
a)
Record the events in general ledger accounts under an
a)
Answer to Problem 33BE
Record the events in general ledger accounts under an
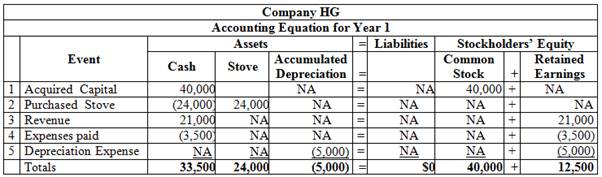
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below.
Straight-line
Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The formula to calculate the depreciation expense is shown below:
Working note:
Calculate the depreciation expense:
Cost of the stove is $24,000. Residual value is $4,000. Estimated life time of the Stove is 4 years.
Hence, the depreciation expense per year on stove is $5,000. Company HG will report $5,000 as its depreciation expense every year, till the completion of 4 years (estimated life time of the stove).
b)
Prepare the
b)
Answer to Problem 33BE
Prepare the balance sheet for the Year 1 accounting period.
| Highland Grill | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As of December 31, Year 1 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Assets: | ||
| Cash | $33,500 | |
| Stove | $24,000 | |
| Less: |
(5,000) | 19,000 |
| Total Assets | $52,500 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Common Stock | $40,000 | |
| 12,500 | ||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 52,500 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $52,500 | |
Table (2)
Prepare the statement of cash flows for the Year 1 accounting period.
| Company HG | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 1 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Revenue | $21,000 | |
| Cash Payment for Salaries | (3,500) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $17,500 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||
| (24,000) | ||
| Net Cash Flow from Investing Activities | (24,000) | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Issue of Stock | 40,000 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities | 40,000 | |
| Net Change in Cash | 33,500 | |
| Plus: Beginning Cash Balance | 0 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | $33,500 | |
Table (3)
Explanation of Solution
Balance Sheet:
Balance Sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Statement of cash flows:
This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period. Statement of cash flows includes the changes in cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities.
c)
Ascertain the net income for Year 1.
c)
Answer to Problem 33BE
$12,500 is the net income for Year 1
Explanation of Solution
Net income:
Net income is the excess amount of revenue which arises after deducting all the expenses of a company. In simple terms, it is the difference between total revenue and total expenses of the company.
Ascertain the net income for Year 1.
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue | 21,000 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Salaries | 3,500 | |
| Depreciation expense | 5,000 | (8,500) |
| Net income | 12,500 |
Table (4)
Hence, the net income for Year 1 is $12,500.
d)
Ascertain the amount of depreciation that would be reported on the Year 2 income statement of Company HG.
d)
Answer to Problem 33BE
$5,000 is the amount that would be reported on the Year 2 income statement of Company HG.
Explanation of Solution
Straight-line Depreciation:
Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The formula to calculate the depreciation cost of the asset using the residual value is shown as below:
Ascertain the amount of depreciation that would be reported on the Year 2 income statement of Company HG.
Cost of the stove is $22,000. Residual value is $2,000. Estimated life time of the Stove is 5 years.
Hence, $5,000 is the amount that would be reported on the Year 2 income statement of Company HG.
e)
Ascertain the amount of accumulated depreciation that would be reported on the Year 2 balance sheet of Company HG.
e)
Answer to Problem 33BE
$10,000 would be reported as accumulated depreciation on the year 2 balance sheet of Company HG.
Explanation of Solution
Accumulated depreciation:
Accumulated depreciation is the aggregation of depreciation expense recognized for the particular asset. Accumulated depreciation refers to the accumulated amount of depreciation that is subtracted from the value of assets in the balance sheet over a period of time.
Ascertain the amount of accumulated depreciation that would be reported on the Year 2 balance sheet of Company HG.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Depreciation expense for Year 1 | 5,000 |
| Depreciation expense for Year 2 | 5,000 |
| Accumulated depreciation | 10,000 |
Table (2)
Hence, $10,000 would be reported as accumulated depreciation on the year 2 balance sheet of Company HG.
f)
State whether the cash flows from the operating activities would be affected by the depreciation expense in the Year 2.
f)
Explanation of Solution
No, depreciation is a non-cash expense. Non-cash expense would not affect the statement of cash flows because, there is no
Therefore, depreciation expense in the Year 2 would not affect the cash flows from operating expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Connect Access Card for Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





