
Concept explainers
Consider the given dinucleotide.
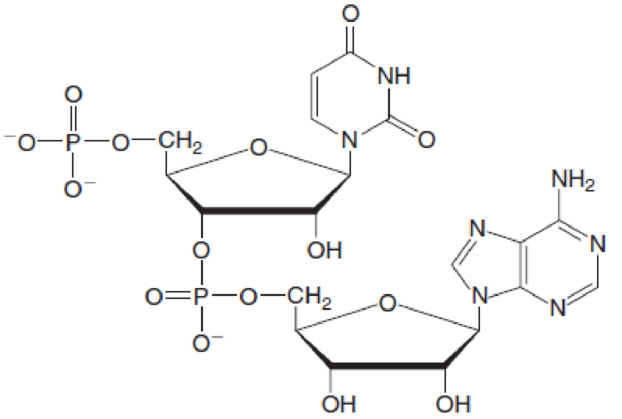
- a. Identify the bases present in the dinucleotide.
- b. Label the 5ˈ and 3ˈ ends.
- c. Give the three- or four-letter abbreviations for the two
nucleotides. - d. Is this dinucleotide a ribonucleotide or a deoxyribonucleotide? Explain your choice.
- e. Name the dinucleotide.
(a)
Interpretation:
Bases present in the below dinucleotide has to be identified.
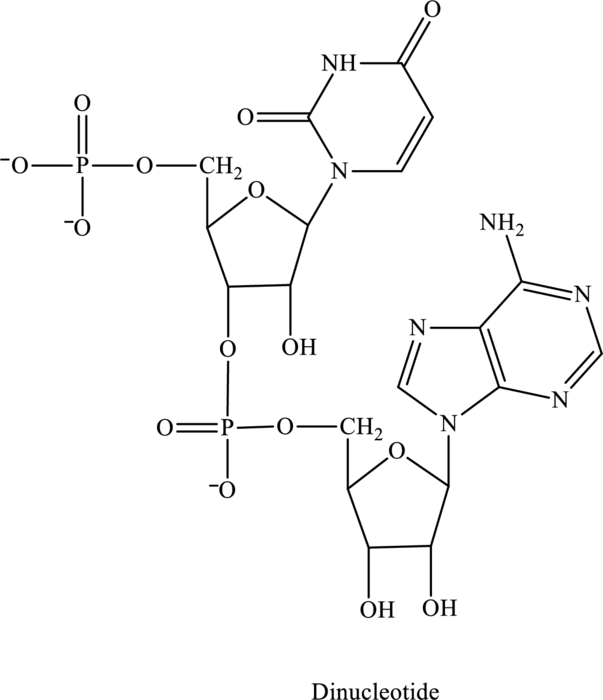
Concept Introduction:
The skeleton structure of base in nucleic acid generally consists of a nitrogen atom in it. There are two types of bases that are pyrimidine base and purine base.
(a) Pyrimidine base consists of one ring and is present in uracil (U), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
(b) Purine base consists of two rings and is present in adenine (A) and guanine (G).
Explanation of Solution
The given structure contains two nucleotides that are nucleotide 1 and nucleotide 2 and is drawn as follows:
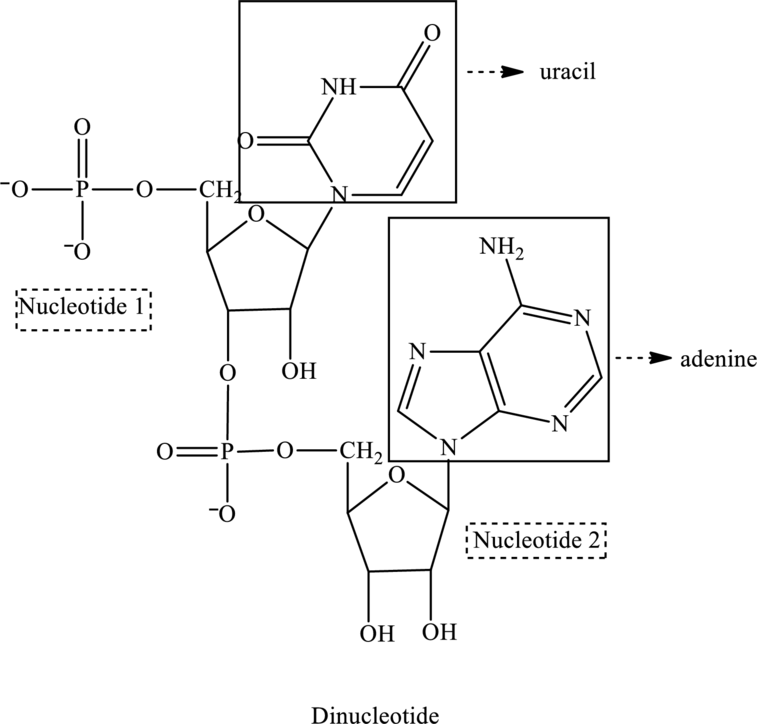
Nucleotide 1 contains a base with one ring in it thus is a pyrimidine base. Therefore, the base is uracil. Whereas nucleotide 2 contains a base with two rings in it thus is a purine base. Therefore, the base is adenine.
