
Overhead:
Overheads are the cost and the expenses a company incurs of the production of a particular goods or services which are not directly related to the production. It does not include labor and direct material.
Direct Material Cost:
Direct material cost is the cost that a company incurs while manufacturing a certain product or service. It includes all the cost and expenses that are directly associated with the production such as raw materials.
Direct Labor Cost:
Direct labor cost is the cost that a company incurs in giving wages to the people that are directly associated with the production work.
Journal entries are the entries that are made in the books of accounts to record every transaction that happens in the business in the chronological order.
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To Increase balance of the account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To Decrease balance of the account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
To Prepare:
Explanation of Solution
a
To record material purchases on credit.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Purchase of raw materials | 41,200 | |||
| Accounts payable | 41,200 | |||
| (To record material purchases on credit) | ||||
| Table (1) |
- Purchase of raw materials is an asset account. Raw material increases as the new raw materials has been brought to the business that increases the assets and all the assets are debited as their values increases.
- Account payable is a liability account. Account payable increases as the raw materials are purchased on credit, hence the liability increases and all the liabilities are credited as their values decreases.
Working Notes:
Receiving report #450
Given,
Units are 150.
Unit price is $200.
Computation of total price,
Total price of receiving report #450 is $30,000.
Receiving report #451
Given,
Units are 70.
Unit price is $160.
Computation of total price,
Total price of receiving report #427 is $16,200.
Computation of total price of both the jobs,
b.
Computation of job cost sheet of job 450
| Job cost sheet | |||||||
| Customers name | Job number | 450 | |||||
| Direct materials | Direct labor | Overhead cost applied | |||||
| Date | Requisition number | Amount ($) |
Time ticket number | Amount ($) |
Date | Rate | Amount ($) |
| #223 | 16,000 | #1-10 | 40,000 | June | 70% | 28,000 | |
| #224 | 9,600 | ||||||
| Total | 25,600 | Total | 40,000 | Total | 28,000 | ||
| Table (2) |
Working note:
Direct labor is $40,000.
Overhead rate is 70%.
Computation of applied overhead,
Hence, the applied overhead is $28,000.
Computation of job cost sheet of job 451,
| Job cost sheet | |||||||
| Customers name | Job number | 451 | |||||
| Direct materials | Direct labor | Overhead cost applied | |||||
| Date | Requisition number | Amount | Time ticket number | Amount ($) |
Date | Rate | Amount ($) |
| #225 | 8,000 | #11-30 | 32,000 | June | 70% | 22,400 | |
| #226 | 4,800 | ||||||
| Total | 12,800 | Total | 32,000 | Total | 22,400 | ||
| Table (3) |
Working notes:
Direct labor is $32,000.
Overhead rate is 70%.
Computation of applied overhead,
Hence, the applied overhead is $22,400.
c.
Computation of material ledger card of M material,
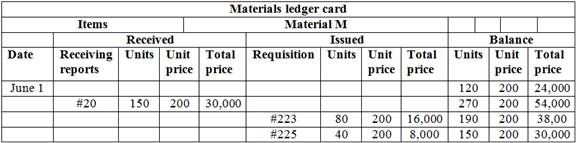
Table (4)
Computation of material ledger card of R,
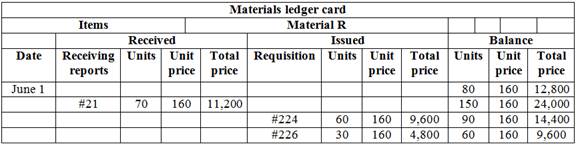
Table (5)
Material ledger card of paint,
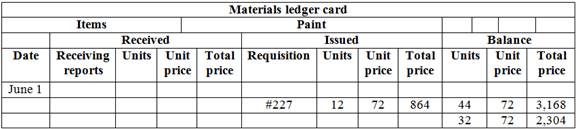
Table (6)
d.
To record factory payroll paid in cash.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Factory payroll | 12,000 | |||
| Inventory | 72,000 | |||
| Cash | 84,000 | |||
| (To record factory payroll paid) | ||||
| Table (7) |
- Factory payroll is an expense account. The account is debited as all the expenses and losses are debited according to the rules.
- Inventory is an asset account. The account increases as the labor used is direct , hence the asset increases and it is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The account decreases as the amount paid for factory payroll is paid in cash, hence the asset decreases and it is credited.
To record the expense for overhead for cash
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Factory Overhead account | 36,800 | |||
| Cash | 36,800 | |||
| (To record the overhead cost) | ||||
| Table (8) |
- Factory overhead is an expense account. The account increases as the expense is paid and all the expenses and losses are debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Cash account decreases as the amount paid for the expense is paid in cash, hence asset decreases and it is credited.
e
To record completion of jobs.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Finished goods inventory | 93,600 | |||
| Work in process | 93,600 | |||
| (To record completion of jobs) | ||||
| Table (9) |
- Finished goods inventory is an asset account. The account increases as the balance of work in process has been transferred to the finished goods account, hence the balance increases and it is debited.
- Work in process is an asset account. The account decreases as the balance of the account has been transferred to the finished goods account, hence the asset decreases and the account is credited.
Working note:
Given,
Direct materials are $25,600.
Direct labor is $40,000.
Over head is $28,000.
Computation of the total cost transferred,
Total cost transferred to finished goods is $93,600.
f.
To record cost of sales.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 93,600 | |||
| Finished goods inventory | 93,600 | |||
| (To record cost of sales) | ||||
| Table (10) |
- Cost of goods sold is an expense account. The account increases as the cost of sales has been ascertained and all expenses are debited.
- Finished goods inventory is an asset account. The account decreases as the balance has been transferred to cost of goods sold account and hence it is credited.
g.
To record sales on discount.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Accounts receivable | 290,000 | |||
| Sales | 290,000 | |||
| (To record credit sales) | ||||
| Table (11) |
- Accounts receivable is an asset account. The account increases as the sale has been made and the debtors increase, hence it is debited.
- Sales are a revenue account. The account generates income and all the incomes and gains are credited as per the rules.
h.
To record direct and indirect materials.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Goods in process | 38,400 | |||
| Factory overhead | 864 | |||
| Raw materials inventory | 39,264 | |||
| (To record direct and indirect materials) | ||||
| Table (12) |
- Goods in process are an asset account. The account increases as the direct labor is directly associated with the goods, hence the asset increases and it is debited.
- Factory overhead is an expense account. The account increases as the indirect labor is treated as an expense and all the expenses are debited.
- Raw materials inventory is an asset account. The account decreases as the amount has been transferred to the goods in process and factory overhead account.
i.
To record the entry to apply overhead.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Goods in process | 50,400 | |||
| Factory overhead | 50,400 | |||
| (To record apply overhead) | ||||
| Table (13) |
- Goods in process account are an asset account. The account increases as the overhead is directly related to production, hence the asset increases and it is debited.
- Factory overhead is an expense account. The account decreases as the expenses decreases and hence it is credited.
Working note:
Overhead applied in job 450 is $28,000.
Overhead applied in job 451 is $22,400.
Computation of total overhead applied,
Hence the total cost is $50,400.
j.
Computation of balance in the factory overhead account,
| Factory overhead | |||||
| Date | Particular | Debit ($) | Date | Particular | Credit ($) |
| Miscellaneous overhead | 36,800 | Goods in process | 50,400 | ||
| Indirect materials | 864 | ||||
| Indirect labor | 12,000 | ||||
| Balance c/f | 736 | ||||
| 124,000 | 124,000 | ||||
| Table (14) |
Hence, the over applied overhead is $736.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card For Managerial Accounting

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





