forwardA becuas eit has 3 bonds?arrow_forwardDraw the electron dot formula and the structural formula for a molecule of SiHClBrl.arrow_forward
- (c) Theoretically, define the following elements in the formulae belowPth = ρghq x ŋarrow_forwardwhich of the following when in its solid form is an example of an ionic solid? aluminum oxide carbon dioxide iron or silicon dioxidearrow_forwardIdentify the chemical formula of the molecule represented here:arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