(b)
Interpretation:
The
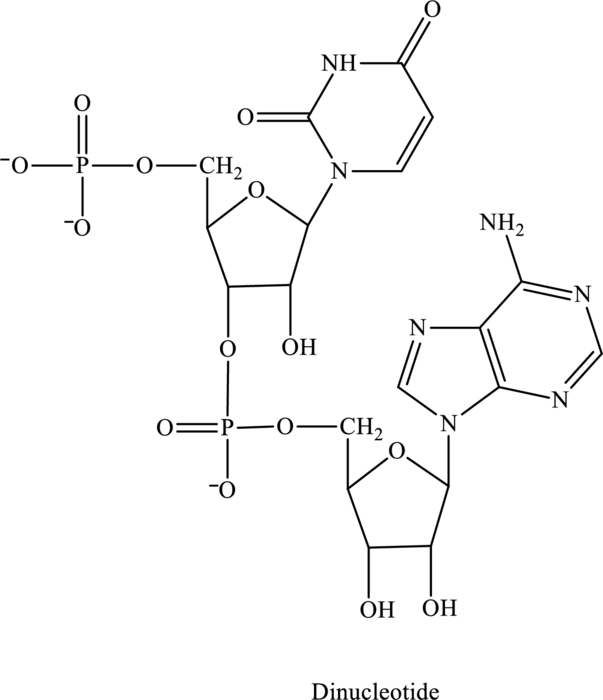
Concept Introduction:
Nucleotide is defined as basic unit for formation of nucleic acid that is essential for completion of metabolic reactions in body. The three basic components of nucleotide are as follows:
1 Nitrogen-containing base
2 Pentose sugar
3 Phosphate group
Dinucleotide is a polymer that is composed of two nucleotide unit either of DNA or RNA that is bonded to each other through a covalent bond.
Explanation of Solution
Phosphate group is attached to
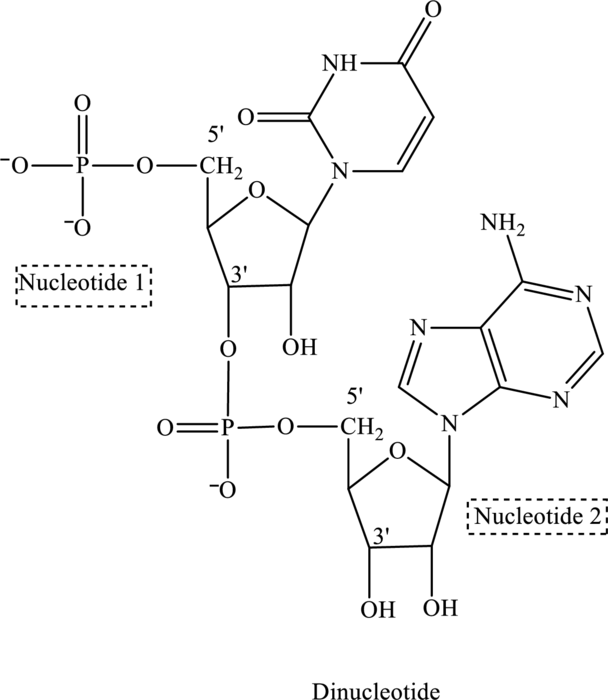
(c)
Interpretation:
Three or four letter abbreviation of below dinucleotide has to be identified.
