
a.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of an exon, intron, promoter sequence, a terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer,and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribes in the m-RNA followed by protein synthesis.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
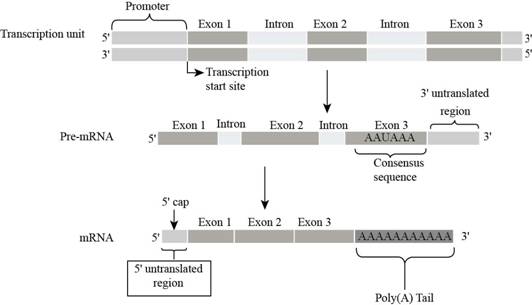
Fig.1:
RNA containsan
In the figure
b.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of an exon, intron, promoter sequence, a terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer,and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribes in
b.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
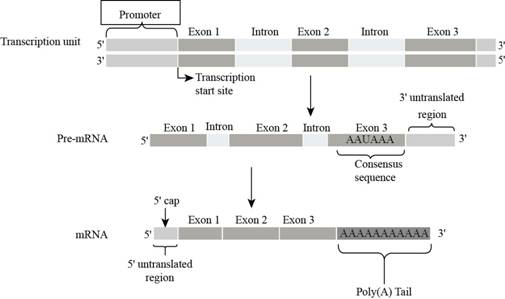
Fig. 2: Promoter.
DNA contains a promoter region in the transcription unite on which RNA polymerase binds in order to start the transcription. It is present upstream to the structural gene, and next to the transcription start site.
In the figure promoter present before the exon 1 on the DNA strand.
c.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of an exon, intron, promoter sequence, a terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer,and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribes in
c.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
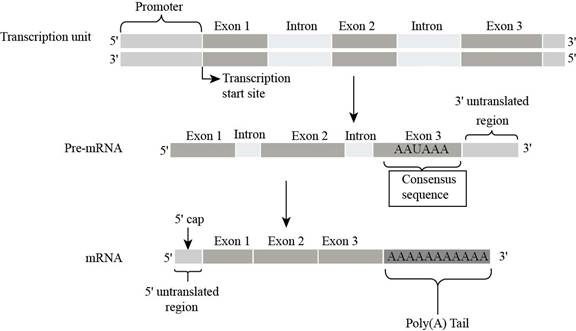
Fig. 3:
In eukaryotic
In the figure
d.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of an exon, intron, promoter sequence, a terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer,and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribes in
d.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
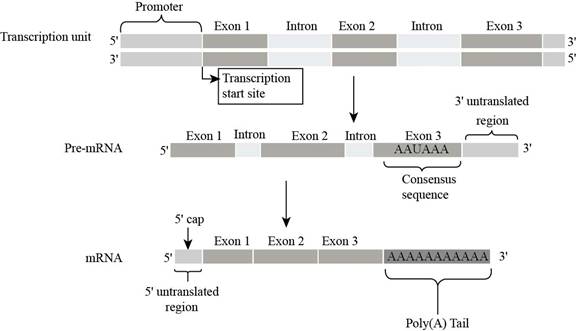
Fig. 4: Transcription start site
The actual site from where the transcription initiation occurs on the DNA template, is termed as transcription start site.
In figure transcription start site present within the starting of exon 1 on DNA strand.
e.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of an exon, intron, promoter sequence, a terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer,and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribes in
e.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
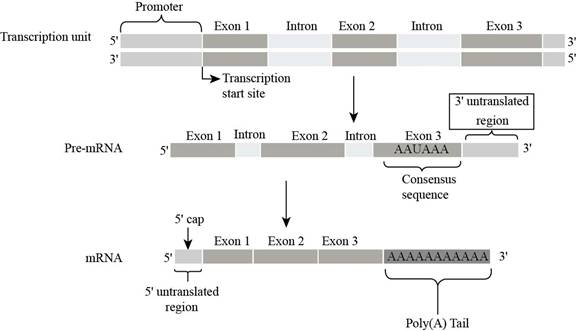
Fig. 5:
The
In the figure
f.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of an exon, intron, promoter sequence, a terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer,and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribes in
f.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
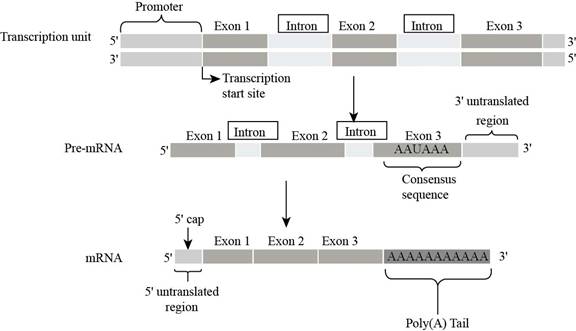
Fig. 6: Introns
DNA contains a particular sequence of
Introns are present in-between the coding sequence (gene) of DNA. Introns are transcribed and produce, but during the splicing process of RNA transcript, the intron segment is eliminated, hence do not code proteins.
In the figure, one intronsis present exon1 and exon2, and second introns are present in between exon 2 and exon 3, on DNA and
g.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of exon, intron, promoter sequence, terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribe in
g.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
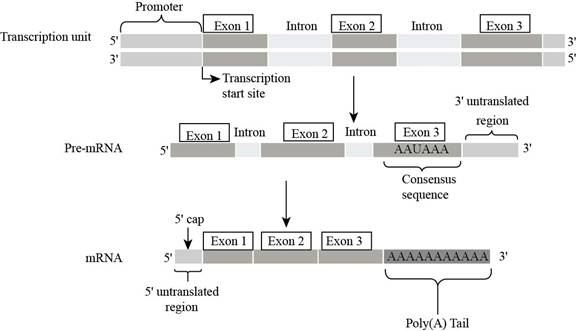
Fig. 7: Exons.
DNA contains a particular sequence of nucleotide which codes for a particular protein, termed as gene. Gene contains the coding regions which codes a particular functional protein is termed as exon.
In the figure, coding sequences marked as exon1, exon 2 , and exon 3, on DNA
h.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of exon, intron, promoter sequence, terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribe in
h.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
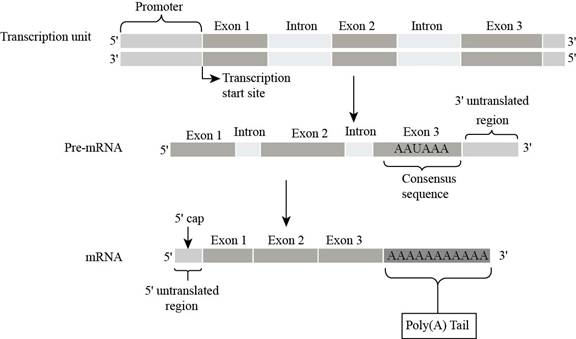
Fig. 8: Poly (A) tail
Eukaryotic
In the figure, poly (A) tail present on the
i.
To determine:
The typical eukaryotic gene and the
Introduction:
The typical eukaryotic gene consists of exon, intron, promoter sequence, terminator sequence, upstream sequence, downstream sequence, enhancer and silencer. A eukaryotic gene transcribe in
i.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
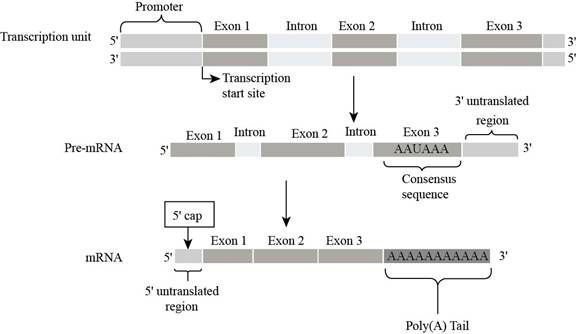
Fig. 9:
Eukaryotic
In the figure,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Genetics: A Conceptual Approach
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





