
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron-pair geometry for each carbon atom in
Concept introduction:
The electron pairs in Lewis diagrams repel each other in real molecule and thus they distribute themselves in positions around the central atoms which are far away from one another. This arrangement of electron pairs is called electron-pair geometry. The electron pairs may be shared in covalent bond, or they may be lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 24E
The Lewis diagram for the molecule
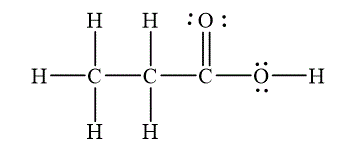
The electron pair geometry for the carbon atoms
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound, first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
The atom which is least electronegative and lesser in number is the central atom. In
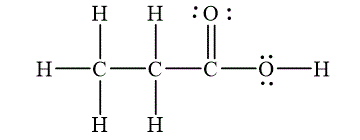
Figure 1
The electron-pair geometry depends on the number of electron pairs around the central atoms. In the molecule
The Lewis diagram for the molecule
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry predicted by the valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory for each carbon atom in the molecule
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the precise term that is used to describe the shape of molecules and arrangement of atoms around the central atom. The molecular geometry of a molecule is predicted by valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory or in short VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory applies to substances in which a second period element is bonded to two, three, four, or other atoms.
Answer to Problem 24E
The Lewis diagrams for
The molecular geometry is tetrahedral for the carbons
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule
The atom which is least electronegative and lesser in number is the central atom. In

Figure 1
The molecular geometry depends on the number of electron pairs as well as number of unpaired electron on the central atoms. In the molecule
The Lewis diagram for the molecule
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Determine the molecular geometry around each carbon atom in propylene, C3H6. Sketch a wedge-and-dash diagram of the molecule.arrow_forwardClassify each of the following statements as true or false: a Molecular geometry around an atom may or may not be the same as electron-pair geometry around the atom. b Electron pair geometry is the direct effect of molecular geometry. c If the geometry of a molecule is linear, the molecule must have at least one double bond. d A molecule with a double bond cannot have trigonal pyramidal geometry around the double bonded atom. e A CO2 molecule is linear, but an SO2 molecule is bent. f A molecule is polar if it contains polar bonds. g A molecule with a central atom that has one lone pair of electrons is always polar. h A molecule with a central atom that has two lone pairs and two bonded pairs of electrons is always polar. i Carbon atoms normally form four bonds. j Hydrogen atoms never form double bonds.arrow_forwardFor each of the following ions/molecules, state the number of bond pairs state the number of lone pairs state the bond angle(s) state, or draw, the shapearrow_forward
- Answer each of the following questions for ClF3. (a) total valence electron count. (b) the Lewis structure. (c) the arrangement (or shape) of the electron grouping (includes lone pairs). (d) ideal bond angle. (e) actual molecular geometry (may be the same or different than answer (c). (f) actual bond angles (may use > or< symbols where appropriate).arrow_forwardNH3 vs BH3 NH3 BH3 polar nonpolar polar nonpolar Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry Question 1b: How does the molecular geometry (trigonal pyramidal vs trigonal planar) affect the polarity?arrow_forwardTo answer the questions, interpret the following Lewis structure for SO42-. For the central sulfur atom: ... The number of lone pairs = The number of single bonds = The number of double bonds = The central sulfur atom: obeys octet rules or expanded octet rules or has incomplete octet rules? 2) To answer the questions, interpret the following Lewis diagram for CO2 .For the central carbon atom: ... The number of lone pairs = The number of single bonds = The number of double bonds = The central carbon atom: obeys octet rules or expanded octet rules or has incomplete octet rules? 3) To answer the questions, interpret the following Lewis structure for BCl3. For the central boron atom: ... The number of lone pairs = The number of single bonds = The number of double bonds = the central boron atom: obeys octet rules or expanded octet rules or has incomplete octet rules?arrow_forward
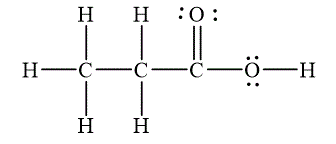
- is this structure polar, nonpolar or slightly polar using carbon ratio rulearrow_forwardPlease refer to the example image to answer. You must use CER, claim-evidence-reasoning. Make sure that your answer is CLEAR. Claim is your answer to the question. Evidence is from the image and reasoning is your explanation. Proper evidence for all Lewis structures include: Carbon or most electronegative atom in center. Octet of electrons surrounding each atom. Total number of electrons depicted equals same total number of valence electrons from each participating atom. Make sure to refer to the example image. It shows what correct Lewis structures include.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