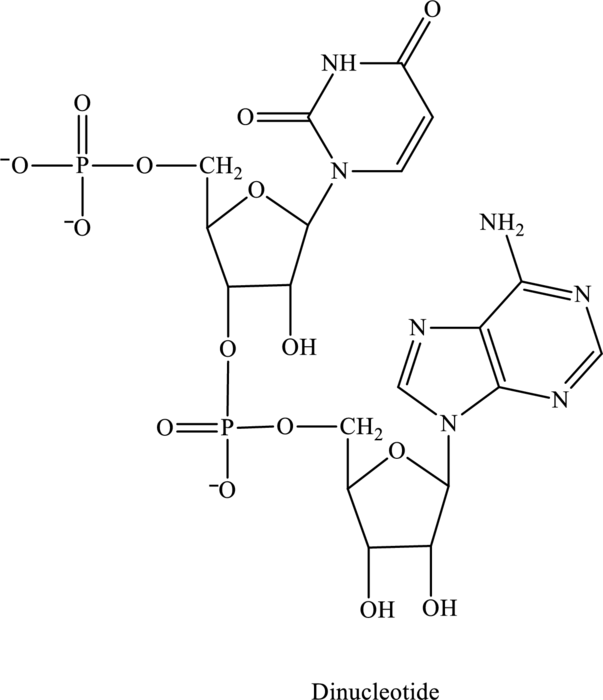
Concept Introduction:
Nucleotides are named accordingly as follows:
1 Identify the type of sugar unit attached is ribose or deoxyribose. If in the structure of nucleoside there is
2 Identify the name of the different nitrogen bases present in the molecule. There are two types of bases that are pyrimidine base and purine base.
(a) Pyrimidine base consists of one ring and is present in uracil, cytosine, and thymine.
(b) Purine base consists of two rings and is present in adenine and guanine.
3 Nucleosides with pyrimidine bases end with the suffix
4 Identify the number of carbon atom to which phosphate group is attached. The prefix is added as mono, di or tri for numbers of phosphate groups present in the nucleotide.
Abbreviation is assigned with respect to the type of sugar. For ribose sugar, 3 letter abbreviation is used and for deoxyribose sugar, 4 letter abbreviation is used followed by d as a prefix.
Explanation of Solution
In the below structure of dinucleotide, base, phosphate group and monosaccharide are labeled as follows:
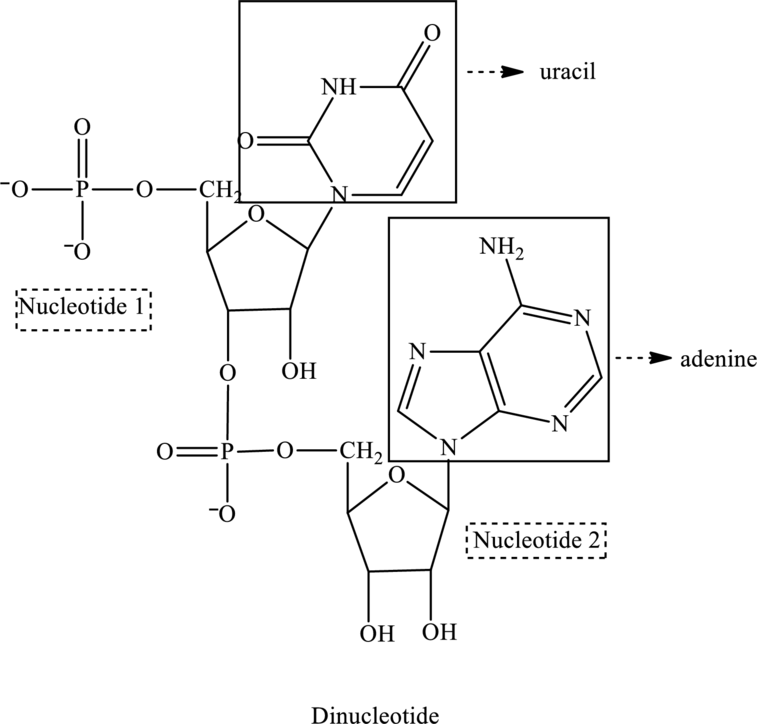
For nucleotide 1:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is
2 It contains one ring, therefore, it is a pyrimidine base called uracil and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
For nucleotide 2:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is an
2 It contains two rings, therefore, it is a purine base called adenine and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the below nucleotide is ribonucleotide or deoxyribonucleotide has to be explained.
