
Concept explainers
a.
Prepare the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the purchase of raw materials on credit:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Raw materials inventory | 41,200 | ||
| Accounts payable (1) | 41,200 | ||
| (To record the purchase of raw materials on credit) |
Table (1)
- Raw materials inventory is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit raw materials inventory with $41,200.
- Accounts payable is a liability account and it is increased. Therefore, credit accounts payable with $41,200.
Working note (1):
Calculate the amount of accounts payable:
Prepare the master ledger card to enter the receiving report information:
Materials ledger card for Material M:
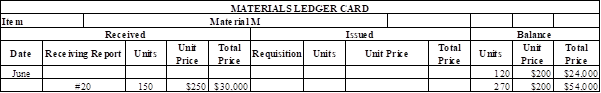
Table (2)
Materials ledger card for Material R:
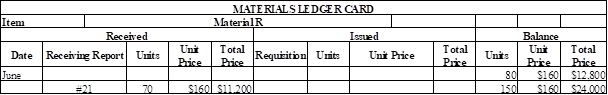
Table (3)
b, c and g:
Prepare the job cost sheet and materials ledger card for the requisition of direct and indirect materials.
b, c and g:
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the job cost sheet for Company M for the requisition of direct materials:

Table (4)
Prepare the master ledger card for requisition of indirect materials (Material R):
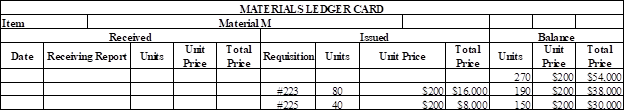
Table (5)
Prepare the job cost sheet for Company R for the requisition of direct materials:

Table (6)
Prepare the master ledger card for requisition of indirect materials (Material R):
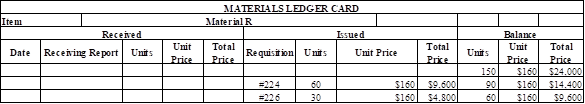
Table (7)
Prepare the master ledger card for requisition of indirect materials (Paint):
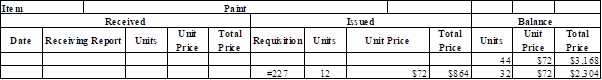
Table (8)
d.
Prepare the journal entry to record the direct and indirect labor cost and the cash payments made.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Direct labor cost: The costs that are related to the labor employed in manufacturing process are known as direct labor costs. The direct labor costs includes not only wages of employees, but also worker’s compensation, life and medical insurance, payroll taxes, training costs, and pension contributions.
Manufacturing overhead costs: The costs, which do not relate directly with the manufacturing of products, are referred to as manufacturing overhead costs or indirect costs. Manufacturing overhead cost per unit is the cost of manufacturing overhead incurred to produce one unit of product.
Prepare the journal entry to record the direct and indirect labor costs:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 72,000 | ||
| Factory overhead | 12,000 | ||
| Cash | 84,000 | ||
| (To record the direct and indirect labor costs) |
Table (9)
- Work in process inventory is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory with $72,000.
- Factory overhead is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit factory overhead with $12,000.
- Cash is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account with $84,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the other factory overheads:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Factory overhead | 36,800 | ||
| Cash | 36,800 | ||
| (To record the other |
Table (10)
- Factory overhead is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit factory overhead with $36,800.
- Cash is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account with $36,800.
e.
Prepare the journal entry to record the completion of the job and its transfer to finished goods.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Finished goods inventory are completely ready for sale after completing the production process.
Prepare the journal entry to record the completion of the job and its transfer to finished goods:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Finished goods inventory | 93,600 | ||
| Work in process inventory | 93,600 | ||
| (To record the direct and indirect labor costs) |
Table (11)
- Finished goods inventory is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit finished goods inventory with $93,600.
- Work in process inventory is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory with $93,600.
f.
Prepare the journal entries to record the sales of Job 450 and the cost of goods sold.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entries to record the sales of Job 450:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 290,000 | |||
| Sales revenue | 290,000 | ||
| (To record the sale of Job 450) |
Table (12)
- Accounts receivable is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit accounts receivable with $290,000.
- Sales revenue is a revenue account and it increases the
stockholders’ equity. Therefore, credit sales revenue with $290,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the cost of goods sold:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 93,600 | ||
| Finished goods inventory | 93,600 | ||
| (To record the cost of goods sold) |
Table (13)
- Cost of goods sold is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold with $93,600.
- Finished goods inventory is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit finished goods inventory with $93,600.
h.
Prepare the journal entry to record the direct and indirect material costs.
h.
Explanation of Solution
Direct materials cost: Manufacturing products arise with raw materials that are altered into finished products. The cost of any material that is an important part of the finished product is categorized as a direct materials cost.
Prepare the journal entry to record the direct and indirect material costs:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 38,400 | ||
| Factory overhead | 864 | ||
| Raw materials inventory | 39,264 | ||
| (To record the direct and indirect material costs) |
Table (14)
- Work in process inventory is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory with $38,400.
- Factory overhead is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit factory overhead with $864.
- Work in process inventory is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory account with $39,264.
i.
Prepare the journal entry to record the total overhead costs applied to jobs.
i.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the total overhead costs applied to jobs.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 50,400 | ||
| Factory overhead | 50,400 |
Table (15)
- Work in process inventory is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory with $50,400.
- Factory overhead is an expense account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit factory overhead with $50,400.
j.
Compute the balance in the factory overhead account as of June.
j.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead Cost: Overhead cost is the expense incurred in the operations of a business. This expense does not include the cost which is incurred on labor. Therefore; this cost is known as overhead cost.
Compute the balance in the factory overhead account as of June:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Actual factory overhead: | |
| Miscellaneous overhead | $36,800 |
| Indirect materials | $864 |
| Indirect labor | $12,000 |
| Total actual factory overhead | $49,664 |
| Factory overhead applied | $50,400 |
| Over applied overhead | ($736) |
Table (16)
Thus, the factory over head as of June is ($736).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting, Chapters 1-17 - With Access (Looseleaf)

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





