
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The binary hydrides shown in the Figure 1 has to be identified as ionic, covalent and interstitial.
Concept Introduction:
The compound containing hydrogen and just one other element is called as binary hydride. Type of hydride formation depends upon the element present in the group. Types of binary compounds are, ionic hydride, metallic hydride and covalent hydride.
Ionic hydride: Ionic hydrides are formed by alkali metals and heavier alkaline earth metals. They contain cations and
Covalent hydride: Covalent hydrides are formed by non-metals. These compound contains hydrogen which is bonded to another element by covalent bond. Most of the covalent hydrides consists of separate, small molecule have relatively weak intermolecular force of attraction, so they are gas or volatile liquid at normal temperature.
Metallic hydride: Metallic hydrides are formed by
(a)
Answer to Problem 18.18CP
In Figure 1,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given representation is shown in Figure 1.
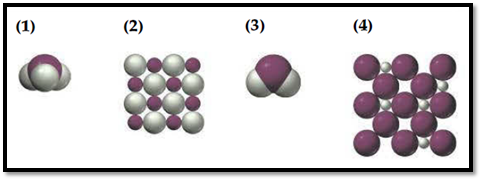
Figure 1
In this picture, ivory spheres denotes Hydrogen atoms or ions and purple spheres denotes an atom or ion of the element.
Picture (1) and (3) shows that hydrides (smaller atoms) are attached to the central atom, smaller molecules have relatively weak intermolecular force of attraction. This type of hydride are known as covalent hydride.
Picture (4) shows interstitial arrangement of hydrogen atom. They are often called as interstitial hydride because they consists of crystal lattice of metals with smaller hydrogen occupying holes or interstitial.
Picture (2) shows that it is slice of face centred arrangement. Ionic hydride only gives face centred arrangement. Thus it is concluded as ionic hydride formed by alkali metals.
So, picture
(b)
Interpretation:
The oxidation state of hydrogen and other element in compound (1), (2) and (3) has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation number: Oxidation number is defined as degree of oxidation (that is loss of an electrons) of an atom within the chemical compound.
There is a slight difference between oxidation state and oxidation number. In oxidation state, the electronegativity of an atom in a bond should be considered. However, while describing oxidation number, electronegativity will not be considered.
(b)
Answer to Problem 18.18CP
In compound (1), oxidation state of hydride is
In compound (2), oxidation state of hydride is
In compound (3), oxidation state of hydride is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given representation is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1
In this picture, ivory spheres denotes Hydrogen atoms or ions and purple spheres denotes an atom or ion of the element.
Picture (1) illustrate a slice of the structure of nonstoichiometric interstitial hydride.
Calculation of oxidation state of hydride and other element in each compound as follows,
Compound (1):
Generally oxidation state of hydride in covalent compound is
Consider x as oxidation state of other element in the compound.
Therefore, the oxidation state of hydride in compound (1) is
Compound (2):
Generally oxidation state of hydride in ionic compound is
Consider x as oxidation state of other element in the compound.
Therefore, the oxidation state of hydride in compound (2) is
Compound (3):
Generally oxidation state of hydride in covalent compound is
Consider x as oxidation state of other element in the compound.
Therefore, the oxidation state of hydride in compound (3) is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First-Solution Manual
- Would the reaction of magnesium, mg with oxygen be more or less vigorous than Al?arrow_forwardWrite the chemical formula for each of the following compounds, and indicate the oxidation state of the group 6A element in each: (a) selenous acid,arrow_forwardWrite the chemical formula for each of the following compounds, and indicate the oxidation state of the halogen or noble-gas atom in each: xenon tetrafluoride.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




