
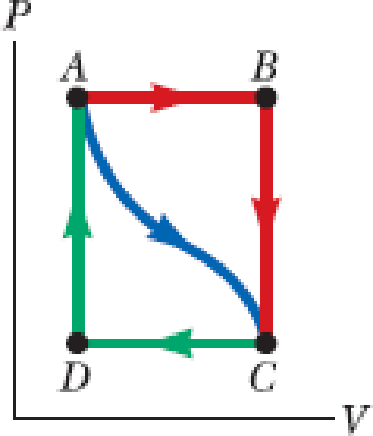
In Figure P17.32, the change in internal energy of a gas that is taken from A to C along the blue path is +800 J. The work done on the gas along the red path ABC is −500 J. (a) How much energy must be added to the system by heat as it goes from A through B to C? (b) If the pressure at point A is five times that of point C, what is the work done on the system in going from C to D? (c) What is the energy exchanged with the surroundings by heat as the gas goes from C to A along the green path? (d) If the change in internal energy in going from point D to point A is +500 J, how much energy must be added to the system by heat as it goes from point C to point D?
Figure P17.32
(a)
The energy added to the system by heat as it goes from
Answer to Problem 32P
The energy added to the system by heat as it goes from
Explanation of Solution
In this case, the change in the internal energy from
Here,
Write the expression for the energy added to the system by heat as it goes from
Here,
Rewrite the above expression,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the energy added to the system by heat as it goes from
(b)
The work done on the system from
Answer to Problem 32P
The work done on the system from
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the work done the system from
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the work done on the system from
(c)
The energy exchanged with the surroundings by heat from
Answer to Problem 32P
The energy exchanged with the surroundings by heat from
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the work done the system from
Here,
Write the expression for the energy exchanged with the surroundings by heat from
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the energy exchanged with the surroundings by heat from
(d)
The energy added to the system by heat from point
Answer to Problem 32P
The energy added to the system by heat from point
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy added to the system by heat as it goes from
Here,
Write the expression for the energy added to the system by heat from point
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the energy added to the system by heat from point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of Physics
- In Figure P19.22, the change in internal energy of a gas that is taken from A to C along the blue path is +800 J. The work done on the gas along the red path ABC is 500 J. (a) How much energy must be added to the system by heat as it goes from A through B to C? (b) If the pressure at point A is five times that of point C, what is the work done on the system in going from C to D? Figure P19.22 (c) What is the energy exchanged with the surroundings by heat as the gas goes from C to A along the green path? (d) If the change in internal energy in going from point D to point A is +500 J, how much energy must be added to the system by heat as it goes from point C to point D?arrow_forwardIf a gas is compressed isothermally, which of the following statements is true? (a) Energy is transferred into the gas by heat. (b) No work is done on the gas. (c) The temperature of the gas increases. (d) The internal energy of the gas remains constant. (e) None of those statements is true.arrow_forwardFigure P21.45 shows a cyclic process ABCDA for 1.00 mol of an ideal gas. The gas is initially at Pi = 1.50 105 Pa, Vi = 1.00 103 m3 (point A in Fig. P21.45). a. What is the net work done on the gas during the cycle? b. What is the net amount of energy added by heat to this gas during the cycle? FIGURE P21.45arrow_forward
- One mole of an ideal gas does 3 000 J of work on its surroundings as it expands isothermally to a final pressure of 1.00 atm and volume of 25.0 L. Determine (a) the initial volume and (b) the temperature of the gas.arrow_forwardA sample of a monatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in Fig. P17.68). It is warmed at constant volume to 3.00 atm (point B). Then it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.00 atm (point C) and at last compressed isobarically to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. Find (b) the temperature at point B, (c) the temperature at point C, and (d) the volume at point C. (e) Now consider the processes A B, B C, and C A. Describe how to carry out each process experimentally. (f) Find Q, W, and Eint for each of the processes. (g) For the whole cycle A B C A, find Q, W, and Eint. Figure P17.68arrow_forwardA gas expands from I to Fin Figure P20.58 (page 622). The energy added to the gas by heat is 418 J when the gas goes from I to F along the diagonal path, (a) What is the change in internal energy of the gas? (b) How much energy must be added to the gas by heat along the indirect path IAF?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




