
a)
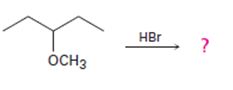
Interpretation:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which it/they is/are formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 23MP
The products formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr are 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
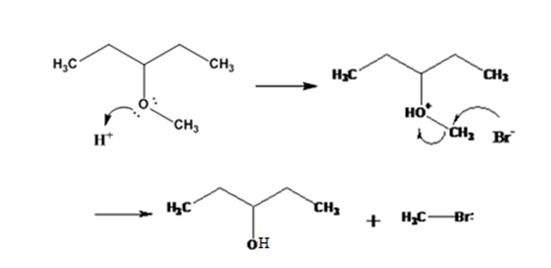
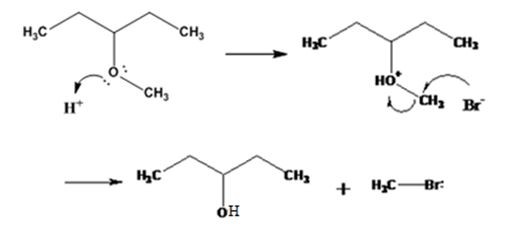
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The Br- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The products formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr are 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
b)
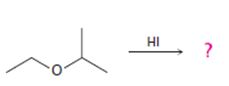
Interpretation:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 23MP
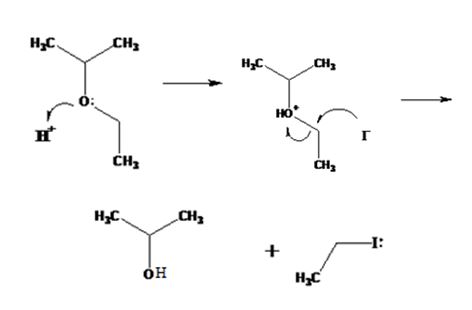
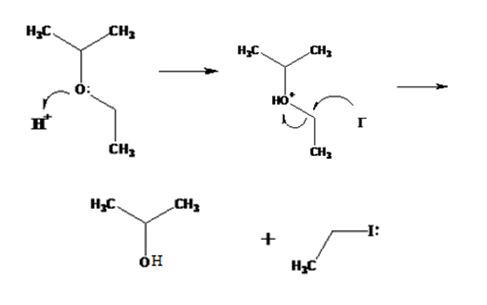
The products formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HBr are 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The I- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The products formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HBr are 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
c)
Interpretation:
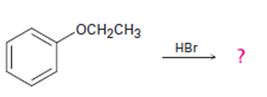
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 23MP
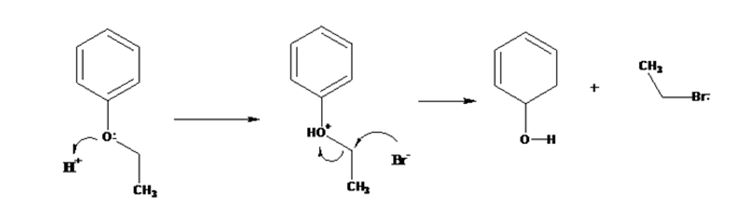
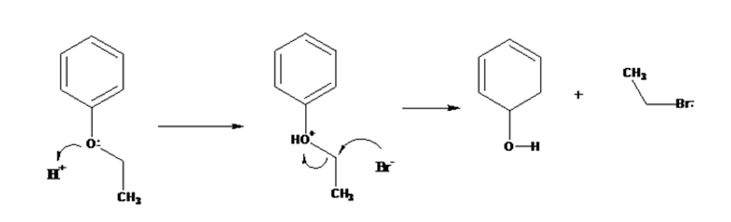
The products formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and ethyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a benzene ring and a methyl group attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The Br- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield phenol and ethyl bromide.
The products formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and ethyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
d)
Interpretation:
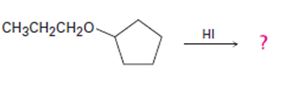
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 23MP
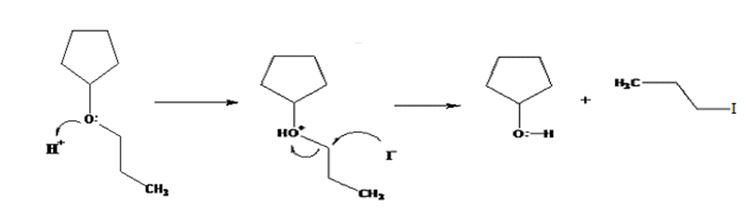
The products formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are cyclopentanol and 1-iodopropane.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The I- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield cyclopentanol and 1-iodopropane.
The products formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are cyclopentanol and 1-bromopropane.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
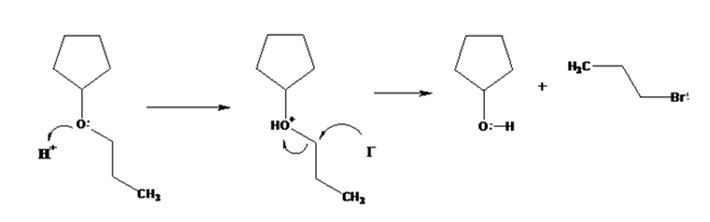
All the reactions, (a), (b), (c) and (d) take place following SN2 mechanism and the attack of the halide ion on the protonated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + LMS Integrated for OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
