
Concept explainers
A 4-lb bar is attached to a 10-lb uniform cylinder by a square pin, P, as shown. Knowing that
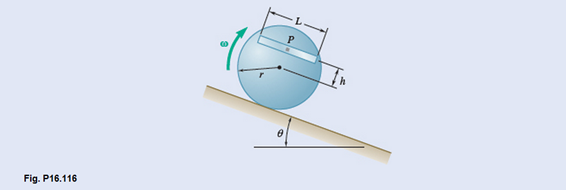
The reactions at P.
Answer to Problem 16.116P
The reactions at P is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Find the mass of the cylinder (mD):
Find the moment of inertia of the cylinder.
Substituting the values we get,
Find the mass of the bar.
Find the moment of inertia for bar.
Substituting all the values we get,
Here, the tangential component of acceleration of point C is zero.
Find the tangential acceleration at point C.
Substituting the required values we get,
Then, the formula for tangential acceleration of point P is
Substituting the values we get,
Find the centripetal acceleration at point P.
Substituting the values we get,
Consider the free body diagram of cylinder.

First, take the moment about point C.
Here, the system of external forces is equal to system of effective forces.
Find the above values.
We get,
Substituting all the required values in equation 4 we get,
Consider the equation (1).
Similarly, consider equation (2).
Take the free body diagram for bar.

Here, also the system of external forces is equivalent to system of effective forces.
And the force is considered to be positive.
Find the value of
Find the value of
Substituting the values in equation (5) we get,
Again the statement of system of external forces is equivalent to system of effective forces.
Find the value of
Find the value of
Consider the equation 6 and substitute the values.
Find the resultant reaction at point P.
Find the resultant angle of reaction.
Take the moment about point P.
Take the moment as clockwise and positive.
Find the value of
Find the value of
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- The 8-in. radius brake drum is attached to a larger flywheel that is not shown. The total mass moment of inertia of the drum and the flywheel is 15 lb.ft.s2 and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the drum and the brake shoe is 0.40. Knowing that the angular velocity of the flywheel is 450 rpm clockwise when a force P of magnitude 65 lbf. is applied to the pedal C, determine the number of the revolutions executed by the flywheel before it comes to rest. (The final answer should be in two decimal places with correct units)arrow_forwardThe 10-in.-radius brake drum is attached to a larger flywheel which is not shown. The total mass moment of inertia of the flywheel and drum is 22 lb ⋅ ft ⋅ s 2 and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the drum and the brake shoe is 0.41. Knowing that the initial angular velocity is 255 rpm clockwise, determine the force which must be exerted by the hydraulic cylinder at point B if the system is to stop in 85 revolutions. DO NOT ROUND OFF IN THE SOLUTION. ROUND OFF ONLY THE FINAL ANSWERarrow_forwardA wheel of radius r and centroidal radius of gyration k is released from rest on the incline shown at time t = 0. Assuming that the wheel rolls without sliding, determine (a) the velocity of its center at time t, (b) the coefficient of static friction required to prevent slipping.arrow_forward
- A uniform disk of mass m = 4 kg and radius r = 150 mm is supported by a belt ABCD that is bolted to the disk at B and C. If the belt suddenly breaks at a point located between A and B, draw the FBD and KD for the disk immediately after the break.arrow_forwardThe 10-in.-radius brake drum is attached to a larger flywheel which is not shown. The total mass moment of inertia of the flywheel and drum is 22 lb ⋅ ft ⋅ s 2 and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the drum and the brake shoe is 0.41. Knowing that the initial angular velocity is 255 rpm clockwise, determine the force which must be exerted by the hydraulic cylinder at point B if the system is to stop in 85 revolutions. determine the force which must be exerted by the hydraulic cylinder at point B if the system is to stop in 85 revolutions. DO NOT ROUND OFF IN THE SOLUTION. ROUND OFF ONLY IN 2 DECIMAL PLACE IN THE FINAL ANSWER.arrow_forwardThe mechanism shown is one of two identical mechanisms attached to the two sides of a 200-lb uniform rectangular door. Edge ABC of the door is guided by wheels of negligible mass that roll in horizontal and vertical tracks. A spring with a constant k is attached to wheel B in such a way that its tension is zero when 0 = 30°, Knowing that the door is released from rest in the position 0 = 45° and reaches the vertical position with an angular velocity of 0.6 rad/s, determine the spring constant k.arrow_forward
- The 4-kg uniform slender bar BD is attached to bar AB and a wheel of negligible mass that rolls on a circular surface. Knowing that at the instant shown bar AB has an angular velocity of 6 rad/s and no angular acceleration, determine the reaction at point D.arrow_forwardThe steel roll shown has a mass of 1200 kg, has a centroidal radius of gyration of 150 mm, and is lifted by two cables looped around its shaft. Knowing that at the instant shown the acceleration of the roll is 150 mm/s2 downward and that for each cable TA = 3000 N, determine (a) the corresponding tension TB, (b) the angular acceleration of the roll.arrow_forwardThe double pulley shown has a mass of 3 kg and a radius of gyration of 100 mm. Knowing that when the pulley is at rest, a force P of magnitude 24 N is applied to cord B, determine (a) the velocity of the center of the pulley after 1.5 s,(b) the tension in cord C.arrow_forward
- A 255-lbf block is suspended from an inextensible cable which is wrapped around a drum of 1.75-ft radius rigidly attached to a flywheel. The drum and flywheel have a combined centroidal moment of inertia 12 lb . ft . s 2 . At the instant shown, the velocity of the block is unknown directed downward. Knowing that the bearing at A is poorly lubricated and that the bearing friction is equivalent to a couple M of magnitude 65 lb .ft, determine the velocity of the block before it has moved 3.5 ft downward if at S2 speed is 13.5ft/sarrow_forwardThe sheet-metal component shown is of uniform thickness and has a mass of 600 g. It is attached to a light axle supported by bearings at A and B located 150 mm apart. The component is at rest when it is subjected to a couple M0 as shown. If the resulting angular acceleration is a = (12 rad/s2)k, determine (a) the couple M0(b)the dynamic reactions A and B immediately after the couple has been applied.arrow_forwardA 9-in-radius cylinder of weight 18 lb rests on a 6-lb carriage. The system is at rest when a force P of magnitude 2.5 lb is applied as shown for 1.2s. Knowing that the cylinder rolls without sliding on the carriage and neglecting the mass of the wheels of the carriage, determine the resulting velocity of (a) the carriage, (b) the center of the cylinder.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