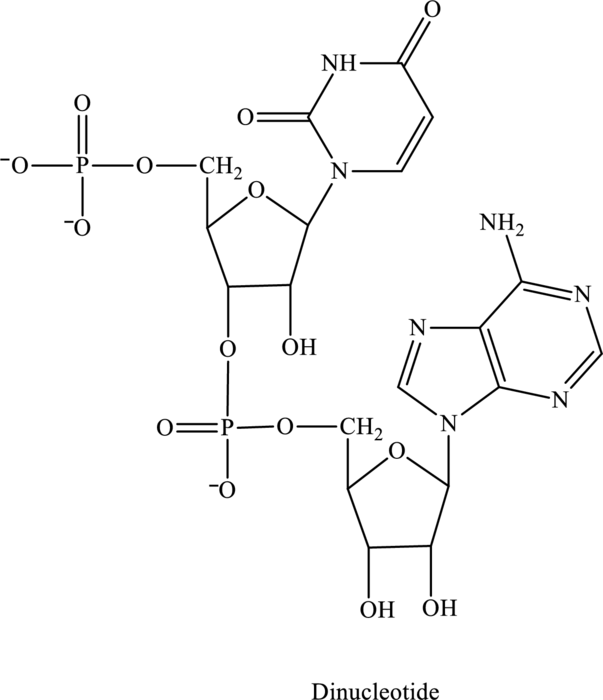
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (c).
Explanation of Solution
Since in the structure of dinucleotide both the nucleotide contains an
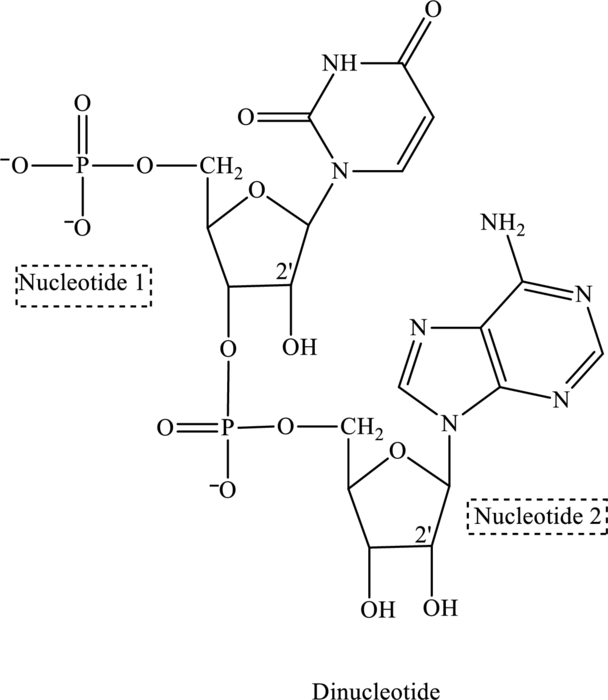
(e)
Interpretation:
Name of the below dinucleotide has to be identified.
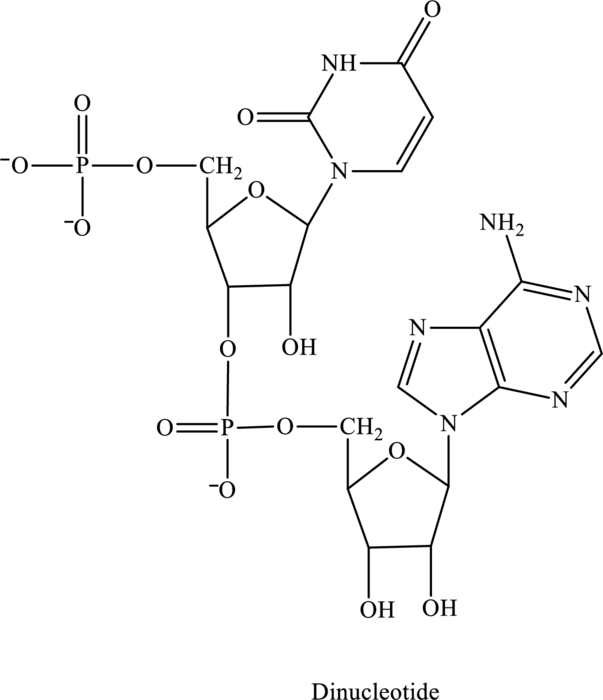
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (c).
