
a)
The computation of magnitude of operating leverage utilising contribution margin approach of each firm.
a)
Answer to Problem 23PSA
the operating leverage of L Company and B Company are 1.5 times and 3 times.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
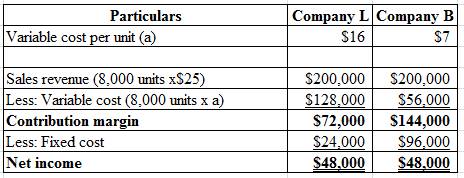
The formula to calculate the magnitudes of operating leverage are as follows:
Calculate the magnitude of operating leverage of L Company and B Company:
Hence, the operating leverage of L Company and B Company are 1.5 times and 3 times.
b)
Determine the change in net income in amount and change in percentage of net income
b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The sales increased by 10% for both Company L and Company B and selling price remain unchanged.
The formula to calculate the percentage change in net income:
Compute the change in net income in dollars:
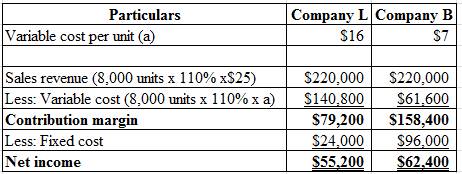
Calculate the percentage change in net income of Company L and Company B:
Hence, the percentage change of net income of Company L and Company B is 15% and 30%
c)
Determine the change in net income in amount and change in percentage of net income.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The sales decreased by 10% for both Company L and Company B and selling price remain unchanged.
The formula to compute the percentage change in net income:
Compute the change in net income in dollars:
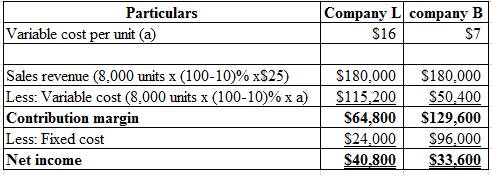
Calculate the percentage change in net income of Company L and Company B:
Hence, the percentage change of net income of Company L and Company B is −15% and −30%
d)
Write a memo regarding the analyses and advice by Person JD.
d)
Explanation of Solution
To,
Person A
From,
Person JD
Subject:
Analysis and recommendation regarding the investment
Date: 11/29/2018
The rewards and risk of both the companies are different even though they have same amount of sales and net income. From the analysis of Person JD the operating leverage is 1.5 for Company L and 3 for Company B.
The analytical data indicates that income of Company B is more volatile than Company L.
Investment in Company B will be the better choice in a economy boom situation. Otherwise, Company L is considering better. An aggressive investor can choice Company B and a conservative investor can go for Company L.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
FUND.MAN.ACC.CONCEPTS W/CONNECT (LL)

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





