
Concept explainers
Sub part (a):
The monopsony market.
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The total labor cost can be calculated by using the following formula.
Substitute the respective value in the equation (1) to calculate the total labor cost at one unit of labor.
The total labor cost is $3.
The marginal resource cost can be calculated by using the following formula.
Substitute the respective values in the equation (2) to calculate the marginal resource cost at one unit of labor.
The marginal resource cost is $3.
Table -1 shows the value of the total labor cost and the marginal resources cost that are obtained by using the equation (1) and (2).
Table -1
| Units of labor | Wage rate | Total labor cost | Marginal resources cost |
| 0 | - | 0 | |
| 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 9 | 18 | 12 |
| 3 | 12 | 36 | 18 |
| 4 | 15 | 60 | 24 |
| 5 | 18 | 90 | 30 |
| 6 | 21 | 120 | 36 |
The total revenue can be calculated by using the following formula.
The
Substitute the respective value in the equation (3) to calculate the total revenue at one unit of labor.
The total revenue is $34.
The marginal product can be calculated by using the following formula.
Substitute the respective values in the equation (4) to calculate the marginal resource cost at one unit of labor.
The marginal product is $17.
The marginal revenue product can be calculated by using the following formula.
The
Substitute the respective values in the equation (5) to calculate the marginal revenue product.
The marginal revenue product is $34.
Table -2 shows the value of the total revenue, the marginal revenue product and the marginal product that is obtained by using the equation (3), (4) and (5).
Table -2
| Units of labor | Total product | Marginal product | Product price | Total revenue | Marginal revenue product |
| 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 17 | 17 | 2 | 34 | 34 |
| 2 | 31 | 14 | 2 | 62 | 28 |
| 3 | 43 | 12 | 2 | 86 | 24 |
| 4 | 53 | 10 | 2 | 106 | 20 |
| 5 | 60 | 7 | 2 | 120 | 14 |
| 6 | 65 | 5 | 2 | 130 | 10 |
Graph -1 shows the firms labor supply and the marginal resources cost.7
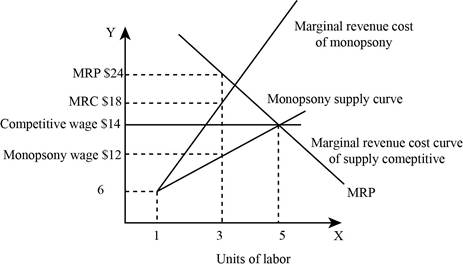
In graph -1, the horizontal axis measures the units of labor and the vertical axis represents the wage rate. The discrete nature of problem requires that the (MRP) marginal revenue product should be equal or greater than the marginal resources cost. This marginal revenue cost curve lies above the labor supply because the employing of the next worker needs a higher wage in the market and will have to pay a higher wage for all the workers.
Concept introduction:
Monopsony: The monopsony market refers to a market which consists of a single buyer who hires a particular type of labor. The workers provide labor to this type of market that has a limited employment opportunity as they need to acquire new skills to be hired. The firm is the wage marker.
Subpart (b):
How many workers should the firm employ.
Subpart (b):
Answer to Problem 3P
The firm should employ 3 workers.
Explanation of Solution
When the marginal revenue product for this worker is greater than the marginal cost, then the firm should employ the workers. From the table, the firm should employ three workers. For the first worker, the marginal revenue product is $34 and the marginal revenue cost is $6. Thus, the firm should employ the first worker. For the second worker, the marginal revenue product is $28 and the marginal revenue cost is $12. So, the firm should employ the second worker. For the third worker, the marginal revenue product is $24 and the marginal revenue cost is $18. So the firm should employ the third worker. But for the fourth worker, the marginal revenue product is $20 and the marginal revenue cost is $24. So, the firm should not employ the forth worker.