Explanation of Solution
The given structure contains two nucleotides that are nucleotide 1 and nucleotide 2 and is drawn as follows:
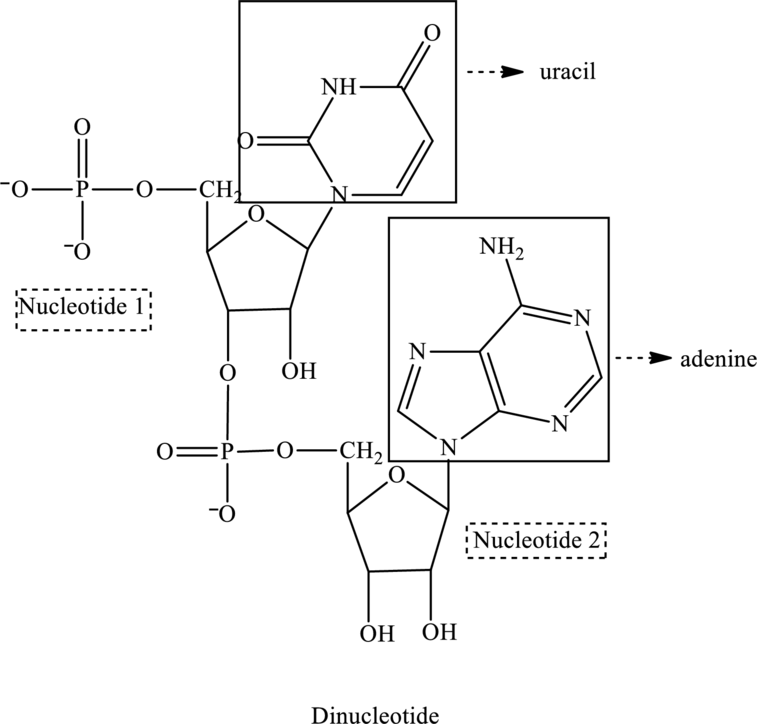
For nucleotide 1:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is an
2 It contains one ring, therefore, it is a pyrimidine base called uracil and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
For nucleotide 2:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is
2 It contains two rings, therefore, it is a purine base called adenine and suffix used is
Since phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- Which of the following statements about the genetic code are true and which are false? Correct each false statement. a.Each codon is composed of four bases. b.Some amino acids are represented by more than one carbon. c.All codons represent an amino acid. d.Each living species is thought to have its own unique genetic code. e.The codon AUG at the beginning of a sequence is a signal for protein synthesis to begin at that codon. f.It is not known if the code contains stop signals for protein synthesis.arrow_forwardFor the trinucleotide 5 UCG 3 a. How many nucleotide subunits are present in its backbone? b. How many nucleotide nonbackbone subunits are present? c. How many phosphodiester linkages are present? d. What is the overall charge carried by the trinucleotide?arrow_forwardWhen a single strand of DNA is making a copy of itself it uses the above code◦ AAT CGC AGG CCA ATG (example DNA code)◦ TTA GCG ____ AAC ___ (example DNA key) AAT-CGT-TCG =arrow_forward
- If 27% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA contain the base adenine (A), what are the percentages of bases T, G, and C?arrow_forwardWhat is the secondary structure of DNA? a. double helix b. random cail c. An alpha-helix d. pleated sheet e. fat sheetarrow_forwardUsing a dark line for the original parental DNA and a wavy line for DNA synthesized from parental DNA, show what the population of DNA molecules would look like in the fourth generationarrow_forward
- Draw an example of the followings: 1- an amino acid; 2- a small peptide; 3- a DNA nucleotide; 4- an RNA nucleotide.arrow_forward. Which of the following is found in a DNA nucleotide? (Sec. 20.6) (a) deoxyribose sugar (b) nitrogen base (c) phosphoric acid (d) all of the above (e) none of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is protein sequence generated by your MRNA ?Be sure to label the N and C termini.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





