
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of polymerization in the given reaction is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Polymers are the large molecules which are made up of many small repeating units bonded together in linear, branched or cross-linked manner.
They are of two types: natural and synthetic. Natural polymers are those which occur naturally, and synthetic polymers are those which are synthesized or man-made.
A process by which the monomer units chemically react together to form chains or three-dimensional structures is known as polymerization.
In condensation polymerization, when monomers react to produce the polymer a by-product is formed which is a small molecule like
In addition-polymerization no by-product is formed during the chain formation and the reaction propagates due to the presence of the catalyst.
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The given reaction is a type of condensation polymerization.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reaction to produce Kevlar
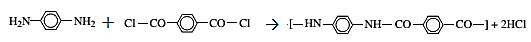
The reaction for the formation of Kevlar is:
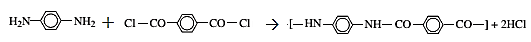
In this reaction,
(b)
Interpretation:
The required weight of terephthaloyl chloride is to be calculated which is completely combined with
Concept Introduction:
Stoichiometry is the calculation of the reactants and the products involved in aa chemical reaction. It is based on the law of mass conservation. According to the stoichiometry, total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products.
Number of moles
Here,
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The amount of terephthaloyl chloride required to completely react with
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reaction for the production of Kevlar
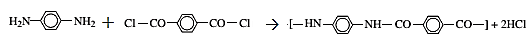
The reaction is
The basis of the calculations is taken as
Molecular formula of paraphenylene diamine is
Now, using equation (1), calculate the moles present in
Molecular formula of terephthaloyl chloride is
As it is given that the reaction has
According to the stoichiometry of the given reaction,
Use equation (1) to calculate the mass of terephthaloyl chloride as:
Therefore,
(c)
Interpretation:
The amount of Kevlar produced is to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The reaction for the production of Kevlar
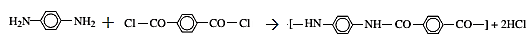
The reaction is
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The amount of Kevlar produced is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reaction for the production of Kevlar
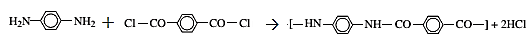
The reaction is
Molecular formula of Kevlar is
As it is given that the reaction has
According to the stoichiometry of the given reaction,
Use equation (1) to calculate the mass of Kevlar as:
Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





