
Programming Language Pragmatics, Fourth Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780124104099
Author: Michael L. Scott
Publisher: Elsevier Science
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Expert Solution & Answer
Chapter 2, Problem 14E
Explanation of Solution
a.
Grammar for LL (1):
Consider the grammar for LL (1) as below:
Grammar for SLR (1):
Consider the grammar for SLR (1) as below:
Explanation of Solution
b.
Parsing table for LL (1) grammar:
| Top-of-stack non-terminal | ( | ) | [ | ] | $$ |
| P | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| S | 2 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
- The entries in the above table indicates the production of predict. The “-” means an error.
- If the top-of-stack is terminal, the appropriate action is always to match it against an incoming token from the scanner.
Parsing table for SLR (1) grammar:
| Top-of-stack | S | ( | ) | [ | ] | $$ |
| 0 | s1 | r4 | r4 | r4 | r4 | r4 |
| 1 | - | s2 | - | s3 | - | b1 |
| 2 | s4 | r4 | r4 | r4 | r4 | r4 |
| 3 | s5 | r4 | r4 | r4 | r4 | r4 |
| 4 | - | s2 | b2 | s3 | - | - |
| 5 | - | s2 | - | s3 | b3 | - |
- The entries in the above table indicates whether to shift (s), reduce (r), or shift and then reduce (d). The “-” means an error.
Explanation of Solution
c.
Parsing tree for LL (1):
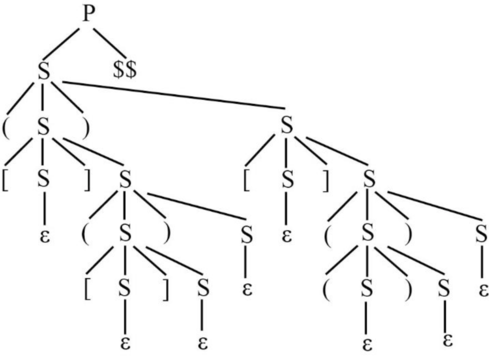
Parsing tree for SLR (1):
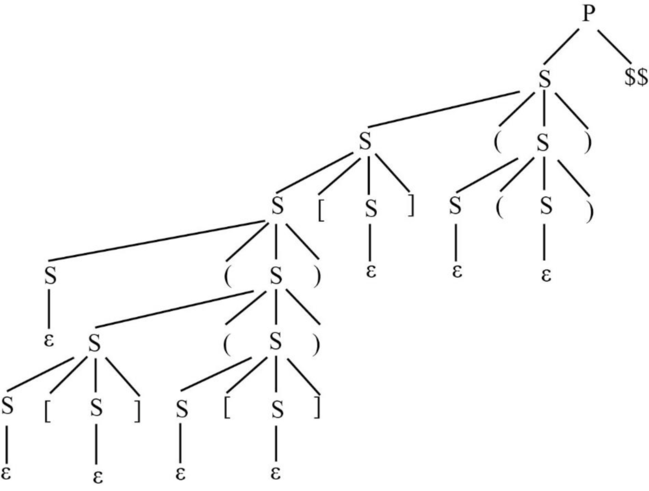
Explanation of Solution
d.
