
(a)
Interpretation:
The compounds mesitylene, toluene, and
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds mesitylene, toluene, and
Explanation of Solution
The structure of mesitylene, toluene, and
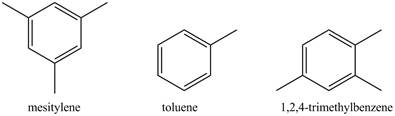
Figure 1
The reaction of any
The methyl group is electron-donating group. It activates the phenyl ring. The toluene has only one methyl group attached to it. Therefore, it will be least reactive towards
The order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(b)
Interpretation:
The compounds chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are to be arranged in increasing order of increasing reactivity toward
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are arranged in increasing order of increasing reactivity toward
Explanation of Solution
The structure of chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are shown below.
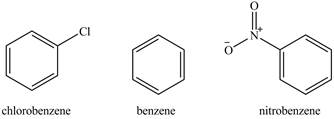
Figure 2
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The nitro and chloro groups are electron-withdrawing groups. Therefore, the reactivity of the chlorobenzene and nitrobenzene will be less than that of benzene. The nitro group is stronger deactivating group than chloro group. Therefore, the order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(c)
Interpretation:
The compounds
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
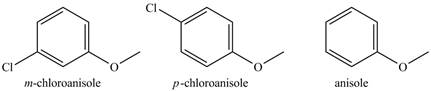
Figure 3
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The methoxy group and chloro groups are ortho and para directing groups. The methoxy group is electron releasing group and chloro group is electron-withdrawing group.
Therefore, the reactivity of anisole will be highest among the rest of the compound toward
The order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(d)
Interpretation:
The compounds acetophenone,
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds acetophenone,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of acetophenone,
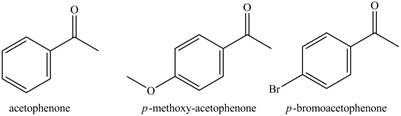
Figure 4
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The acetyl group and bromo group is electron-withdrawing groups and methoxy group is electron releasing group. Acetophenone has a ring activating group attached on it. Therefore, it is most reactive toward nitration reaction among the rest of the compound. The compound
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Suggest reactivity of compound A, B and C in increasing order of E2 reactionarrow_forwardExplain the differences in acidity between p-cyanobenzoic acid and m-cyanobenzoic acid. Illustrate your answer appropriately, showing the acid-base reaction that takes place with each of these and explaining in such terms as electronic (inductive or resonance) and/or steric effects.arrow_forwardCompound A is an alcohol that undergoes oxidation to produce compound B.Compound B is a ketone that gives positive triiodomethane reaction. Compound B isthen reacted with phenyl magnesium bromide, C6H5MgBr in the presence of aqueousacid to form compound C. Compound C has the molecular formula of C9H12O. Deducethe structure for compound A, B and C. PLEASE PROVIDE CLEAR DRAWINGS AND EXPLANATIONSarrow_forward
- Suggest with explanation on how you would prepare the compound, 4-chloroaniline from anilinearrow_forwardWhich compound (i or ii) is the stronger base? Discuss your answer comprehensively by amongst other providing an acid base reaction for one of the compounds.arrow_forwardHow does bromobenzene react differently from benzyl chloride under SN1 and SN2 conditions, and why?arrow_forward
- 3) Outline an acceptable step by step mechanism for the Nucleophilic aromatic substitution of ortho-fluoronitrobenzene with methylamine. Do not forget to include the formal charges of all non-hydrogen atoms that do not have a neutral charge.arrow_forwardCompound A, C3H7Br, does not react with cold dilute potassium permanganate solution. Upon treatment with potassium hydroxide in ethanol, A gives only product B, C3H6. Unlike A, B decolourises potassium permanganate solution. Ozonolysis of Bgives C, C2H4O, and D, CH2O. Suggest the structural formulae of A, B, C and D.Write the equations for all the reactions involved.arrow_forwardCompound A was oxidized with periodic acid to give B, which after acid hydrolysis gave C. Bromine oxidation of C gave D. Suggest structural formulas, including stereochemistry, for compounds B, C, and D.arrow_forward
- Wolff-Kishner reduction of compound W gave compound A. Treatment of A with m-chloroperbenzoic acid gave B which on reduction with LiAH4 gave C. Oxidation of compound C with chromic acid gave D (C9H14O). Suggest the structures for A, B, C, and D.arrow_forwardProvide the structure of the major organic product of the following reaction and? explain the stereochemistry which results in this product. 2-Pentanol reacting with 1.) PBr3, pyridine 2.) NaCNarrow_forwardGiven the sequence of reactions shown below assume the reactions are stoichiometric fill in the reagents needed for steps A B and C and explain what happens in each step of the reactions, by also namearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
