
a)
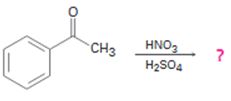
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction in which actophenone reacts with HNO3 and H2SO4 is to be predicted. The observed regiochemistry is to be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl group is an electron withdrawing group. Hence in
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which actophenone reacts with HNO3 and H2SO4.
To explain:
The observed regiochemistry by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Answer to Problem 77AP
Actophenone reacts with HNO3 and H2SO4 to produce m-nitroacetophenone.
Explanation of Solution
The electrophile, NO2+, attacks the aromatic ring in the first step to produce a resonance stabilized carbocation (sigma complex). In the second step the carbocation deprotonates to yield the product. For the meta attack the intermediate is more stabilized as shown.
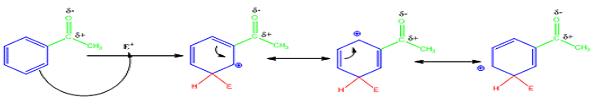
For ortho and para attack one of the resonance forms will be unstable as there will be a positive charge on the carbon to which the carbonyl group is attached.
Actophenone reacts with HNO3 and H2SO4 to produce m-nitroacetophenone.
b)
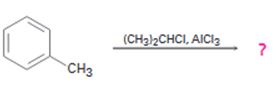
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction in which toluene reacts with isopropyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3 is to be predicted. The observed regiochemistry is to be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl groups are an electron releasing groups. Hence during aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions the alkyl groups will activate the ring and orient the electrophile to the ortho and para positions.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which toluene reacts with isopropyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3.
To explain:
The observed regiochemistry by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Answer to Problem 77AP
When toluene reacts with isopropyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3 the products obtained are o- and p-isopropylbenzenes. The p-isomer will predominate.
Explanation of Solution
The electrophile, (CH3)2CH+, attacks the aromatic ring in the first step to produce a resonance stabilized carbocation (sigma complex). In the second step the carbocation deprotonates to yield the product. For the ortho and para attacks, one of the the resonance structures has a positive charge on a carbon adjacent to the methyl group. This form is stabilized by electron release from the methyl group. Such stabilization is not possible for the meta attack. Hence a mixture of ortho-para products is produced in which the p-isomer predominates.
For ortho attack:
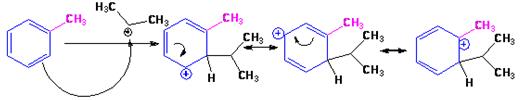
For para attack:
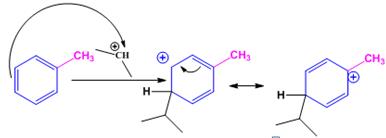
When toluene reacts with isopropyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3 the products obtained are o- and p-isopropylbenzenes. The p-isomer will predominate.
c)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction in which benzonitrile reacts with chlorine in the presence of FeCl3 is to be predicted. The observed regiochemistry is to be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Concept introduction:
The nitrile group is an electron withdrawing group. Hence in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions the nitrile group will deactivate the ring and orient the electrophile to the meta position.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which benzonitrile reacts with chlorine in the presence of FeCl3.
To explain:
The observed regiochemistry by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Answer to Problem 77AP
When benzonitrile reacts with chlorine in the presence of FeCl3 meta chlorobenzonitrile will be produced.
Explanation of Solution
The electrophile, Cl+, attacks the aromatic ring in the first step to produce a resonance stabilized carbocation (sigma complex). In the second step the carbocation deprotonates to yield the product. For the meta attack the intermediate is more stabilized as shown.
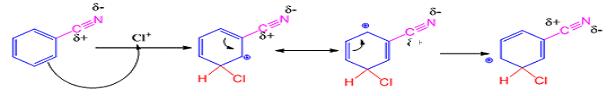
For ortho and para attack one of the resonance forms will be unstable as there will be a positive charge on the carbon to which the nitrile group is attached.
When benzonitrile reacts with chlorine in the presence of FeCl3 meta chlorobenzonitrile will be produced.
d)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction in which methoxy benzene reacts with iodine in the presence of CuCl2 is to be predicted. The observed regiochemistry is to be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Methoxy group is an electron releasing group. Hence during aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions the methoxy group will activate the ring and orient the electrophile to the ortho and para positions.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which benzene reacts with iodine in the presence of CuCl2.
To explain:
The observed regiochemistry by drawing the resonance structures of the intermediates.
Answer to Problem 77AP
When methoxybenzene reacts with iodine in the presence of CuCl2, the products obtained are o- and p-iodobenzenes.
Explanation of Solution
Iodine itself is unreactive toward aromatic rings. CuCl2 accelerate the iodination reaction by oxidizing iodine to a more powerful by electrophilic species that reacts like I+.
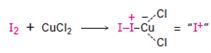
The electrophile, I+, attacks the aromatic ring in the first step to produce a resonance stabilized carbocation (sigma complex). In the second step the carbocation deprotonates to yield the product. For the ortho and para attacks, one of the the resonance structures has a positive charge on a carbon adjacent to the methoxy group. This form is stabilized by electron release from the methoxy group. Such stabilization is not possible for the meta attack. Hence a mixture of ortho-para products is produced.
Ortho attack:
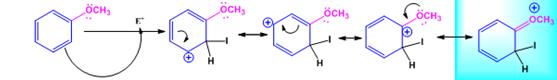
Meta attack:
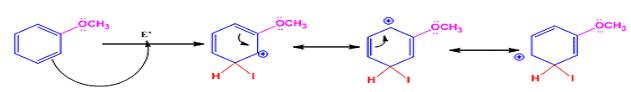
When methoxybenzene reacts with iodine in the presence of CuCl2, the products obtained are o- and p-iodobenzenes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM.(LL)-W/OWL V2 >CUSTOM<
- Predict the product(s) and provide the mechanism for each reaction below.arrow_forwardCompeting SN and E reactions. Predict whether the following reactions will proceed via substitution (SN1 or SN2), or elimination (E₁ or E₂), or whether the two will compete. Identify the major product.arrow_forwarda. Draw the major product(s) of the reaction of 1-methylcyclohexene with the following reagents, disregarding stereoisomers: 1. NBS/Δ/peroxide 2. Br2/CH2Cl2 3. HBr 4. HBr/peroxide b. For each reaction, show which stereoisomers are obtained.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product(s) of the reaction of 1-methylcyclohexene with the following reagents, disregarding stereoisomers: 1. NBS/∆/peroxide 2 . Br2/CH2Cl2 3. HBr 4. HBr/peroxideb. For each reaction, show which stereoisomers are obtained.arrow_forwardIn a strongly acidic solution, cyclohexa-1,4-diene tautomerizes to cyclohexa-1,3-diene.Propose a mechanism for this rearrangement, and explain why it is energetically favorablearrow_forward