LL (1) trace:
| Parse stack | Input stream | Comment |
| P | ( [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | |
| S $$ | ( [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict P →S $$ |
| ( S ) S $$ | ( [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →( S ) S |
| S ) S $$ | [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match ( |
| [ S ] S ) S $$ | [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →[ S ] S |
| S ] S ) S $$ | ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match [ |
| ] S ) S $$ | ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S ) S $$ | ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match ] |
| ( S ) S ) S $$ | ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →( S ) S |
| S ) S ) S $$ | [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match ( |
| [ S ] S ) S ) S $$ | [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →[ S ] S |
| S ] S ) S ) S $$ | ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match [ |
| ] S ) S ) S $$ | ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S ) S ) S $$ | ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match ] |
| ) S ) S $$ | ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S ) S $$ | ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S → |
| ) S $$ | ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S $$ | [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match ) |
| [ S ] S $$ | [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →[ S ] S |
| S ] S $$ | ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Match [ |
| ] S $$ | ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S $$ | ( ( ) ) $$ | Match ] |
| ( S ) S $$ | ( ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →( S ) S |
| S ) S $$ | ( ) ) $$ | Match ( |
| ( S ) S ) S $$ | ( ) ) $$ | Predict S →( S ) S |
| S ) S ) S $$ | ) ) $$ | Match ( |
| ) S ) S $$ | ) ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S ) S $$ | ) $$ | Match ) |
| ) S $$ | ) $$ | Predict S → ε |
| S $$ | $$ | Match ) |
| $$ | $$ | Predict S → ε |
SLR (1) trace:
| Parse stack | Input stream | Comment |
| 0 | ( [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | |
| 0 | S ( [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 | ( [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 | [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift ( |
| 0S1 ( 2 | S [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 | [ ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 [ 3 | ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift [ |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 [ 3 | S ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 [ 3 S 5 | ] ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 | ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S [ S ] |
| 0S1 ( 2 | S ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 | ( [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 | [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift ( |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 | S [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 S 4 | [ ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 S 4 [ 3 | ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift [ |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 S 4 [ 3 | S ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 S 4 [ 3 S 5 | ] ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 | ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S [ S ] |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 | S ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 S 4 | ) ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 | ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S ( S ) |
| 0S1 ( 2 | S ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 | ) [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0 | [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S ( S ) |
| 0 | S [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 | [ ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 [ 3 | ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift [ |
| 0S1 [ 3 | S ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 [ 3 S 5 | ] ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0 | ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S [ S ] |
| 0 | S ( ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 | ( ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 | ( ) ) $$ | Shift ( |
| 0S1 ( 2 | S ( ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 | ( ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 | ) ) $$ | Shift ( |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 | S ) ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 ( 2 S 4 | ) ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0S1 ( 2 | ) $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S ( S ) |
| 0S1 ( 2 | S ) $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 ( 2 S 4 | ) $$ | Shift S |
| 0 | $$ | Shift and reduce by S→ S ( S ) |
| 0 | S $$ | Reduce by S→ ε |
| 0S1 | $$ | Shift S |
| 0 | P | Shift and reduce by S→ S ( S ) |
| [done] |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Chapter 2 Solutions
Programming Language Pragmatics, Fourth Edition
Ch. 2.1 - Prob. 1CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 2CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 3CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 4CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 5CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 6CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 7CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 8CYUCh. 2.1 - Prob. 9CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 10CYU
Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 11CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 12CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 13CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 14CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 15CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 16CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 17CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 18CYUCh. 2.2 - Prob. 19CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 20CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 21CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 22CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 23CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 24CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 25CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 26CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 27CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 28CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 29CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 30CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 31CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 32CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 33CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 34CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 35CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 36CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 37CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 38CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 39CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 40CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 41CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 42CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 43CYUCh. 2.3 - Prob. 44CYUCh. 2 - Prob. 3ECh. 2 - Prob. 4ECh. 2 - Prob. 5ECh. 2 - Prob. 9ECh. 2 - Prob. 10ECh. 2 - Prob. 11ECh. 2 - Prob. 12ECh. 2 - Prob. 13ECh. 2 - Prob. 14ECh. 2 - Prob. 15ECh. 2 - Prob. 16ECh. 2 - Prob. 17ECh. 2 - Prob. 18ECh. 2 - Prob. 19ECh. 2 - Prob. 20ECh. 2 - Prob. 24ECh. 2 - Prob. 26ECh. 2 - Prob. 27ECh. 2 - Prob. 28ECh. 2 - Prob. 38EQCh. 2 - Prob. 40EQ
Knowledge Booster
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education