Subpart (c):
What happens to the monopolist employment and equilibrium wage rate.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
In this, the monopolist employment decreases by 2 units and the equilibrium wage rate is $2 which is less than the competitive wage.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
MICROECONOMICS
- 4. Suppose that low-skilled workers employed in clearing woodland can each clear one acre per month if each is equippedwith a shovel, a machete, and a chainsaw. Clearing one acrebrings in $1,000 in revenue. Each worker’s equipment coststhe worker’s employer $150 per month to rent and each workertoils 40 hours per week for four weeks each month. LO17.6 a. What is the marginal revenue product of hiring one lowskilled worker to clear woodland for one month?b. How much revenue per hour does each worker bring in?c. If the minimum wage were $6.20, would the revenue perhour in part b exceed the minimum wage? If so, by howmuch per hour?d. Now consider the employer’s total costs. These includethe equipment costs as well as a normal profit of $50 peracre. If the firm pays workers the minimum wage of$6.20 per hour, what will the firm’s economic profit orloss be per acre?e. At what value would the minimum wage have to be set sothat the firm would make zero economic profit fromemploying an…arrow_forward3) Suppose that the supply curve for the labour to a firm is given by L = 100W and the marginal expense of labour curve is given by MEL = L/50 where W is the (nominal) market wage. Suppose also that the firm’s demand for labour (marginal revenue product) curve is given by L = 1, 000 − 100MRPL. a) If the firm acts as a monopsonist, how many workers will it hire in order to maximise profits? What wage will it pay? How will this wage compare to the MRPL at this employment level? b) Assume now that the firm must hire its workers in a perfectly competitive labour market. How many workers will the firm hire now? What wage will it pay? c) What is the deadweight loss from the labour market for a monopsonist? Graph your results and show the DW Larrow_forwardMa2. Required: Question 3.(LO3 Apply) Simon Ltd is run by Simon Leather who makes leather belts for designers. He uses the finest Argentinean leather and needs highly trained machinists to make the belts up to the quality designers expect. His beits usually sell for £50 per item and use 0.2m² of leather and 30 minutes of labor. Simon Ltd has 5 staff. They work a standard 8-hour day, 5 days a week, 48 weeks of the year. They earn £15 per hour. Leather costs £20 per meter. Simon also has some variable overheads of £6 per unit. Fixed overheads are £28,800. a) Calculate the number of belts Simon will have to sell to break even. Simon decides to branch out and start to also sell handbags to the same market. The handbags sell for €250 each and use 1.5m² of leather with 1 hour of labor being required. Variable overheads are £20 per handbag. There has been a bad case of foot and mouth in Argentina. Simon can only use the leather he has currently being shipped to him for the next…arrow_forward
- A firm produces output (y) using two inputs, labor (L) and capital (K), according to the following Cobb-Douglas production function: y = f(L, K) = Lº25 K0.75. Assuming that we draw the isoquant map with labor on the horizontal axis and capital on the vertical axis, what is the slope of this firm's isoquant when L = 120 and K = 60? Give your answer to two decimal places and remember that the sign matters when describing the slope of an isoquant.[_____________] Part 2 : See Hint Assume that L = 120 and K = 60 and suppose that the firm decides to reduce its use of capital and replace those machine hours with some additional labor hours. Approximately how many labor hours will the firm need to add for each machine hour it cut in order to maintain the same level of output (i.e., stay on the same isoquant)? Give your answer to two decimal places. [__________] labor hoursarrow_forwardAn economist estimated that the cost function of a single-product firm isC(Q) = 100 + 20Q + 15 Q^2+ 10 Q^3Based on this information, determine: (LO4, LO5)a. The fixed cost of producing 10 units of output.arrow_forward32. Assuming labor is the only cost for production, a firm hires labor up to the point at which the wage equals (i) the value of the marginal product of labor, (ii) the marginal cost of an additional unit of output, (iii) output price multiplied by the marginal product of labor, for maximum profit. O (i) and (iii) only O (i) and (ii) only (ii) and (iii) only O (i), (ii), and (iii)arrow_forward
- Suppose the demand curve for union labor is given by the equation: L = 450 − 3W.Suppose the current wage is $20. Now suppose the union is successful in raising the wage of its members to $28. At the same time, it is able to shift the demand for labor out to: L = 510 − 3W. Has the higher wage negotiated by the union reduced the employment opportunities of its members? If so, by how much? c. Who has benefitted and who has lost as a result of this negotiation. Be specific and complete.arrow_forwardA software company in Silicon Valley uses programmers (labor) and computers (capital) to produce apps for mobile devices. The firm estimates that when it comes to labor, MPL = 5 apps per month while PL = $1,000 per month. And when it comes to capital, MPC = 8 apps per month while PC = $1,000 per month. If the company wants to maximize its profits, it should: LO16.5 a. Increase labor while decreasing capital. b. Decrease labor while increasing capital. c. Keep the current amounts of capital and labor just as they are. d. None of the above.arrow_forwardDiscuss the impact of the following factors on the optimal method of procuring an input. (LO1, LO3) a. Benefits from specialization. b. Bureaucracy costs. c. Opportunism on either side of the transaction. d. Specialized investments. e. Unspecifiable events. f. Bargaining costs.arrow_forward
- In the short run, the marginal cost of the first unit of output is $25, the marginal cost of producing producing the third unit of output is $14. The firm's total variable cost of producing three units of O a. $39. O b. $25 O c. $33.. O d. $57.arrow_forwardConsider a firm that sells output at P = 5 and has a short-run production function:Q(L) = 20L − L^2. Its wage rate function is w = 40 + 2L. - Suppose the firm is a monopsonist, how much labor will it hire to maximize profits?How much wage will it pay?- Solve for the rate of monopsonistic exploitation.- If instead, the firm is operating in a perfectly competitive market, how much laborwill it hire to maximize profits? How much wage will it pay?arrow_forwardImagine there is a firm that only uses labor to produce goods and that its production function is given by Y(L)=5L-L^2. The price of the firm’s output is equal to 1. Let’s assume the firm is a price taker on the product market but is a local monopsony for employment. Imagine that its marginal cost is given by 2+L. Imagine that labor supply is given by 1+L How much labor does the firm want to use? What will be the wage it pays? How many people will work if the government imposes a minimal wage of 2.25? How will this affect the firm’s profit? Calculate and compare before and after the introduction of the minimum wage.arrow_forward
