
Concept explainers
We have said repeatedly that blue light undergoes more extinction than red light, which is true for visible and shorter wavelengths. Is the same true for X-rays? Look at Figure 20.19. The most dust is in the galactic plane in the middle of the image, and the red color in the image corresponds to the reddest (lowestenergy) light. Based on what you see in the galactic plane, are X-rays experiencing more extinction at redder or bluer colors? You might consider comparing Figure 20.19 to Figure 20.14.

Figure 20.14 Barnard 68 in Infrared. In this image, we see Barnard 68, the same object shown in Figure 20.9. The difference is that, in the previous image, the blue, green, and red channels showed light in the visible (or very nearly visible) part of the spectrum. In this image, the red color shows
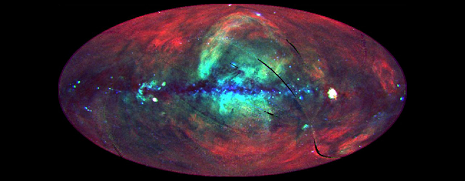
Figure 20.19 Sky in X-Rays. This image, made by the ROSAT satellite, shows the whole sky in X-rays as seen from Earth. Different colors indicate different X-ray energies: red is 0.25 kiloelectron volts, green is 0.75 kiloelectron volts, and blue is 1.5 kiloelectron volts. The image is oriented so the plane of the Galaxy runs across the middle of the image. The ubiquitous red color, which does not disappear completely even in the galactic plane, is evidence for a source of X-rays all around the Sun. (credit: modification of work by NASA)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Astronomy
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
University Physics (14th Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
- Consider the following five kinds of objects: open cluster, giant molecular cloud, globular cluster, group of O and B stars, and planetary nebulae. A. Which occur only in spiral arms? B. Which occur only in the parts of the Galaxy other than the spiral arms? C. Which are thought to be very young? D. Which are thought to be very old? E. Which have the hottest stars?arrow_forwardHow would the density inside a cold cloud (T=10K) compare with the density of the ultra-hot interstellar gas (T=106K) if they were in pressure equilibrium? (It takes a large cloud to be able to shield its interior from heating so that it can be at such a low temperature.) (Hint: In pressure equilibrium, the two regions must have nT equal, where n is the number of particles per unit volume and T is the temperature.) Which region do you think is more suitable for the creation of new stars? Why?arrow_forwardDescribe the life cycles of both low mass and high mass stars, understand how their properties change during each evolutionary stage and how their evolution can be represented on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagramarrow_forward
- As a cluster of stars begins to age, which type of star in the cluster will move off the main sequence of the H-R diagram first? 1) all the stars in a cluster are born at the same time; so they will all move off the main sequence at the same time, as they evolve 2) G type stars, like our Sun 3) M type stars, which are the coolest 4) the lowest mass stars, which have the least amount of fuel for fusion 5) the O and B type starsarrow_forwardHotter, more massive stars are virtually absent from globular clusters. What does this tell us? a) Only that for some reason, massive stars never formed in these clusters. b) Globular clusters are among the youngest objects in our galaxy. c) Globular clusters are among the oldest objects in the Galaxy.arrow_forwardThe Milky Way grew through merging with many smaller galaxies. What are the observational signatures of this process? O The motion of old stars in the bulge and halo of our galaxy are randomly orientated, meaning they were formed from collisions of small, accreted, galaxies all on different paths. O The ordered motion of the bulge / halo stars means that they came from many objects. The random motions of stars in the disk means it was formed from collisions of small, accreted, galaxies. O The motion of young stars in the disk are all in the same direction, meaning they came in as seperate objects.arrow_forward
- Consider the Milky Way disk, which has a 50 kpc diameter and a total height of 600 pc. Suppose that the Sun orbits precisely at the mid-plane of the disk in a circular orbit. Supernovae explosions happen randomly throughout the disk at a rate of about 2 per 100 years. Consider a spherical region around the Sun with a radius of 300 pc. Ignore the Milky Way bulge and halo in this problem; assume the Milky Way disk is perfectly uniform and extends all the way through the region of the bulge. (I.e., the Milky Way is modeled *only* as a cylindrical disk--like a hockey puck-- with constant density throughout.) If a particular supernova goes off at a random location within the disk, what is the probability that it went off in the 300 pc radius spherical region near the Sun? Express your probability as a percentage (but without writing the percent sign). [Hint: there is a 100% probability that the supernova went off somewhere in the volume of the Milky Way disk; there is a 50% probability that…arrow_forwardA two-arm spiral density wave is moving through the Galactic disk. At the 8-kpc radius of the Sun's orbit around the Galactic center, the wave's speed is 120 km/s, and the Galactic rotation speed is 220 km/s. How many times has the Sun passed through a spiral arm since the Sun formed 4.6 billion years ago?arrow_forwardA galaxy's rotation curve is a measure of the orbital speed of stars as a function of distance from the galaxy's centre. The fact that rotation curves are primarily flat at large galactocen- tric distances (vrot(r) ~ constant) is the most common example of why astronomer's believe dark matter exists. Let's work out why! Assuming that each star in a given galaxy has a circular orbit, we know that the accelera- tion due to gravity felt by each star is due to the mass enclosed within its orbital radius r and equal to v?/r. Here, ve is the circular orbit velocity of the star. (a) Show that the expected relationship between ve and r due to the stellar halo (p(r) xr-3.5) does not produce a flat rotation curve. (b) Show that a p(r) ∞ r¯² density profile successfully produces a flat ro- tation curve and must therefore be the general profile that dark matter follows in our galaxy.arrow_forward
- Suppose the Hubble constant were not 22 but 12.1 km/s per million light-years. Then what would the critical density (in kg/m³) be? (For H = 22 km/s per million light-years, the critical density is 9.6 x 10-27 kg/m³.) kg/m³1 I Ih SAMSUNGarrow_forwardLet’s say you’re looking for extrasolar planets. You observe a star that has a spectral shift in the line that is supposed to be at at 656.28011 nm – this star shows this line at 656.28005 nm. What is the radial velocity of star (in m/s) and in what direction in relation to you? a) 27.4 m/s, towards b) 27.4 km/s, away c) -27.4 m/s, toward d) -27.4 km/s, awayarrow_forwardImagine that you are observing the light from a distant star that is located in a galaxy 100 million lightyears away from you. By analysis of the starlight received, you are able to tell that the image we see is of a 10- million-year-old star. You are also able to predict that the star will have a total lifetime of 50 million years, at which point it will end in a catastrophic supernova. a) How old does the star appear to be to us here on Earth now? b) How long will it be before we receive the light from the supernova event? c) Has the supernova already occurred? If so, when did it occur?arrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning




