
Available-for-Sale Securities Holly Company invests its excess cash in marketable securities. At the beginning of 2016, it had the following portfolio of investments in available-for-sale securities:

During 2016, the following transactions occurred:

The December 31 closing market prices were as follows: Igor Company common stock, $25 per share; Ozone Company common stock, $31 per share; Union Company 8% bonds, 101.
Required:
- 1. Prepare
journal entries to record the preceding information. - 2. Show what is reported on Holly’s 2016 income statement.
- 3. Assuming the investment in Igor Company stock is considered to be a current asset and the remaining investments are noncurrent, show how all the items are reported on Holly’s December 31, 2016, balance sheet.
- 4. If GAAP required that unrealized holding gains and losses on available-for-sale securities be included in income, how much would Holly recognize in 2016?
1.
Prepare the journal entries to record the available-for-sale securities transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Investment: It refers to the process of using the currently held excess cash to earn profitable returns in future. The investments can be made in equity securities such as shares or debt securities such as bonds.
Available for sale securities: these are the securities which are not intended to be sold in the near future and there is no intension to hold the securities till their maturity.
Record the purchase of 8% bonds on March 31, 2016.
On March 31, 2016, Company H purchased 8%, bond with a par value of $10,000 for $10,000 plus accrued interest for 3 months from March 31 to June 30.
Determine the amount of interest income paid by Company H.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| March 31, 2016 | Investment in Available-for-sale Securities | $10,000 | |
| Interest income | $200 | ||
| Cash | $10,200 | ||
| (To record the purchase of 8% bond from Company U) |
Table (1)
- Investment in available-for-sale securities is an asset. It is increased. Therefore, debit the investment in available-for-sale securities account.
- Interest income is decreasing here, because Company H paid the accrued interest to purchase the bond. Therefore, it is debited.
- Cash is an asset and decreased. Therefore, credit the cash account.
Record the sale of Company O’s 200 share for $30 per share on May 17.
Step 1: Determine the cash received from sale of 200 shares.
Step 2: Determine the purchase price of 200 shares of Company O.
Step 3: Record the entry.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| May 17, 2016 | Cash | $6,000 | |
| Loss on sale of Available-for-sale securities (Balancing figure) | $600 | ||
| Investment in Available-for-sale securities | $6,600 | ||
| (To record the realized loss on sale of 200 shares of Company O) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an asset and increased. Therefore, debit the cash account.
- Loss on sale of available-for-sale securities is a loss. It decreases the equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Investment in available-for-sale securities is an asset. It is decreased here due to sale. Therefore, credit the investment in available-for-sale securities account.
On May 17, 2016, reverse the cumulative unrealized loss for 200 shares that had accumulated at the end of December 31, 2015.
Company O’s 700 shares is purchased for $23,100, whose fair value as at December 31, 2015 is recorded as $21,700. Hence, the difference of $1,400
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| May 17, 2016 | Allowance for change in fair value of investment | $400 | |
| Unrealized holding gain/loss: Available-for-sale securities | $400 | ||
| (To record the allowance adjustment and reverse the unrealized loss on holding the Securities) |
Table (3)
Record the receipt of semiannual interest on Company U’s bond on June 30, 2016.
Step 1: Calculate the amount of interest income.
Step 2: Record the entry.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| June 30, 2016 | Cash | $400 | |
| Interest income | $400 | ||
| (To record the receipt of semi-annual interest on Company U's bond) |
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset and increased. Therefore, debit the cash account.
- Interest income is revenue; it increases the equity. Therefore, it is credited.
Record the sale of Company I’s 100 share for $24 per share on October 12.
Step 1: Determine the cash received from sale of 100 shares.
Step 2: Determine the purchase price of 100 shares of Company I.
Step 3: Record the entry.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| October 12, 2016 | Cash | $2,400 | |
|
Gain on sale of Available-for-sale securities (Balancing figure) | $300 | ||
| Investment in Trading Securities | $2,100 | ||
| (To record the realized gain on sale of 100 shares of Company I) |
Table (5)
- Cash is an asset and increased. Therefore, debit the cash account.
- Gain on sale of available-for-sale securities is an income. It increases the equity. Therefore, it is credited.
- Investment in available-for-sale securities is an asset. It is decreased here due to sale. Therefore, credit the investment in available-for-sale securities account.
On October 12, 2016, reverse the cumulative unrealized gain for 100 shares that had accumulated at the end of December 31, 2015.
Company I’s 400 shares is purchased for $8,400, whose fair value as at December 31, 2015 is recorded as $9,400. Hence, the difference of $1,000
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| October 12, 2016 | Unrealized holding gain/loss: Available-for-sale securities | $250 | |
|
Allowance for change in fair value of investment | $250 | ||
| (To reverse the allowance and the unrealized gain on holding the Securities) |
Table (6)
Record the semiannual interest income received from Company U’s bond, and dividend income received for Company I and Company O on December 31, 2016.
Step 1: Determine the amount of interest income earned from Company O.
Step 2: Determine the amount of dividend income recieived from Company I.
Step 3: Determine the amount of dividend income recieived from Company O.
Step 4: Determine the total amount of dividend income recieived from both the Company.
Step 5: Record the entry.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2016 | Cash (Balancing figure) | $1,450 | |
| Interest income | $400 | ||
| Dividend income | $1,050 | ||
| (To record the receipt of semi-annual interest on Company U's bond and dividend income from Company I and Company O) |
Table (7)
Determine the fair value of the investment as at December 31, 2016.
Determine the net amount of unrealized gain or loss on available-for-sale securities.
| Investment | Cost (a) | Fair value at December 31, 2016 (b) | Cumulative change in fair value |
| 300 shares of Company I | $6,300 | $7,500 | $1,200 |
| 500 shares of Company O | $16,500 | $15,500 | ($1,000) |
| $10,000 face value of Company U's 8% bond | $10,000 | $10,100 | $100 |
| Total | $32,800 | $33,100 | $300 |
Table (8)
Determine the amount of allowance to be adjusted to have $300 debit balance in allowance account at the end of the year 2016, using T-account.
Credit balance in allowance account on January 1, 2016 is $400
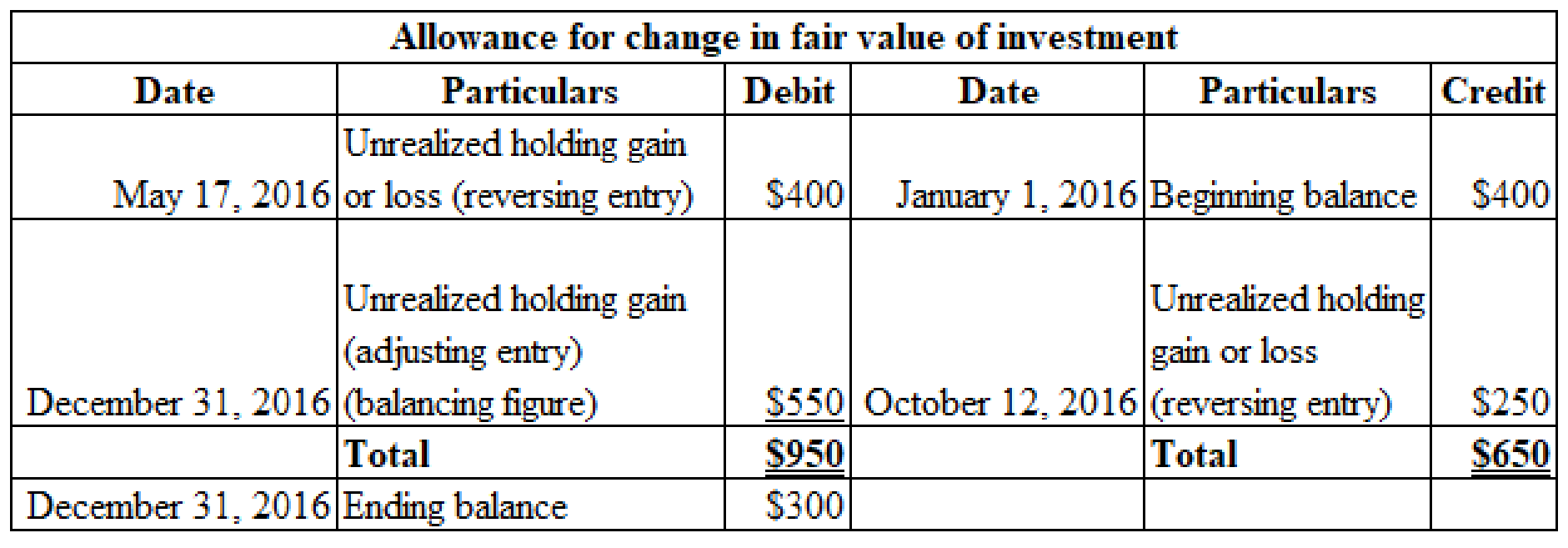
Table (9)
Record the adjusting entry at the end of the year 2016.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2016 | Allowance for change in fair value of investment | $550 | |
|
Unrealized holding gain/loss: Available-for- sale securities | $500 | ||
| (To record the allowance adjustment and the gain unrealized loss on holding the Securities) |
Table (10)
- Unrealized holding gain increases the equity. Therefore, it is credited.
- Allowance is a contra asset. It is decreased. Therefore, it is debited.
2.
Show how Company H would report its available-for-sale securities at its income statement for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Show how Company H would report its available-for-sale securities at its income statement for the year ended December 31, 2016.
| Company H | |
| Income Statement (Partial) | |
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Interest income | $600 |
| Dividend income | $1,050 |
| Loss on sale of available-for-sale securities | -$600 |
| Gain on sale of available-for-sale securities | $300 |
Table (11)
3.
Show how Company H would report its available-for-sale securities at its balance sheet at December 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements that summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Show how Company H would report its available-for-sale securities at its balance sheet at December 31, 2016.
| Company H | |
| Balance sheet Statement (Partial) | |
| As at December 31, 2016 | |
| Assets | Amount |
| Current assets: | |
| Investment in available-for-sale securities (at cost) | $6,300 |
| Add: Allowance for change in fair value of investment | $1,200 |
| Investment in available-for-sale securities (at fair value) | $7,500 |
| Noncurrent assets: | |
| Investment in available-for-sale securities (at cost) | $26,500 |
| Less: Allowance for change in fair value of investment | -$900 |
| Investment in available-for-sale securities (at fair value) | $25,600 |
| Shareholders' equity: | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | |
|
Unrealized holding gain: Available-for-sale securities | $300 |
Table (12)
4.
Determine the amount of income would be recognized by Company H, if the unrealized holding gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included income.
Explanation of Solution
If GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) requires to include unrealized holding gains and losses on available-for-sale securities in income, then Company H would recognize $700 as unrealized holding gain in income statement.
Note:
$700 arrived from the difference between -$400 and +$300. -$400 is an unrealized loss of the portfolio as on December 31, 2015.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Managerial Accounting
Advanced Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
Principles Of Taxation For Business And Investment Planning 2020 Edition
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
- Trading Securities Pear Investments began operations in 2020 and invests in securities classified as trading securities. During 2020, it entered into the following trading security transactions: Purchased 20,000 shares of ABC common stock at $38 per share Purchased 32,000 shares of XYZ common stock at $17 per share At December 31, 2020, ABC common stock was trading at $39.50 per share and XYZ common stock was trading at $16.50 per share. Required: 1. Prepare the necessary adjusting entry to value the trading securities at fair market value. 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What is the income statement effect of this adjusting entry?arrow_forwardInvestments in Equity Securities Manson Incorporated reported investments in equity securities of 60,495 as a current asset on its December 31, 2018, balance sheet. An analysis of Mansons investments on December 31, 2018, reveals the following: During 2019, the following transactions related to Mansons investments occurred: Required: 1. Assuming Manson prepares quarterly financial statements, prepare journal entries to record the preceding information. 2. Show the items of income or loss from investment transactions that Manson reports for each quarter of 2019. 3. Show how Mansons investments are reported on the balance sheet on March 31, 2019; June 30, 2019; September 30, 2019; and December 31, 2019.arrow_forwardInvestments in Equity Securities Noonan Corporation prepares quarterly financial statements and invests its excess funds in marketable securities. At the end of 2018, Noonans portfolio of investments consisted of the following equity securities: Dunne the first half of 2019, Noonan engaged in the following investment transactions: Required: 1. Record Noonans investment transactions for January 6 through June 30, 2019. 2. Show the items of income or loss from investment transactions that Noonan reports for each of the first and second quarters of 2019. 3. Show how the preceding items are reported on the first and second quarter 2019 ending balance sheets, assuming that management expects to dispose of the Keene and Sachs securities within the next year.arrow_forward
- During 2021, Anthony Company purchased debt securities as a long-term investment and classified them as trading. All securities were purchased at par value. Pertinent data are as follows: The net holding gain or loss included in Anthonys income statement for the year should be: a. 0 b. 3,000 gain c. 9,000 loss d. 12,000 lossarrow_forwardThe investments of Steelers Inc. include a single investment: 33,100 shares of Bengals Inc. common stock purchased on September 12, 2016, for 13 per share including brokerage commission. These shares were classified as available-for-sale securities. As of the December 31, 2016, balance sheet date, the share price declined to 11 per share. a. Journalize the entries to acquire the investment on September 12 and record the adjustment to fair value on December 31, 2016. b. How is the unrealized gain or loss for available-for-sale investments disclosed on the financial statements?arrow_forwardInvestments On October 4, 2019, Collins Company purchased 100 bonds of Steph Company for 6,400 as a short-term investment in securities classified as available for sale. On December 31, 2019, the bonds had a fair value of 6,300, and on February 8, 2020, Collins sold the bonds for 6,700. Required: In journal entry form, prepare the spreadsheet entries to record these transactions for Collins Companys 2019 and 2020 statement of cash flows.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning




