
Consider the function whose domain is the interval .
(a) Graph .
(b) Approximate the area under the graph of f from to 1 by dividing into five subintervals, each of equal length.
(c) Approximate the area under the graph of f from to 1 by dividing into five subintervals, each of equal length.
(d) Express the area as an
(e) Evaluate the integral using a graphing utility.
(f) What is the actual area?
To solve: The function is defined on the interval ,
a. Graph .
Answer to Problem 32AYU
a.
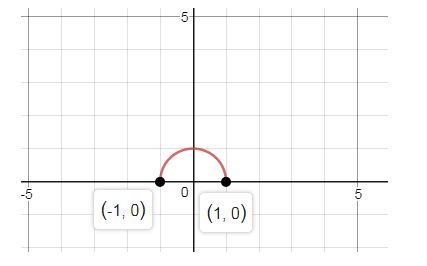
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is defined on the interval .
Calculation:
; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
a. Graph

To solve: The function is defined on the interval ,
b. Approximate the area under from to 1 into five subintervals of equal length.
Answer to Problem 32AYU
b. 18
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is defined on the interval .
Calculation:
; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
b. Approximate the area under from to 1 into five subintervals of equal length,
The area is approximated as,
To solve: The function is defined on the interval ,
c. Approximate the area under from to 1 into ten subintervals of equal length.
Answer to Problem 32AYU
c. 12
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is defined on the interval .
Calculation:
; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
c. Approximate the area under from to 1 into ten subintervals of equal length,
The area is approximated as,
To solve: The function is defined on the interval ,
d. Express the area as an integral.
Answer to Problem 32AYU
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is defined on the interval .
Calculation:
; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
d. Express the area as an integral,
The area as an integral is .
To solve: The function is defined on the interval ,
e. Evaluate the integral using graphing utility.
Answer to Problem 32AYU
e.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is defined on the interval .
Calculation:
; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
e. Use a graphing utility to approximate the integral,
That is evaluate the integral,
The value of the integral is , so the area under the graph of from to 1 is .
To solve: The function is defined on the interval ,
f. What is the actual area ?
Answer to Problem 32AYU
f. 12
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is defined on the interval .
Calculation:
; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
f. The actual area under the graph of from to 1 is the area of the semi-circle whose radius is 1. The actual area is,
Therefore,
Chapter 14 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus & Its Applications (14th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Precalculus: Concepts Through Functions, A Unit Circle Approach to Trigonometry (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Thomas' Calculus: Early Transcendentals (14th Edition)
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





