
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780321910417
Author: Theodore E. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Bruce E. Bursten, Catherine Murphy, Patrick Woodward, Matthew E. Stoltzfus
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 97IE
Write the equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium
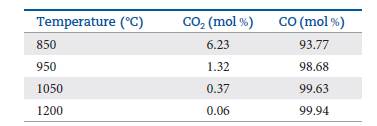
The table that follows shows the relative mole percentages of CO2 (g) and CO (g) at a total pressure of 1 atm for several temperatures. Calculate the value of Kp at each temperature.
Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
Ch. 15.2 - Molybdenum metal must absorb radiation with a...Ch. 15.2 - Titanium metal requires a photon with a minimum...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 15.2.1PECh. 15.2 - Classify each of the following statements as...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 15.3.1PECh. 15.3 -
6 38 Indicate whether energy is emitted or...Ch. 15.3 - Using Equation 6.5. calculate the energy of an...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 15.4.2PECh. 15.4 - The visible emission lines observed by Balmer all...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.5.2PE
Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.6.1PECh. 15.4 - The hydrogen atom can absorb light of wavelength...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.7.1PECh. 15.5 - Prob. 15.7.2PECh. 15.5 - Use the de Brogue relationship to determine the...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.8.2PECh. 15.6 - Neutron diffraction is an important technique for...Ch. 15.6 - The electron microscope has been widely used to...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.10.1PECh. 15.6 - An AM radio station broadcasts at 1010 kHz, and...Ch. 15.6 - One type of sunburn occurs on exposure to UV light...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.11.2PECh. 15.7 - Prob. 15.12.1PECh. 15.7 - A stellar object is emitting radiation at 3.55 mm....Ch. 15 - Prob. 1DECh. 15 - Prob. 1ECh. 15 - Identify the group of elements that corresponds to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 3ECh. 15 - Using the periodic table as a guide, write the...Ch. 15 -
Arrange Be, C, K, and Ca in order of increasing...Ch. 15 - Prob. 6ECh. 15 - Prob. 7ECh. 15 - Prob. 8ECh. 15 - Consider the isoelectronic ions F- and Na+. (a)...Ch. 15 - Prob. 10ECh. 15 - Prob. 11ECh. 15 - Prob. 12ECh. 15 - Give the values for n, I,and mlfor each orbital in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 14ECh. 15 - Prob. 15ECh. 15 - Which of the following represent impossible...Ch. 15 - For the table that follows, write which orbital...Ch. 15 - Sketch the shape and orientation of the following...Ch. 15 - Prob. 19ECh. 15 - Prob. 20ECh. 15 - Two possible electron configurations for an Li...Ch. 15 -
6.70 An experiment called the Stern—Gerlach...Ch. 15 - Prob. 23ECh. 15 - Prob. 24ECh. 15 - What are "valence electrons"? What are "core...Ch. 15 - For each element, indicate the number of valence...Ch. 15 - Write the condensed electron configurations for...Ch. 15 - Write the condensed electron configurations for...Ch. 15 - Identify the specific element that corresponds to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 30ECh. 15 - Prob. 31ECh. 15 - Prob. 32ECh. 15 - Prob. 33ECh. 15 - Prob. 34ECh. 15 - Prob. 35ECh. 15 - Prob. 36ECh. 15 - Prob. 37ECh. 15 - In an experiment to study the photoelectric...Ch. 15 - Prob. 39ECh. 15 - Prob. 40ECh. 15 - Prob. 41ECh. 15 - Prob. 42ECh. 15 - Prob. 43ECh. 15 - Prob. 44ECh. 15 - Prob. 45ECh. 15 - Prob. 46ECh. 15 - Prob. 47ECh. 15 - [6.100] The Chemistry and Life box in Section 6.7...Ch. 15 - Prob. 49ECh. 15 - [6.104] In the experiment shown schematically...Ch. 15 - Microwave ovens use microwave radiation to heat...Ch. 15 - Prob. 52ECh. 15 - The discovery of hafnium, element number 72,...Ch. 15 - Account for formation of the following series of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 55ECh. 15 - The two most common isotopes of uranium are 235U...Ch. 15 - Hypothetical elements X and Y form a molecule XY2,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 58ECh. 15 - Prob. 59ECh. 15 - Prob. 60ECh. 15 - Prob. 61ECh. 15 - Prob. 62ECh. 15 - Prob. 63ECh. 15 - Prob. 64ECh. 15 - Consider the following statements about first...Ch. 15 - Prob. 66ECh. 15 - Prob. 67ECh. 15 -
Write the electron configurations for (a) Ga3+...Ch. 15 - Prob. 69AECh. 15 - Prob. 70AECh. 15 - Prob. 71AECh. 15 - Prob. 72AECh. 15 - Prob. 73AECh. 15 - Prob. 74AECh. 15 - Consider the hypothetical reaction A(g) 2B(g). A...Ch. 15 - 15.76 As shown in Table 15.2, the equilibrium...Ch. 15 - Prob. 77AECh. 15 - Prob. 78AECh. 15 - Prob. 79AECh. 15 - Prob. 80AECh. 15 - Prob. 81AECh. 15 - Prob. 82AECh. 15 - Prob. 83AECh. 15 - Prob. 84AECh. 15 - Prob. 85AECh. 15 - Prob. 86AECh. 15 - Prob. 87AECh. 15 - Prob. 88AECh. 15 - Prob. 89AECh. 15 - Prob. 90AECh. 15 - Prob. 91AECh. 15 - Prob. 92AECh. 15 - Prob. 93IECh. 15 - Prob. 94IECh. 15 - Prob. 95IECh. 15 - Prob. 96IECh. 15 - Write the equilibrium-constant expression for the...Ch. 15 - In Section 11.5, we defined the vapor pressure of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 99IECh. 15 - Prob. 100IE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)2NH3(g) show that Kc = Kp(RT)2 Do not use the formula Kp = Kc(RT)5n given in the text. Start from the fact that Pi = [i]RT, where Pi is the partial pressure of substance i and [i] is its molar concentration. Substitute into Kc.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant Kc for the synthesis of methanol, CH3OH. CO(g)+2H2(g)CH3OH(g) is 4.3 at 250C and 1.8 at 275C. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic?arrow_forwardNitrosyl chloride, NOC1, decomposes to NO and Cl2 at high temperatures. 2 NOCl(g) ⇌ 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) Suppose you place 2.00 mol NOC1 in a 1.00–L flask, seal it, and raise the temperature to 462 °C. When equilibrium has been established, 0.66 mol NO is present. Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc for the decomposition reaction from these data.arrow_forward
- Write equilibrium constant expressions for the following reactions. For gases, use either pressures or concentrations. (a) 2 H2O2(g) 2 H2O(g) + O2(g) (b) CO(g) + O2g CO2(g) (c) C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) (d) NiO(s) + CO(g) Ni(s) + CO2(g)arrow_forwardA solution is prepared by dissolving 0.050 mol of diiodocyclohexane, C5H10I2, in the solvent CCl4.The total solution volume is 1.00 L When the reaction C6H10I2 C6H10 + I2 has come to equilibrium at 35 C, the concentration of I2 is 0.035 mol/L. (a) What are the concentrations of C6H10I2 and C6H10 at equilibrium? (b) Calculate Kc, the equilibrium constant.arrow_forwardDistinguish between the terms equilibrium constant and reaction quotient. When Q = K, what does this say about a reaction? When Q K, what does this say about a reaction? When Q K. what does this say about a reaction?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemical Equilibria and Reaction Quotients; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1GiZzCzmO5Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY