Concept explainers
Draw the products of each acid-base reaction, and using the
a. 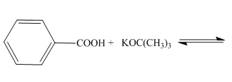 d.
d. 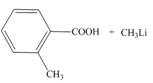
b. 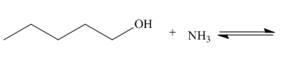 e.
e.
c. 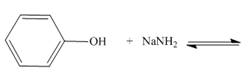 f..
f.. 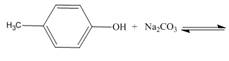
(a)
Interpretation: The products of the given acid-base reaction are to be drawn. Whether the equilibrium favors the reactants or the product is to be determined.
Concept introduction: An acidic substance in a reaction donates a proton, whereas base in a reaction accepts a proton. The
Answer to Problem 19.36P
The products of the given acid-base reaction are,
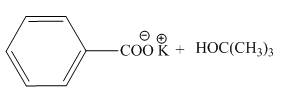
The
Explanation of Solution
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown below.
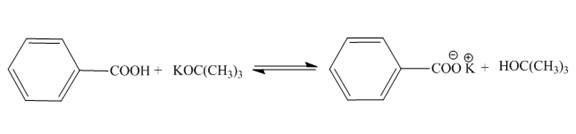
Figure 1
The
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown in Figure 1. The
(b)
Interpretation: The products of the given acid-base reaction are to be drawn. The equilibrium favors the reactants or a product is to be determined.
Concept introduction: An acidic substance in a reaction donates a proton, whereas base in a reaction accepts a proton. The
Answer to Problem 19.36P
The products of the given acid-base reaction are,
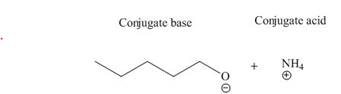
The
Explanation of Solution
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown below.

Figure 2
The
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown in Figure 2. The
(c)
Interpretation: The products of the given acid-base reaction are to be drawn. Whether the equilibrium favors the reactants or the product is to be determined.
Concept introduction: An acidic substance in a reaction donates a proton, whereas base in a reaction accepts a proton. The
Answer to Problem 19.36P
The products of the given acid-base reaction are,
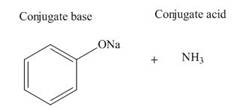
The
Explanation of Solution
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown below.
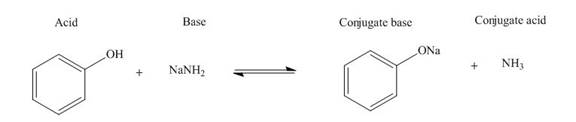
Figure 3
The
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown in Figure 3. The
(d)
Interpretation: The products of the given acid-base reaction are to be drawn. Whether the equilibrium favors the reactants or the product is to be determined.
Concept introduction: An acidic substance in a reaction donates a proton, whereas base in a reaction accepts a proton. The
Answer to Problem 19.36P
The products of the given acid-base reaction are,
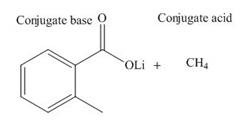
The
Explanation of Solution
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown below.
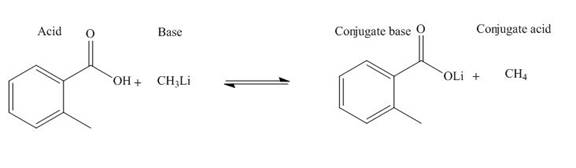
Figure 3
The
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown in Figure 3. The
(e)
Interpretation: The products of the given acid-base reaction are to be drawn. Whether the equilibrium favors the reactants or the product is to be determined.
Concept introduction: An acidic substance in a reaction donates a proton, whereas base in a reaction accepts a proton. The
Answer to Problem 19.36P
The products of the given acid-base reaction are
The
Explanation of Solution
The products of the given acid-base reaction are,
The
The products of the given acid-base reaction are
(f)
Interpretation: The products of the given acid-base reaction are to be drawn. Whether the equilibrium favors the reactants or the product is to be determined.
Concept introduction: An acidic substance in a reaction donates a proton, whereas base in a reaction accepts a proton. The
Answer to Problem 19.36P
The products of the given acid-base reaction are,
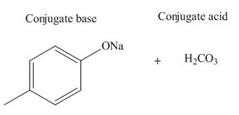
The
Explanation of Solution
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown below.
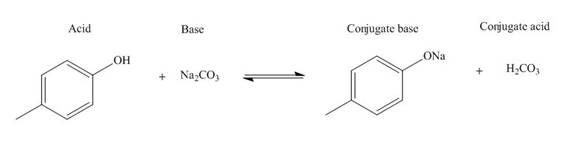
Figure 4
The
The products of the given acid-base reaction are shown in Figure 4. The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- BF3(solv) + NaF(solv) Na+(solv) + BF4-(solv) is best described as reaction. (A) an Arrhenius acid/base(B) a Brønsted-Lowry acid/base (C) a Lewis acid/base (D) all of the above (E) none of the above (F) A & B (G) A&C(H) B&C(I) World Seriesarrow_forwardConsider the acid-base reaction below: Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 ----> Compound A + H2O (OR Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca left parenthesis OH right parenthesis 2 ----> Compound A + H2O) One of the single ions that is used to form compound A is ____.arrow_forwardWhat is the conjugate base of HSO4- is ???? a. SO4 2- b. H2SO4 c. H3O+ d. None correctarrow_forward
- When comparing a solution of HNO3([HNO3=0.3M]) and a solution of H2SO4 ([H2SO4 = 0.3M]) - which solution would have most acidic pHarrow_forwardPhenol, C6H5OH, has a Ka = 1.3x 10 -10 (a) Write out the Ka reaction for phenol (b) Calculate Kb for phenols conjugate base (c) Is phenol a stronger or weaker acid than water?arrow_forwardIdentify each species in the reaction: (CH3)3N(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ (CH3)3NH+(aq) + OH-(aq) - A. B. C. D. (CH3)3N - A. B. C. D. H2O - A. B. C. D. (CH3)3NH+ - A. B. C. D. OH- A. Conjugate base B. Conjugate acid C. Base D. Acidarrow_forward
- . What type of acid-base reaction is shown below? HSO4- (aq) + NH2- (aq) <=> SO42- (aq) + NH3 (g) A strong acid- weak base B weak acid- weak base C strong base- strong acid D strong base- weak acidarrow_forwarda. Draw the conjugate acid of each base: NH3, Cl−, (CH3)2C=O. b. Draw the conjugate base of each acid: HBr, HSO4−, CH3OH.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


